Content:
Tomatoes are the most commonly grown crops outdoors and in greenhouses. The cultivation of this vegetable crop is a rather simple task, because almost all varieties and hybrids of tomatoes are undemanding to care, grow on almost any type of soil, and their yield is almost always high.
But it should be remembered that with improper care, tomatoes can lose their positive qualities, slow down their growth, their productivity deteriorates, and this vegetable crop can also be attacked by pathogenic organisms.
Separately, it is worth talking about the mode of watering tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse and in the open field, because an excessive amount of water and high humidity are also destructive for them, as well as a lack of moisture. The basic rules for watering this vegetable plant will be outlined below.
Basic description of tomatoes
Tomatoes are an annual vegetable crop from the nightshade family; they can be grown in a greenhouse or greenhouse, in the beds in the garden. Planting and growing these vegetables hydroponically has also become very popular recently.
It is important to properly prepare the area where the grower will plant the tomatoes. This vegetable crop requires a fertile and loose soil, which has been pre-applied with fertilizers containing basic minerals (including phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen). The soil should not be acidic, the best will be neutral or slightly alkaline. If on the site there is only acidic soil, in the fall, in addition to organic fertilizers, lime or dolomite flour must be added for digging.
In the open field for the normal cultivation of this culture, the air temperature should be at least 21-23⸰С, and in greenhouse conditions - 25-30⸰С.
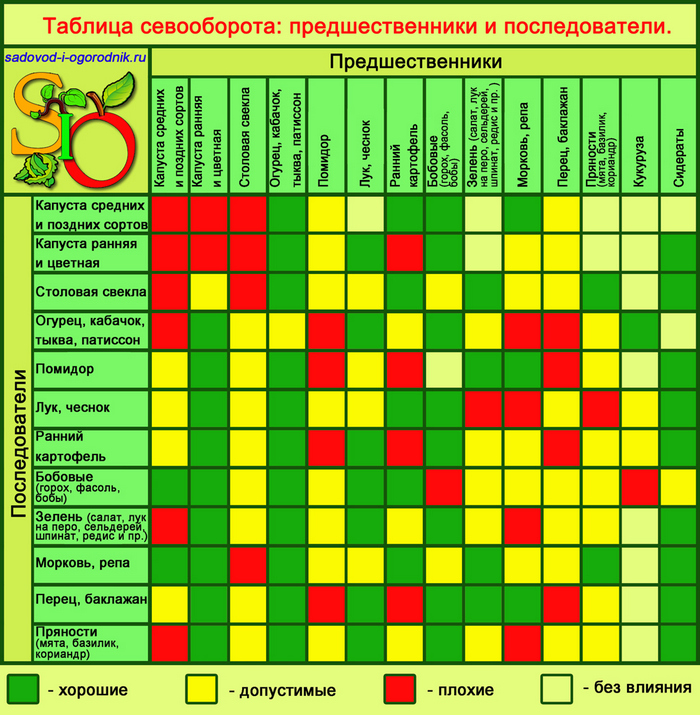
When growing them, the rules of crop rotation should be observed. The best precursors for tomatoes: onions, beets, carrots, cucumbers, turnips, greens, cauliflower and various green manures.
You cannot plant this vegetable after potatoes, peas, physalis, eggplant, pepper and zucchini. Also, it is not necessary to grow tomatoes in the same place every season.
Melons (watermelons, melons), corn, radish, herbs, garlic, and basil will be good neighbors for this vegetable crop. And if you plant marigolds, nasturtium and calendula in the aisles, their aroma will scare away insect pests from tomato bushes.
Soil and seedling preparation
In the greenhouse, you should first disinfect the soil by spilling it with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
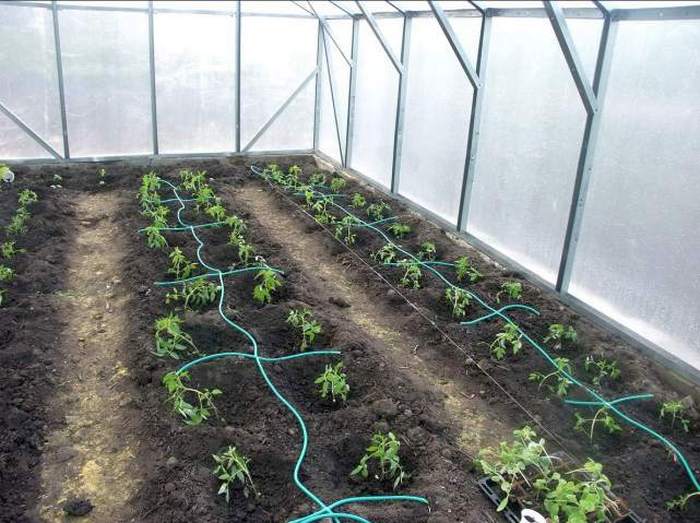
In most regions of our country, tomatoes are grown by seedlings in order to get a harvest earlier, besides, the summer in many regions is short, so the fruits may not have time to ripen in such conditions.
Seeds for seedlings are planted 45-60 days before transferring to a permanent place. To make them germinate faster, you can soak the seed in a boric acid solution. When planting, they should be deepened by 1-1.5 cm. Before the seedlings appear, containers with planted tomatoes are covered with plastic wrap for faster germination.
Seedlings need to be buried when transplanting to the cotyledonous foliage, in this case they will have additional roots, thanks to which more nutrients will flow to the aerial part.
Caring for adult plants includes regular watering, loosening the near-stem circles while removing weeds, applying a layer of mulch, as well as regular feeding at all stages of tomato growth and development. Organic matter, solutions containing the necessary mineral elements are used as fertilizers. You can also use folk recipes to accelerate growth and good fruiting. They usually contain cow dung, bird droppings, yeast or iodine.
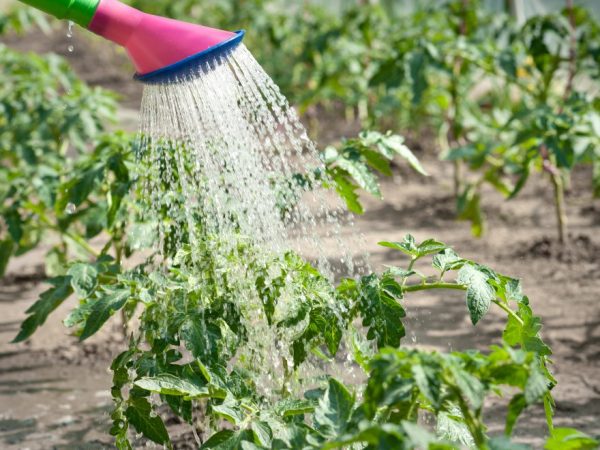
How to water tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse and outdoors
The opinion is erroneous that in any conditions tomatoes can be watered almost every day and in large quantities. If in the open field, excess water can evaporate on a hot day and such watering will bring less harm to tomatoes, then in greenhouse conditions, excessive moisture and high temperatures can cause the development of fungal diseases or various types of rot.
What humidity regime should be maintained indoors and how often should tomatoes be watered in the greenhouse so as not to harm them? In summer, the humidity in the greenhouse can fluctuate from 55 to 76%, but if the weather is dry and hot, this figure can drop to 35-45%.
If sunny days are replaced by rainy days, then the humidity in closed ground can jump sharply to 85% and higher.
And if the irrigation regime of tomatoes is violated, the moisture indicator may be higher. But such a microclimate is definitely harmful to tomatoes. They really need the constant presence of water in the soil, but high humidity harms the normal development of the vegetative mass and ripening of fruits.
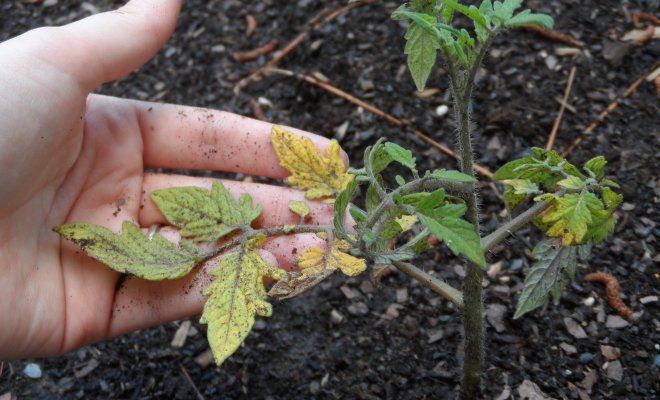
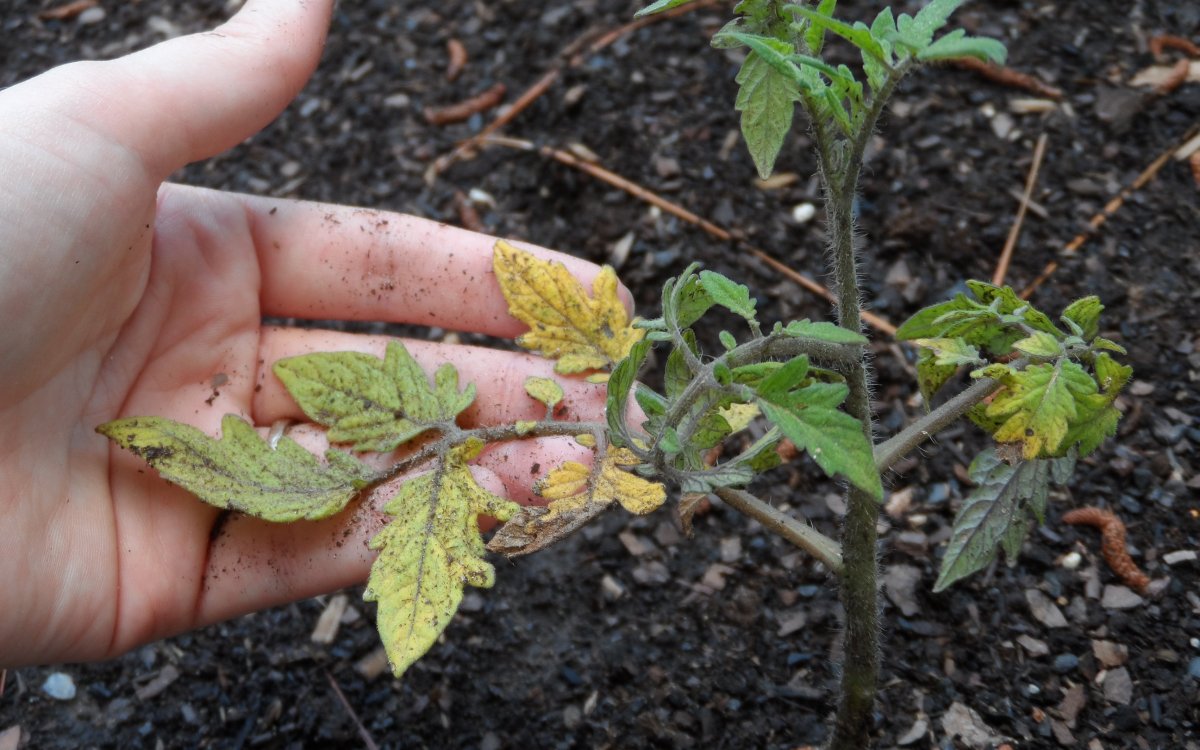
A large amount of moisture in the soil and a lack of it are equally harmful to this vegetable. The root system is unable to absorb excess moisture and begins to rot. With a shortage of water, the leaves become dehydrated, which leads to overheating of the aerial part and to the death of the bush.
How often should tomatoes be watered in the greenhouse to provide the plants with the right microclimate? The correct irrigation regime is achieved with the strict observance of the following rules:
- depending on the humidity and temperature in the greenhouse, this vegetable crop is watered every 3-4 days;
- half a bucket of liquid is added under each plant;
- watering is carried out strictly under the base of the bush. Drops of moisture should not remain on the foliage, otherwise burns will appear on the leaves when sunlight hits;
- the best time for this procedure is morning or evening, otherwise, under the influence of sunlight, most of the moisture will evaporate, increasing the humidity of the air.
You can water the plants in the greenhouse with a watering can or a hose. In this case, water flows directly to the base of the bushes, without falling on the foliage. When watering from a watering can, you can immediately see how much moisture has got to the plant, moreover, you can always pour warm, settled water into this device. But with the help of a hose, watering is carried out from a lake, river or other reservoir, and the water temperature will be lower than necessary.
Drip irrigation is organized in large greenhouses, since it is difficult to water a large number of plants manually in such rooms. The advantages of drip irrigation are undeniable:
- moisture can be fed directly to the root system, preventing evaporation. At the same time, the humidity in the room does not increase;
- water does not get on the aboveground part of the tomatoes, including on the buds during the flowering period;
- watering is carried out at a convenient time for the summer resident;
- leaching and salting of the soil is prevented.
In specialized stores, you can purchase the necessary equipment in order to mount a drip irrigation system in your greenhouse.
Which type of watering to equip in the greenhouse depends on the desire and capabilities of the grower.
It is easier to water tomatoes in the open field, since there is high air humidity only in rainy weather, and on sunny days, the optimal level of moisture in the air is usually established, and the amount of water in the soil can be adjusted by irrigation.
The amount of water consumed by tomato bushes is different and depends on the stage of plant development:
- after planting seedlings in a permanent place, it is watered abundantly (up to 5 liters for each plant) and left for further acclimatization. For 1-1.5 weeks, the seedlings of these vegetables do not need moisture;
- in the period between planting and flowering, these vegetable plants are watered every 3-4 days, the water rate for each bush is 2.5 liters;
- during the flowering period (from mid-June to mid-July, depending on the ripening time of the variety), half a bucket of water is added under each bush, but watering is carried out once every 7 days;
- during the period when fruits appear, tomatoes (from mid-July to early August) are watered every 3 days, you need to ensure that the top layer of the soil is moist all the time;
- as soon as the first reddening fruits appear, watering is again reduced. It is enough to add water under the plants every 7-9 days, but in a small amount.
What is the danger of violation of the irrigation regime
Violation of the regime of watering tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses sometimes leads to irreversible consequences:
- plants are affected by fungal or putrefactive diseases due to too abundant watering and stagnant moisture in the soil. As a result, the roots begin to rot, the bushes do not receive sufficient nutrition, weaken and may die;
- lack of moisture can lead to wilting of tomatoes, poor absorption of calcium, as a result, the bushes are affected by apical rot. As a result, you can lose some of the harvest, and sometimes the whole plant dies;
- with daily watering, when insufficient moisture is applied, the immunity of tomatoes decreases, and they can be affected by pathogens.
Therefore, when growing tomatoes, it is imperative to adhere to the watering regime in order to prevent deterioration of the condition of the plants and grow a good harvest.