Content:
The level of tomato harvest largely depends on agricultural technology in the cultivation of vegetables, which becomes important even when growing seedlings. It is especially necessary for plants to timely provide all the necessary nutrients, as a result of which feeding tomato seedlings at home takes on particular importance.
Brief description of culture
Tomatoes are perennial bushy plants that are one of the most common vegetable crops in our country and around the world. The fruits of the vegetable are large juicy fleshy berries, characterized by high taste and marketability. Among the breeding methods, the most common seedling method. When cultivating seedlings, it is extremely important to provide young seedlings with fertilizers.
The need for feeding
Before feeding tomato seedlings at home, you need to make sure that this is really necessary. Deficiency of a particular substance can be determined by external signs:
- Nitrogen. With a lack of this element, the foliage at the bottom of the plant begins to turn yellow. This is because the plant moves nutrients from there to the more promising top of the seedling. At the same time, growth processes slow down. Sometimes yellowing of foliage with a nitrogen deficiency is confused with a similar symptom with an excess of moisture and growing in cool conditions, however, in this case, all the leaves change color, not just the lower ones.
- Phosphorus. The lack of an element causes the formation of a purple tint on the underside of the leaf blade. Until the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place, it is not recommended to take decisive steps to solve this problem, if this does not interfere with the normal growth and development of seedlings.
- Potassium. The element deficiency negatively affects the condition of the seedling root system. By the time the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place, they do not have time to grow roots in sufficient volume. Subsequently, this negatively affects the growth and development of tomatoes.
- Iron. The element is extremely important for plants in the first phases of the growing season, its deficiency later manifests itself in the form of an insufficient level of immunity. You can determine the lack of iron by light spots on the leaves, on which veins of green color are clearly visible.
- Calcium. This component is responsible for the normal formation of the stem. The deficiency of the element makes the stem thinned, makes it stretch in length.
Terms of dressing
Their effectiveness largely depends on the correct selected period of fertilization. A rough plan for how to fertilize plants consists of the following points:
- The first - when the first leaves appear on the plant.
- The second - 2 weeks after picking the seedlings.
- Third - after another one and a half to two weeks.
- Fourth - a few days before disembarkation in open ground.
Top dressing when diving
Picking causes the plants to experience severe stress, but nevertheless, it is a necessary measure.Timely application of fertilizer allows you to transfer it painlessly.
The first time you need to feed one and a half weeks before the pick. It should be aimed at strengthening the immune system. After two weeks, fertilizer is applied again. Thanks to this, the seedlings will restore strength and resume the growth of the root system and the aerial part of the plant.
Seedling feeding scheme
At the first stage vital development for plants, nitrogen and phosphorus are especially important, therefore it is necessary to focus on these elements. It is recommended to root fertilize with minerals, being careful not to get on the foliage.
In the second stage feeding is repeated if the development of the seedlings proceeds normally. If there is a stretching of seedlings, then it is recommended to refrain from feeding with nitrogen. It is also necessary to technically increase the length of daylight hours and set the temperature at + 18 ° C.
In the third stage, which usually falls on the period after the pick, carry out foliar top dressing with organic fertilizers. This will strengthen the seedlings and increase the vegetative mass.
At the fourth stage it is allowed to carry out top dressing both by foliar and root methods. In the first case, the treatment is carried out in the mornings and evenings, so as not to provoke the appearance of sunburns on the leaves. You can use both mineral and organic fertilizers, but the main emphasis must be placed on saturation of plants with potassium, due to which the formation of flower ovaries occurs.
Feeding methods
Feeding tomato seedlings at home involves two main methods of application:
- root;
- foliar.
The first method involves dissolving the nutrient in water and applying it by watering the seedlings at the root. This method is especially important at stages 1-2 of plant development, when it is desirable not to moisten their foliage, since during this period the seedlings are particularly susceptible to the influence of fungal diseases.
At 3-4 periods of development of tomato seedlings, root feeding with the use of a spray bottle becomes a priority. By this time, the foliage is already quite well developed and has the ability to absorb nutrients, as a result of which the effectiveness of such feeding increases dramatically. Under the influence of sunlight, in this case, burns may appear on the foliage, so it is better to postpone the procedure to the morning or evening.
Fertilizers
The list of drugs and substances with which to feed tomato seedlings at home is very wide and includes mineral, organic fertilizers, as well as a number of folk remedies. The described preparations can also be used for feeding seedlings of other cultivated plants - pepper, cucumbers, etc.
Mineral
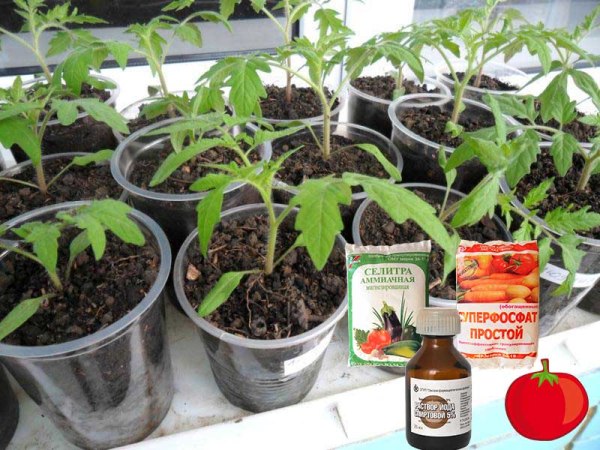
The most common type of fertilizer. They contain nutrients necessary for plants. The most common among them are:
- urea (urea) - nitrogen concentrated fertilizer, the action of which is aimed at ensuring the full growth and development of the root part of the seedlings;
- ammonium nitrate - nitrogen fertilizer, contributing to the full growth and development of shoots and leaves;
- superphosphate - fertilizer that saturates the plant with phosphorus and other essential nutrients, intensifies metabolic processes and stimulates the normal development of a strong and strong root system;
- potassium sulfate - a chlorine-free potassium fertilizer, the use of which allows the plant to build up a strong root system and increase immunity, intensify the development of flower ovaries, and increase the quantity and quality of the crop.
For feeding, it is recommended to prepare the following composition:
- Mix 1 g of carbamide, 3 g of potassium sulfate and 8 g of superphosphate.
- The resulting mixture is diluted with 2 liters of water.
- The solution is stirred until all ingredients are completely dissolved.
- The resulting substance is used for root dressing.
For use in root and foliar dressings, the following preparation is prepared:
- Mix 600 mg of ammonium nitrate, 1.5 g of potassium sulfate and 4 g of superphosphate.
- Dissolve the mixture in a liter container with water.
- After complete dissolution, the fertilizer is ready for use as intended.
Organic
Fertilizers of this category are characterized by their relative cheapness and availability. Most of these substances contain a significant amount of nitrogen, so their use is especially justified at the initial stages of plant development. The most common fertilizers in this category include:
- Bird (primarily chicken) droppings. 1 kg of the substance is dissolved in 10 liters of water and infused for 3-4 days, after which the fertilizer is ready for use.
- Cow dung used in a semi-rotten state. 1 kg of mullein is diluted in 10 liters of water and infused for a day, after which a fertilizer for root and foliar feeding is obtained.
Folk remedies
When choosing how to feed tomatoes at home on the window, many gardeners often choose products from this category. They are often found in everyday life and are suitable for those gardeners who do not want to expose the bushes to chemicals. The most common ones are:
- Ash... 30 g of the substance is diluted in 2 liters of hot water and left to infuse for a day, after which the liquid is filtered and used for spraying and watering.
- Iodine. The tool is able not only to saturate plants with nutrients, but also to increase their resistance to fungal diseases. A drop of the substance is diluted in 3 liters of heated water. The resulting fertilizer is recommended for use at the last two stages of seedling development.
- Yeast... The substance is used at 2-3 stages of growing seedlings. 10 g of the substance are diluted in a bucket of water, insisted for a day and immediately used for feeding, trying not to store the finished fertilizer for too long.
- Ammonia. Top dressing with this substance is carried out 2 weeks after the pick, as well as by seedlings. To prepare fertilizer, one and a half tablespoons of the substance are diluted in a bucket of water.
- Hydrogen peroxide. The tool is used for root dressing. 20 drops of a 3% drug are diluted per liter of water, after which the fertilizer is ready for use.
Diseases and pests of tomato seedlings
Tomato seedlings can be damaged by the following categories of diseases:
- fungal;
- viral;
- bacterial.
The most numerous is the first category, which includes:
- late blight;
- white leaf spot;
- rot;
- alternaria (dry rot);
- blackleg;
- fusarium wilting;
- olive spot (cladosporium);
- powdery mildew.
Viral diseases include:
- mosaic;
- streak (streak);
- aspermia (seedlessness).
Bacterial diseases include:
- brown leaf spot;
- bacterial mottling;
- bacterial wilting;
- black bacterial spot;
- stolbur;
- bacterial cancer.
Controlling these diseases involves treating the seed before planting and spraying it with an appropriate fungicide.
Chemical preparations and mechanical collection are used to combat pests of tomato seedlings, which include:
- Colorado beetles;
- bear;
- aphid;
- whitefly;
- spider mite, etc.
Top dressing of tomato seedlings ensures the normal development of plants. In the long term, this leads to a high and high-quality harvest.