Content:
Bacterial burn, or fireworm, is a dangerous disease of fruit trees that requires mandatory treatment. If you do not take action, the pear will begin to dry out and die in 3-4 years. The disease came to our territory from abroad and is spreading at a terrible speed. Today, fulminant forms of this disease have appeared. In order to cure a bacterial burn in a timely manner, it is important to know the symptoms and causes of its occurrence.
Popular varieties of pear
More than 1000 varieties of pears are grown, each of which has its own qualities that are necessary for growing in a specific climate, taking into account the composition of the soil, the amount of precipitation and other characteristics.
Summer
Summer varieties of pears ripen by the end of July, and by the beginning of September they have already ceased to bear fruit. Their popular representatives are:
- Lemon... An unpretentious variety that gives fruits weighing 80-100 g, covered with a thin lemon-colored skin. Fruiting from the 7th year of life. Gives high yields, is hardy. Disadvantages include a tendency to scab and rapid overripe.
- Lada... The tree begins to bear fruit early (3-4 years), gives abundant harvests. Good frost resistance. Fruit of sweet and sour taste weighing 150g.
- Rogneda... A frost-resistant high-yielding variety. The harvest ripens in August. The fruits have a weight of 120-130 g and a loose yellow skin with a reddish blush. The pear has a sweet taste with nutmeg notes. She is not afraid of disease. The fruits can be stored for up to 3 months in a cool place.
- Skorospelka... Her trees are already harvesting in early June. Fruiting from 5-7 years, increasing fruits weighing 120-170 g. The peel of pears is green with a red blush. Not afraid of drought and frost. Among the shortcomings are poor keeping quality of fruits and susceptibility to scab.
Summer pears often have a loose flesh, which reduces shelf life. The crop must be removed from the tree in a timely manner, not allowing it to overripe.
Autumn
In autumn varieties, the harvest ripens from September to early November. The shelf life of this species is also not very long - about 1.5 months. Pears must be picked 5-7 days after they are ripe. The most famous autumn pears:
- Duchess... French variety producing 350-600 g fruits with delicate pulp and pleasant aroma. The pear begins to bear fruit at the age of 5-6, it is considered whimsical to care for. The disadvantages of the variety are considered low frost resistance, exactingness to the soil.
- Otradnenskaya... She won the love of summer residents with her winter hardiness and rich regular harvests. The variety is resistant to weather and disease. The pear begins to give fruits weighing up to 130 g after 5-6 years of life. They tolerate transportation very well. A weak taste is considered a disadvantage.
- Memory Zhegalova... Late autumn variety of Russian selection with average growth and productivity. The first fruiting occurs at 5-6 years. The pulp of the fruit has a sweet and sour taste and a bright aroma. The average weight of fruits is 120-150 g. The disadvantage of the variety is self-infertility (pollinators are needed). Good frost resistance.
- Cheremshina... A fast growing pear with a high pyramidal crown. Fruiting starts at 5-6 years of age. The harvest ripens in October-November. Fruits of yellow or orange color gain weight up to 250 g, are stored for 4-5 months. The variety is resistant to scab and frost.
The fruits of autumn varieties are most often used for processing and conservation. Delicious juice, compote and jam are made from these pears.
Winter
Winter pear varieties ripen in mid-October. It is advisable to pick them later to extend the shelf life of the crop. But at the same time, if the fruits are overexposed on the branches, they can crumble. Famous varieties of winter pears:
- Kyrgyz winter... Medium-sized pear, which ripens in October. The crop is removed in 2 steps. The fruits are perfectly transported and can be stored until spring. The weight of each pear is 220-250 g. The pulp has a tart, unusual taste, coarse-grained. The variety is resistant to frost, drought and scab.
- Curé... Tall pear with a dense crown and early winter ripening period. The crop is harvested in late November or early December. Pears lie until early February. The variety is considered unpretentious and high-yielding. Fruiting occurs at 6-7 years. Fruit weight - 200 g. The pulp is slightly tart, with a moderate aroma. High frost resistance.
- November... Despite the name, it bears fruit in October. Very large fruits. The weight of individual specimens can reach 700 g. The pulp is tender, sweet and sour, with a pleasant aroma. The November pear is appreciated for its frost resistance, scab resistance and fire blight, excellent taste.
- Etude Kievsky... A pear with a good yield, despite its compact crown. Fruiting occurs in November. The tree begins to produce crops at 3-4 years of age. The fruits have a juicy, sweet and sour pulp with a rose aroma. The variety is scab resistant and has high winter hardiness, but is prone to wilting.
Fruits of winter varieties have the longest shelf life and lie quietly until mid-spring. Store them in a cool place at temperatures between 0 ° C and 1 ° C.
Symptoms and treatment of bacterial burn
If there is a bacterial blight of a pear, treatment should be started immediately, otherwise the tree will be "eaten" completely. How does the disease manifest itself, what are its first signs?
Signs of illness
Inflorescences are primarily affected. Then the disease spreads to the buds, branches and young shoots. They stop growing, turn black and dry out, the leaves curl. At the next stage, a fire blight affects the trunk and rapidly covers the entire tree.
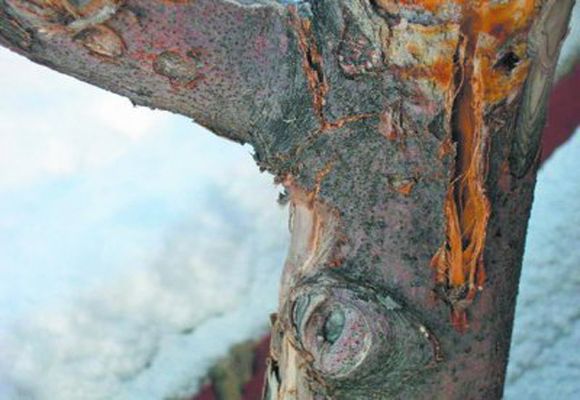
If the disease is left untreated, the tree turns completely black and dies shortly thereafter. At the final stage, the trunk is covered with brown stains, on which white drops of bacterial liquid appear.
Causes of occurrence
The infection is transmitted to healthy trees from sick pears through insects and birds. This is not the only way the disease spreads. The protruding bacterial liquid under the influence of the wind forms long thin filaments that are carried through the air over a distance of several kilometers.
When the infection spreads to healthy tissue, bacteria begin to multiply. This is facilitated by high humidity and normal air temperature. Bacteria are able to secretly develop inside the flower, then the disease spreads to the rest of the plant.
Damage to the trunk and branches can contribute to the fire. In this case, the infection enters the tissue of the tree along with the rain. In cold weather, pathogens hide deep in the trunk, and in the spring they become active. White droplets appearing on the bark are the accumulation of bacteria in a special liquid.
How quickly the disease affects the pear depends on the variety, age, weather conditions and soil composition. Often the fireworm goes unnoticed due to the fact that the disease spreads from top to bottom and is initially mistaken for crown wilting due to lack of moisture.
Often, the grower will recognize a fire blight when the tree is already half infected.Sometimes the infection is mistaken for other diseases and is not treated properly. The bacterial burn quickly spreads to neighboring trees and as a result, you can lose the entire plantation.
Control and prevention methods
It is recommended to uproot and burn heavily affected trees. If the symptoms appear only on individual branches, you need to cut off the diseased shoots, and treat the tree with a solution of copper sulfate, for the preparation of which 100 g of the substance is diluted in 10 liters of water.
In the treatment of fireworm, pears are also treated with antibiotics in a certain dosage. The garden must be sprayed with the prepared solution several times at intervals of 3 weeks. At the same time, drugs are used to control pests that can be carriers of the disease. Bactericidal solutions are prepared according to the following recipes:
- using Streptomycin for pears, 1 ampoule of the drug is diluted in 5 liters of water and trees are treated with a spray bottle;
- when treating pears with Tetracycline, a spray solution is prepared from 2 tablets of the drug for 3 liters of water;
- the powerful antibiotic Ofloxacin also helps against fire, it is used in the same dosage as tetracycline.
Gardeners often use Fitosporin and Fitolavin for this disease. These drugs belong to the group of fungicides and have proven to be effective against fire blight. Each of them is bred according to the instructions and used to process trees. They are also used for prophylactic purposes, carrying out treatment before bud break. Often these fungicides cannot be used, otherwise they will lose their effectiveness, causing addiction.
Other common diseases
In addition to firewood, pears are susceptible to a number of common diseases. Many of them can be avoided if you follow correct agricultural techniques and take preventive measures.
Bacterial cancer
Another disease caused by bacteria is bacteriosis or bacterial pear cancer. The disease is manifested by the death of the bark, which begins to flake off. In the future, decay passes to the wood, the process is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Often, for the first time, bacteriosis is manifested in the spring by the browning of young shoots and buds. If bacterial cancer is suspected, the affected branches are cut to healthy tissue and the sections are treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, and then covered with a layer of oil paint.
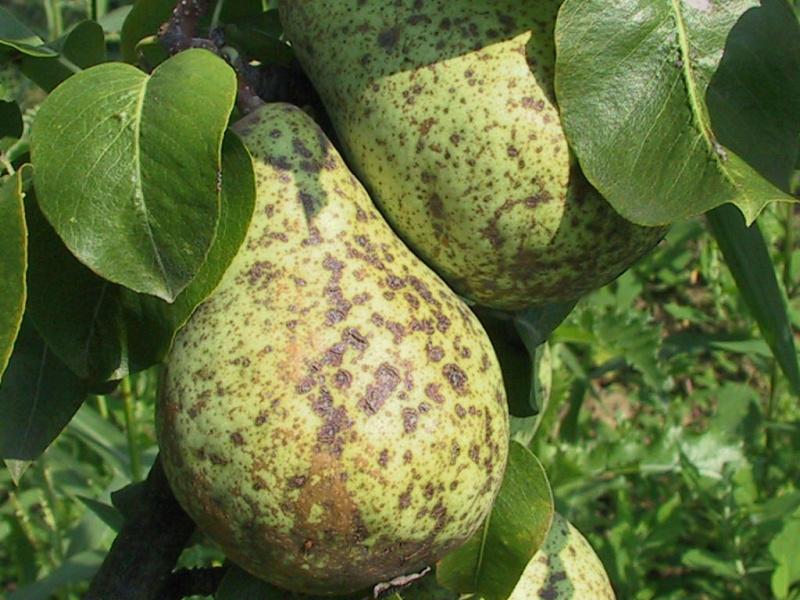
Scab
Garden pears often suffer from scab. The disease manifests itself by the appearance on the underside of the leaves of yellowish spots with a small fluff, which is an accumulation of fungal spores. The scab is quickly transmitted to the fruit. Pears become covered with rotting spots, where the skin bursts. The fruits become deformed, lose their taste. To prevent the disease, trees are sprayed three times per season with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, the crown is thinned out and plant residues are removed. If symptoms have already appeared, it is necessary to deal with the scab with the preparation Skor.
Fruit rot, or moniliosis
The disease is caused by the fungus Monilia fructigena, which parasitizes the fruit. In pears affected by moniliosis, the pulp begins to rot. Brown spots form on the skin, which later become covered with a gray bloom, consisting of fungal spores. The wind carries spores over considerable distances, which contributes to the spread of the disease. Affected fruits fall to the ground or dry out directly on the branches. Hot and humid weather contributes to moniliosis. Preventive treatments are carried out twice - in spring and autumn. The trees are sprayed with 1% Bordeaux mixture or lime milk - this will help save the crop.
Sooty fungus
Some beginners wonder why their pear suddenly turned black.The reason for the blackening of fruits and leaves is a sooty fungus. The disease often occurs against the background of a weakened immune system or after an attack by insect pests. Fitoverm is used to prevent the disease, it suppresses the reproduction of fungal spores. You can get rid of pests with the help of Calypso.
Powdery mildew
Another fungal disease. It manifests itself by the appearance of white powdery spots on leaves and flowers. The affected leaves begin to curl up into a tube, and the inflorescences dry out and fall off. Most often, young shoots suffer from powdery mildew. For prevention, pears are treated with a foundation or soda solution with the addition of soap. The affected plant parts are removed and burned.
To protect your pears from disease, you must first of all provide them with proper care. After all, trees deprived of care become weakened and vulnerable to any infection. It is necessary to support their immunity in every possible way and do not forget about preventive measures.