Content:
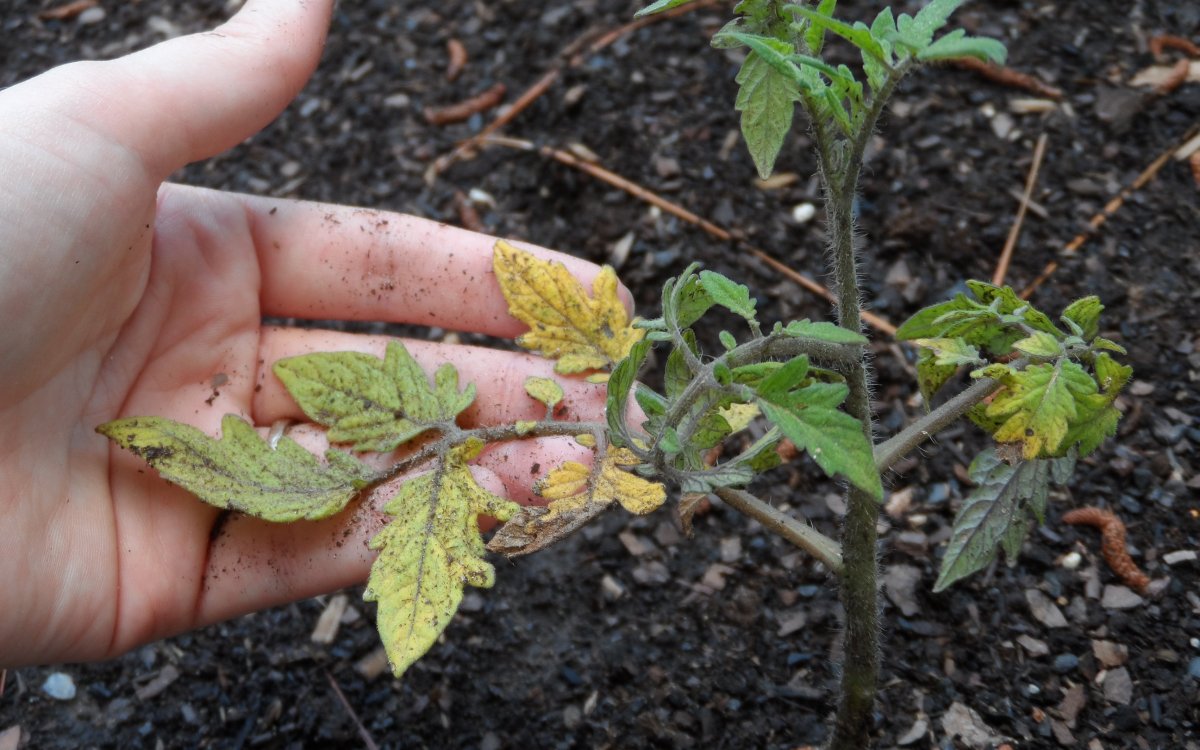
Sometimes, even with the observance of agrotechnical rules and sufficient care, the ovary does not appear, and the tomato bushes begin to hurt. The reason lies in the wrong planting of seedlings.
Why thickening plantings is dangerous
If the bushes are planted too densely, this leads to their shading, which means to late ripening of the fruits. Plants with a strong root system inhibit the development of weaker ones.
Thickening of the planting complicates care. The likelihood of diseases and pests due to contact of the leaves of a diseased bush with a healthy one increases.
However, with the rare placement of seedlings in the greenhouse, the use of the area will be irrational. Therefore, when purchasing seeds, it is necessary to find out what species the variety belongs to. The distances that must be maintained during planting and the care that the plant will require depends on this.
That is why gardeners need to know at what distance to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse, what should be the scheme for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse. The information provided will help give
At what distance can you plant tomatoes in a greenhouse
When planting seedlings in a greenhouse, you need to remember that during the entire time of growth, fruiting and harvesting, tomatoes need to create comfortable growing conditions. The whole season requires watering, weeding, feeding, pinching, spraying and hilling bushes. That is, it is necessary to provide free access to each plant.
To provide the best conditions for the growth and development of tomatoes in the greenhouse, it is necessary to comply with the established rules and conditions, one of the main ones is the use of a certain planting scheme: planting tomatoes at a certain distance between the bushes. The frequency of planting bushes depends on the variety.
Observing certain landing patterns, there are obvious advantages:
- prevention of the appearance of pests and diseases, the likelihood of which increases with thickened plantings;
- supplying tomatoes with sufficient area for development;
- ease of caring for tomato plantings, ease of performing all necessary procedures (watering, feeding, etc.).
The distance between the bushes when planting seedlings is determined by the type of tomatoes, there are three of them.
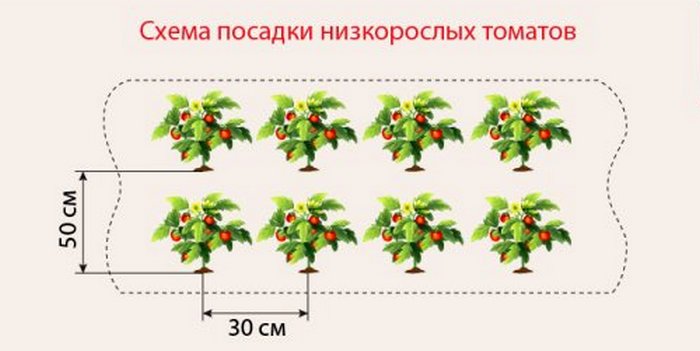
Low-growing or standard:
- plant height does not exceed 50 cm;
- the root system is compact;
- thick strong trunks;
- no garter needed.
Low-growing varieties are planted in 6 - 7 bushes per square meter.
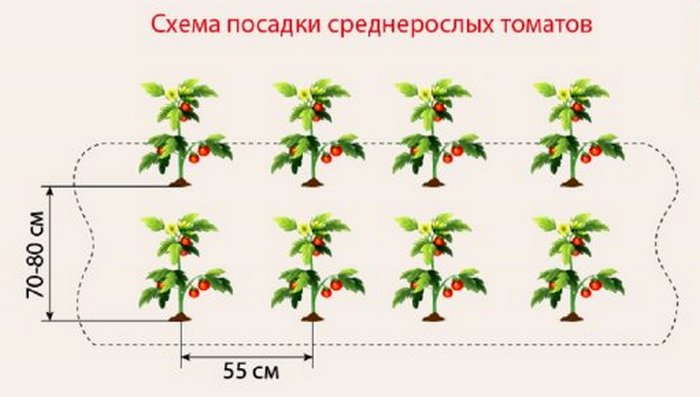
Medium height (determinant):
- height up to 1.5 m (the plant itself limits growth);
- it is necessary to form a bush;
- Planted in 3 - 4 bushes per square meter.
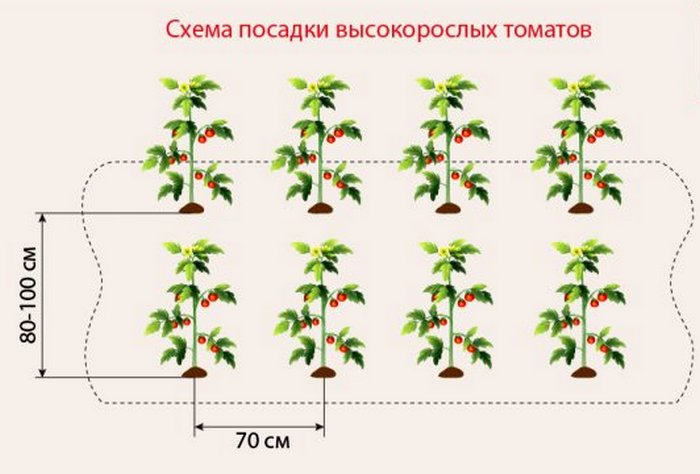
Tall (indeterminate):
- intensive growth;
- height over 3 m;
- need a garter, pinching, pinching.
There are several technologies for planting seedlings.
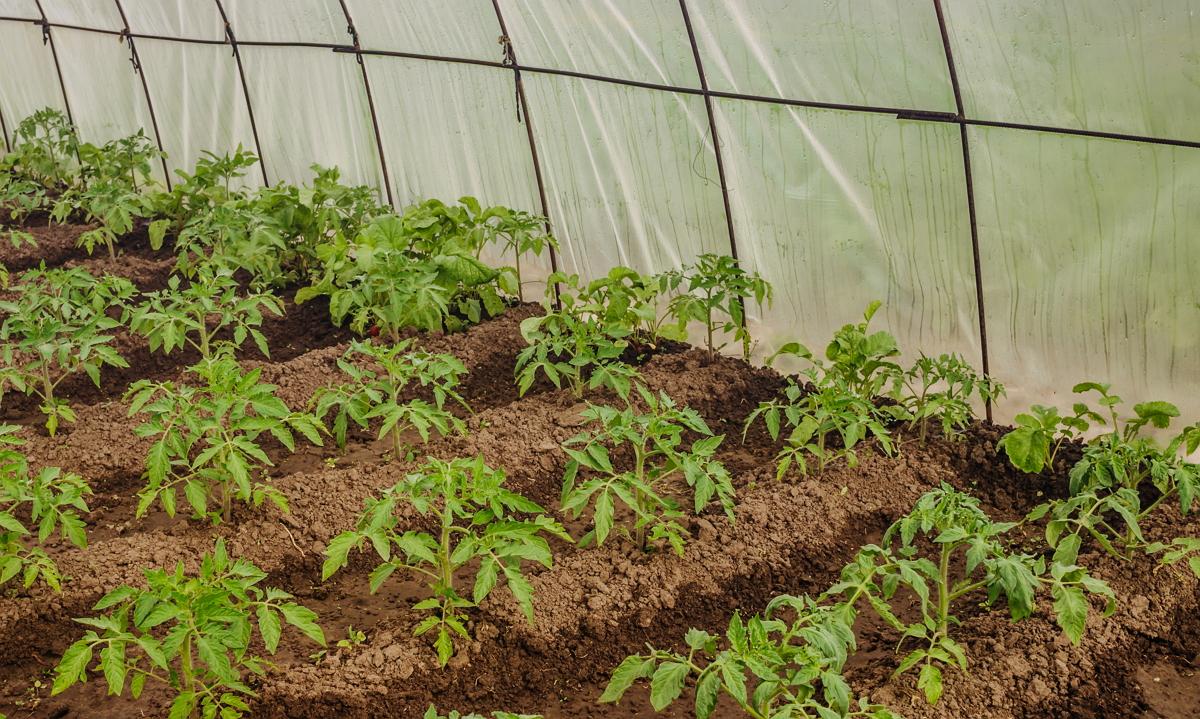
The most common is planting in rows.With this method, markings are made and seedlings are planted in rows. This method requires large areas, which is not suitable for greenhouses.
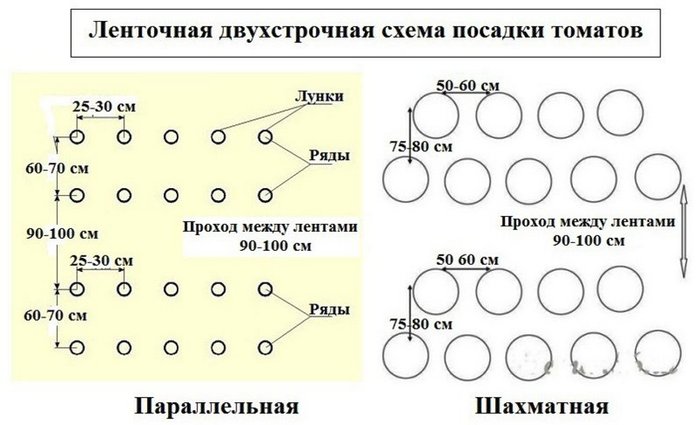
With a parallel planting, two rows are made between the aisles, which saves space, but the convenience of caring for the plants remains. So you can plant any variety, regardless of the height of the bushes. The distance between bushes in a row varies from 60 to 65 cm, between rows - 25-45 cm, depending on the height of the bushes. The passage between the beds is left 80-100 cm. This scheme is used when planting seedlings in a greenhouse.
With the simultaneous planting of undersized and tall varieties, they use a combined planting scheme, when tall ones are planted in the center of the garden, and undersized ones - along the edges, which provides free access to any bush. Space is saved, the method is suitable for greenhouses.
How to calculate the planting density of tomatoes
For planting, 2 - 3 beds are used - this is the best scheme for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse measuring 3 × 6 meters.
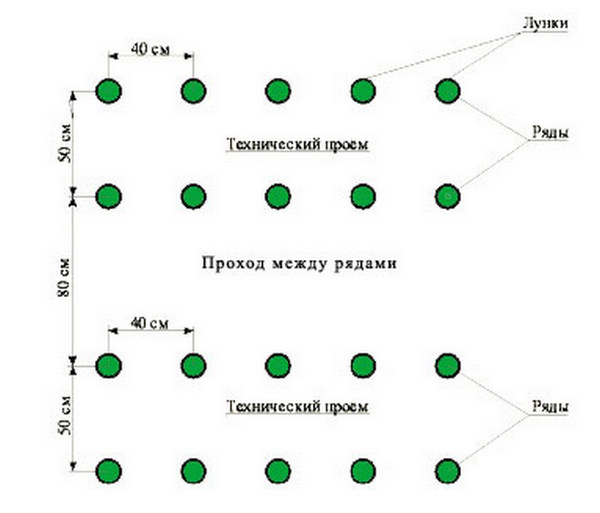
Two beds are placed along the side walls of the polycarbonate greenhouse, their width does not exceed 1 m. You can use a parallel planting of seedlings, but it is better to place the bushes in a checkerboard pattern. This will plant approximately 60 bushes. Tomatoes are planted in the greenhouse so that the distance between the bushes meets the standards for a particular variety.
If you organize 3 beds according to the scheme: the outer ones along the walls are 60 cm wide, and the middle one is 1 m, the width of each path between the beds will be 40 cm.
It is recommended to plant low-growing early varieties on the outer beds, and mid-season tall tomatoes on the middle one. This placement will provide sufficient lighting for all bushes.
In a greenhouse of 3 × 8 m, it will be possible to place 40 more bushes.
Planting rules for tall tomato varieties in a greenhouse
Each tomato variety should be planted according to a specific pattern.
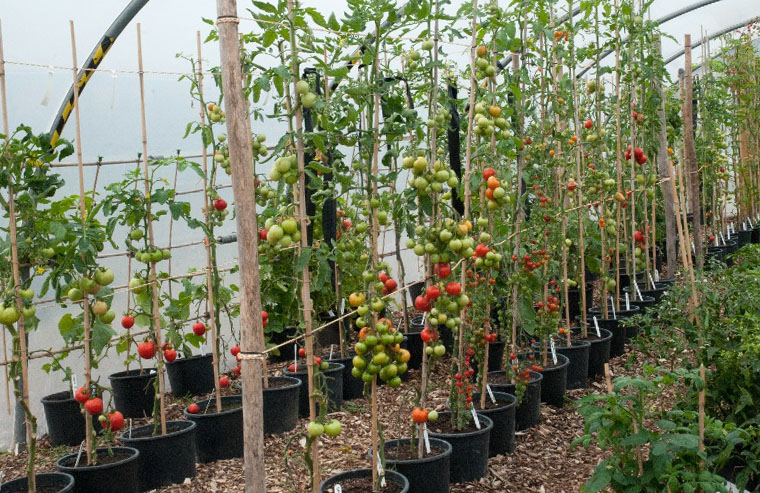
Most gardeners prefer to grow tall varieties in a greenhouse; with a smaller number of bushes and occupied area, you can get a high yield and they will bear fruit until autumn.
When growing tall varieties, space is significantly saved, because one stem gives up to 10 fruit clusters and it is not necessary to plant a large number of bushes to get a good harvest.
Tall varieties are planted, keeping the distance between the bushes 50 - 70 cm, and between the rows - 70 - 100 cm.
Low-growing varieties are grown in a greenhouse and a greenhouse, mainly early ripening, due to an early harvest. They do not require much space: it is enough to leave up to 30 cm between the bushes, and the row spacing - up to 50 cm.
Tips and tricks for gardeners
Before planting seedlings, you need to carefully prepare the greenhouse.
They start with preparing the soil. In the spring it is dug up, adding humus and complex mineral fertilizers. 7 - 10 days before planting seedlings, it is necessary to disinfect the ground in order to destroy the larvae of wintering pests and free them from pathogens of various diseases.
If you have to plant a small number of bushes (10 - 15), you can do without planning. When planting whole beds, it is necessary to calculate the required number of seedlings. Decide on the size of the beds and the aisles between them. Have all the tools and materials for marking:
- ropes;
- pegs;
- measuring meter or marker (made of wood) to clearly mark the location of the holes.
When choosing the location of seedlings in a greenhouse or greenhouse, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the placement of bushes, which differ from planting in open ground. Due to the limited area of greenhouses, you have to save usable area, using it rationally.
It is necessary to take into account the average recommended rates when placing seedlings:
- provide an area of at least 0.3 square meters per plant;
- the distance between the bushes in one row is 40 cm;
- between rows 50 - 60 cm.
These values vary depending on the type and variety of tomato.
The plantings should not be allowed to thicken, the plants will not receive enough light and nutrients, in addition, the likelihood of diseases and pests increases.
When choosing a place, you must take into account what crops were grown here last season. Unwanted predecessors:
- bell pepper;
- potatoes;
- eggplant.
Tomatoes will feel comfortable where they previously grew:
- cucumbers;
- cabbage;
- zucchini;
- peas;
- garlic;
- bow.
After marking the beds, they begin to create holes, their diameter depends on the selected varieties:
- 20 cm - for low-growing tomatoes;
- 30 cm - for tall people.
Hole depth: 12 - 15 cm.
2 liters of a hot solution of potassium permanganate of a slightly pink color are poured into the prepared wells. When the liquid is absorbed, a seedling with an earthen clod is placed in the hole, deepening to the first lower leaves. Loose earth is poured on top, slightly compacted and mulched with peat or humus.
To obtain a high yield, the placement of seedlings in the greenhouse plays an important role. When planting tomato seedlings, you must adhere to the recommended standards, correctly mark the beds and the aisles between them in order to create favorable conditions for the development of tomatoes, get free access to each plant and provide proper care.