Content:
There are several pear hybrids that were bred over 200 years ago. Despite their venerable age, they continue to be bred because of their pleasant taste and neat appearance. These varieties are used by breeders to obtain new hybrids.
The history of the origin of the pear
Pear Williams was bred in the southern part of England by the scientist Wheeler, who used varieties that have been lost today to hybridize a new tree. This happened at the end of the 18th century. The species was named in honor of R. Williams. He presented the new pear at a gardening meeting in 1816. Then the plant began to be cultivated in France and other European countries.
It entered the Russian Empire in 1861, where it was spread throughout the southern provinces of the country by the gardener N.P. Makukhin. There are several varieties of the pear hybrid. But the most famous of them, obtained by long-term breeding varieties: Williams Winter (Curé), Bon-Chretien, Barlet, summer red Duchess.
All these pear trees passed tests in 1946-47 and are included in the State Register of Fruit Crops of the North Caucasus, Rostov Region, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, etc. The Primorsky variety, which is now widespread throughout the Black Sea coast of Russia and Ukraine, was specially developed for the Crimea.
Some information and technical data
The description of the Williams pear variety is as follows:
- The height of the tree ranges from 2.6 to 3.4 m. The crown is similar in shape to a rounded, often irregular pyramid.
- Regardless of the variety, pear seedlings grow quite quickly, but by the age of 9-11 years, this process slows down greatly.
- The plant is covered with bark colored in various shades of yellow. The skeletal branches of the pear tree are thick and have a grayish tint.
- The leaves (they are large in size) are equipped with small teeth at the edges of their smooth, shiny plates. Green streaks are visible above their surface.
- Flowers on the tree are arranged in groups of 6-7 units. They appear before the formation of leaves.
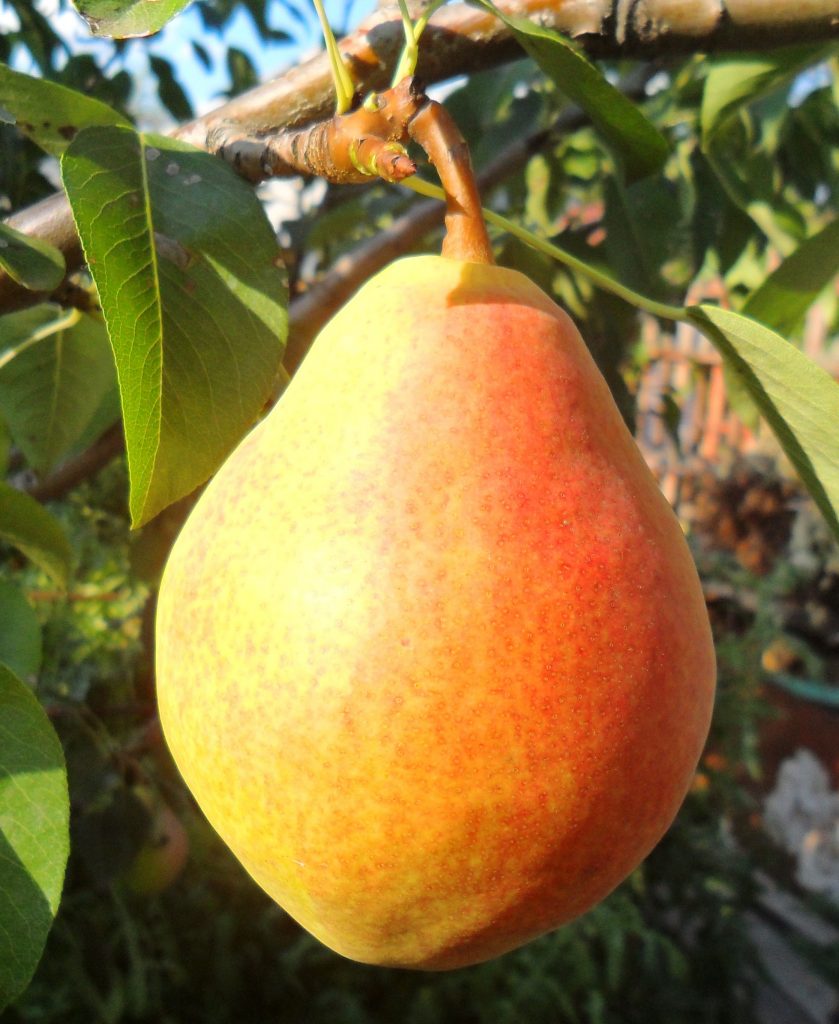
The Williams pear description continues the characteristics of its fruits:
- fruits are tied at once in 2-3 pieces;
- they are firmly attached to the branches by stalks;
- the average weight of a pear ranges from 150-170 grams, but specimens weighing up to 180 grams are sometimes formed on young trees;
- the surface of the fruit is covered with bumps and thin skin, which is painted in greenish shades;
- when the pear ripens, its color turns yellow;
- gray blotches appear on the surface of a ripe pear fruit;
- inside the pulp are small seeds.
The yield of Williams pear hybrid is 50-150 kg from each tree. It depends on the place of cultivation of the variety. The seedling begins to bear fruit at the age of 5 or 6 years.
Pears ripen in August. They can be stored for 15 days. If the fruit is placed in the refrigerator, it will last about 45 days.
Fruits are used fresh, compotes, marinades, and preserves are prepared from them. Pears can even be dried.They are useful in the treatment of various diseases in people with cardiovascular damage. They are often used to feed diabetics (the Williams variety has a low calorie content - 42 kcal).
Agrotechnics
If the gardener wants to plant the Williams pear variety, you need to pick up seedlings 130-150 cm long, which are 1-2 years old. The selected pear tree should have 3-5 branches. Their distance from the side shoots to the root collar ranges from 0.5 to 0.6 m. The bark of the tree should not have chips, cracks or other damage. Cuttings are bought without leaves, and the length of their roots is selected within 0.2-0.3 m.
Groundwater should pass at a distance of at least 2 m from the roots of the pear hybrid.
The farmer can plant pear trees in the fall or spring (until the buds are full). It is forbidden to plant seedlings in the garden in frost.
To plant a tree, they dig a hole with dimensions of 0.6 X 0.6 X 0.8 m.A mixture of 1 part of humus and the same amount of earth is poured inside. Potassium sulfate and superphosphate (0.35 kg each) are added. Pear roots are soaked in a stimulant. The procedure lasts from 3 to 12 hours.
A seedling is installed in a hole, covered with earth, and compacted. A peg is placed next to the pear, to which a tree is tied.
Watering
Caring for Williams' pear hybrid begins with the organization of proper irrigation.
For 2-3 years, young seedlings should be regularly watered with warm, settled water throughout the growing season. It is recommended to moisturize adult hybrids at least 3, but not more than 7 times per season. The intensity of watering depends on the weather and climate at the place where the trees are planted.
Irrigation must be carried out:
- before blooming buds;
- after the flowers have fallen;
- at the end of the season, in the fall.
In hot weather or drought, the intensity of watering Williams pears is increased by 3-4 times.
Fertilizers
Williams' seedlings are fed annually. This continues until they begin to bear fruit. Manure, azofoska or Kemir's drug are introduced into the ground (0.1-0.15 g for each hybrid).
Adult pear trees are fed in the fall, when they are digging. Mullein and superphosphate are used as fertilizers. I scatter them over the entire area of the trunk circle and over the shade of the crown. After that, all the soil around the pear is dug to a depth of 0.25 to 0.35 m.
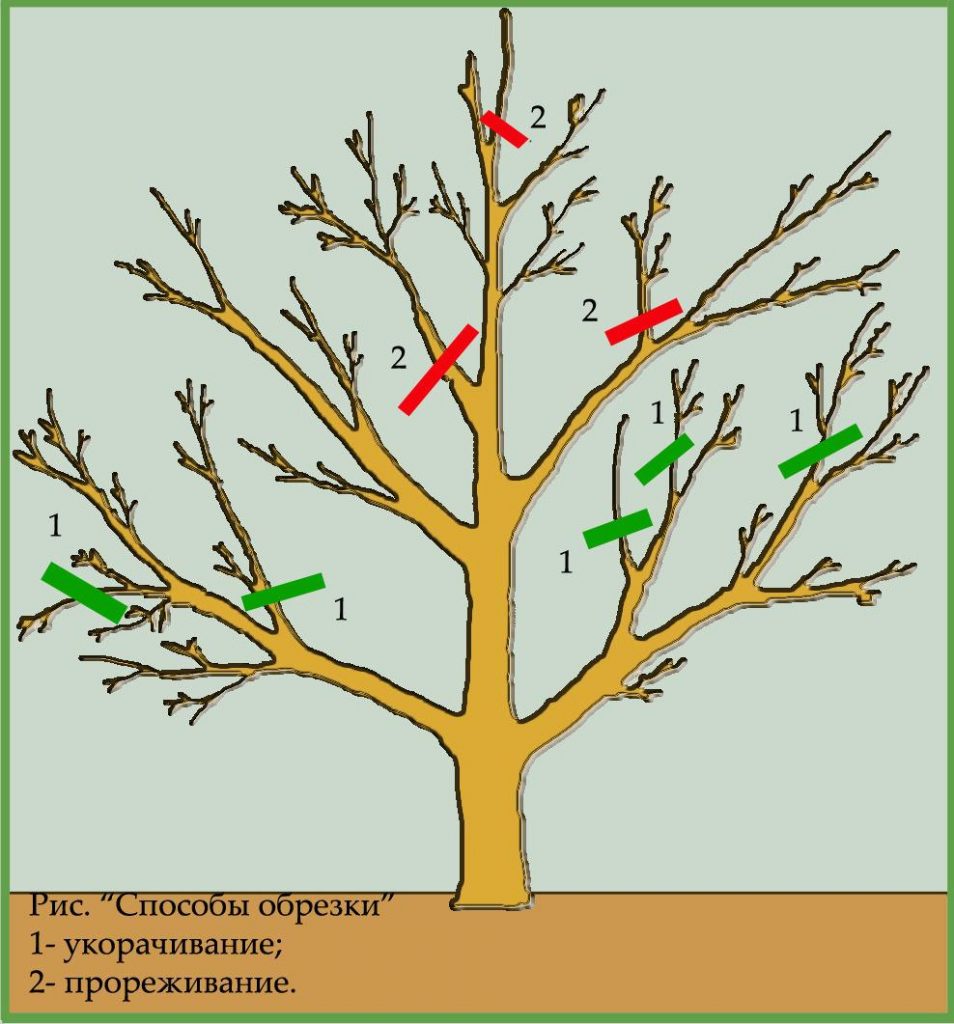
Pruning
Pruning is a must in the care of pear hybrids. If the tree is young, then in early spring 3-5 branches are left on it at a height of 0.5-0.7 m above the ground, and the remaining shoots are cut off. The trunk should rise above the lateral processes (their length should not exceed 0.3 m) by 0.2-0.3 m.
Mature Williams pear trees are pruned 2 times in 12 months. When sanitizing, remove all old, diseased or broken branches. This pear variety is rejuvenated by shortening perennial shoots to their length at 3-5 ages. When thinning the crown, part of the old fruiting branches is cut out. If the trees do not grow well, then it is recommended to increase the pruning.
Possible problems
The variety is susceptible to various diseases that can destroy not only the entire crop, but also kill the tree itself. To eliminate these lesions, seedlings are treated with 4% Bordeaux liquid or 2% colloidal sulfur mixture. Spraying with chemicals is carried out 2 times: before the appearance of flowers, and then 15 days after they fall.
Scab is fought by destruction of damaged fruits, regular harvesting of fallen leaves and processing. If a farmer finds symptoms of this disease on a tree, then he must process the branches of Williams pears 3 times. The first procedure is carried out before bud development, the second after flowering. The last time the trees are watered with Bordeaux liquid or colloidal sulfur after another 14 days.
The crop can die from the invasion of pests. You can destroy garden parasites if you use modern insect control products.
For the extermination of aphids, the drugs "Corsair", "Olecuprite" and "Isofren" are used. They get rid of the honeydew by spraying the trees 3 times (with swelling of the buds, in the middle of summer and autumn) with the means of "Commander", "Iskra", "Aktara", "Inta-Vir". Other pests are eliminated by treating pear hybrids with an aqueous solution of wood ash.
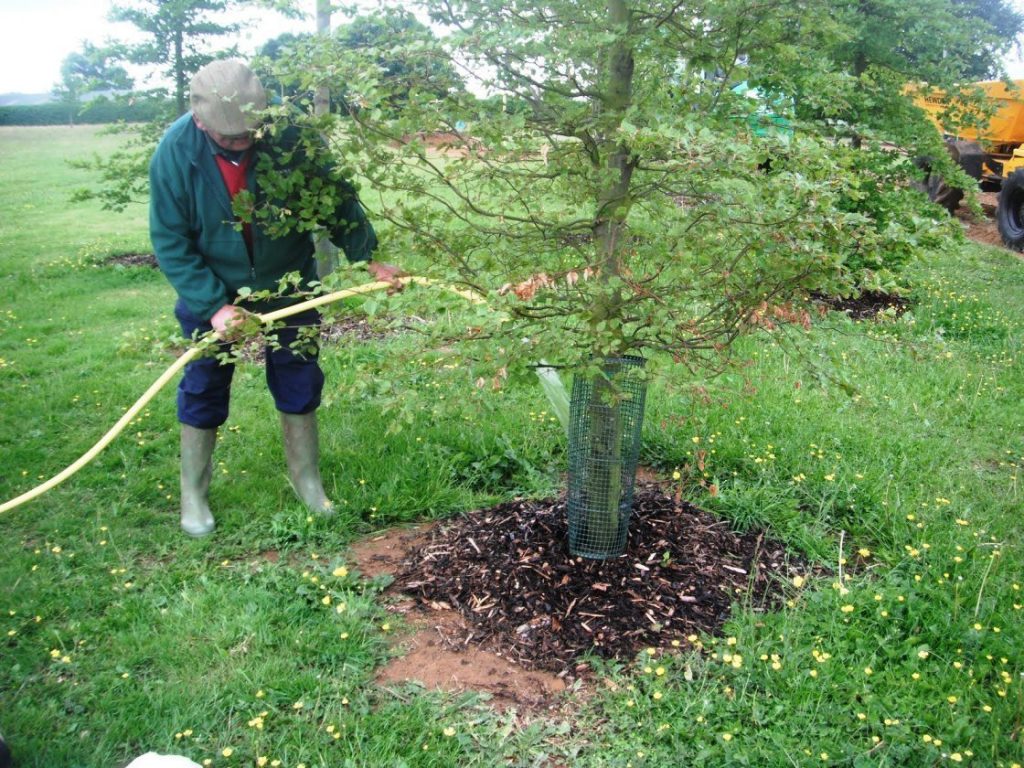
The Williams variety does not tolerate cold well. Therefore, for the winter, pear seedlings should be wrapped with warm material, and when the cold intensifies, it is advisable to fumigate them with smoke. To protect against small rodents, a wire mesh is installed around the tree trunks.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The advantages of Williams pear are:
- early ripening of fruits;
- regularity of obtaining a high yield;
- the formation of large, beautiful pears on the branches;
- adaptability to growing on any soil.
The disadvantages of a pear hybrid are:
- low frost resistance;
- poor adaptation to heat and drought;
- impossibility of pear fertilization without pollinator trees;
- frequent scab damage;
- Williams' inability to resist pests such as aphids or honeydew.
This ancient pear can be cultivated by any farmer. But to get the harvest, you need to adhere to and timely implement all the recommendations of specialists.