Content:
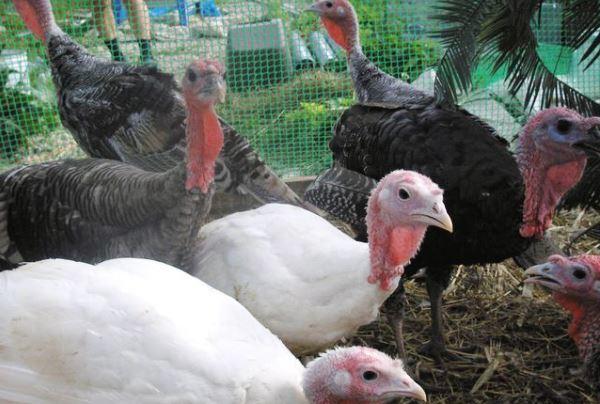
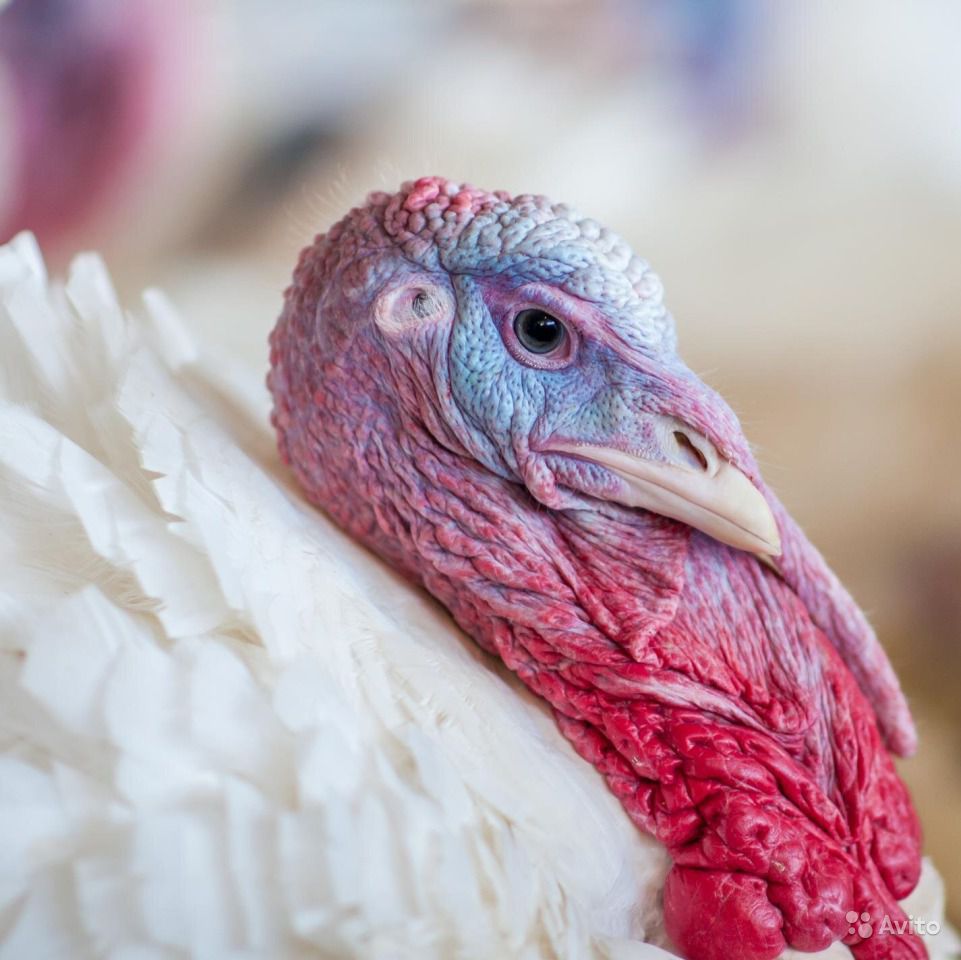
Histomoniasis is an infection caused by protozoa of the genus histomonads. It affects most of its birds. The foci of infection are the liver and organs of the gastrointestinal tract, while young birds often die. The disease in poultry goes away with severe inflammation, intoxication and weakness. Treatment of histomoniasis is long and prolonged, and the recovered bird will be less fertile than its healthy peers.
Pathogens and causes of the disease
The disease is caused by the protozoa of the Trichomonas family, a genus of histomonads, to which one species belongs - Histomonas melegridis. He is the causative agent of the disease of the same name. In their development process, they pass through two forms - flagellate and amoebic. In the course of their development, parasites enter the internal organs of the bird with food and begin to actively reproduce. The parasite penetrates deep into the bird's body with food, and is excreted with feces, this explains the rapid rate of infection.
Young turkeys are most often infected. If the treatment is delayed, the mortality rate of young animals reaches 70%.
In the flagellar stage of development, the parasite has a round shape, the size reaches 20 micrometers, the number of flagella is from one to four. Some organelles characteristic of Trichomonas are missing. In the amoeba-like form, flagella are absent, the body diameter slightly increases. The parasite reproduces by dividing in half while maintaining all the functions of the daughter cell.
The disease is not dangerous to humans. The birds are characterized by acute and chronic course of the disease. If the disease persists chronically, parts of the animal's body remain affected for the rest of its life and the turkey affected by the parasite infects the rest of the offspring. The acute course of protozoonosis is typical for young birds, and it is characterized by a high mortality rate.
The most common causes of the disease are:
- Damp premises, contaminated bedding, bird feed in contaminated feeders;
- Tightness;
- Improper rearing of young animals;
- Keeping different in age and type of livestock in one room;
- Unrefined feed, unwashed roots, storage of grain in an unsuitable condition;
Parasites also enter the body of animals with insects or worms.
Histomonads parasitize among the cells of the intestinal epithelial tissue and in the liver, where they spend most of their life cycle. Penetrates the gastrointestinal tract of turkeys with food, passes through the esophagus and hatches in the intestines. From there, it enters the liver through the portal vein system.
Most often, young turkey poults are prone to histomonosis from the moment they hatch from the egg to 2-3 months.
In late autumn or winter, mature turkeys are infected. The parasite can survive in the larval form of heterokis or roundworms.
Symptoms accompany the disease
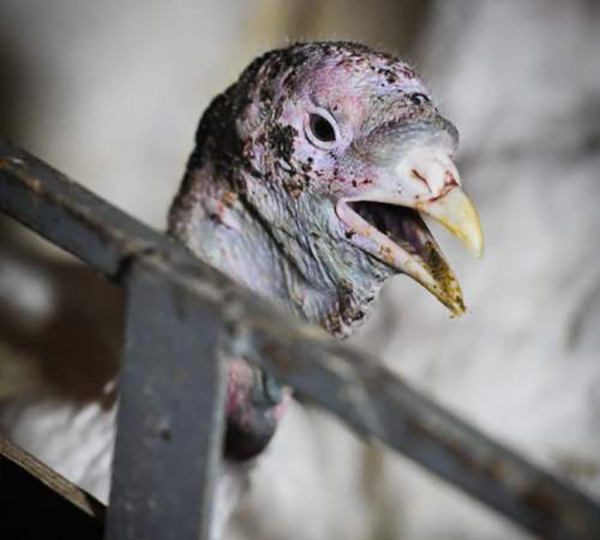
Histomoniasis in turkeys is acute and chronic. Manifestations of the acute form of histomonosis:
- The bird becomes weak, inactive. At the same time, the wings are in a lowered state for a long time;
- The turkey refuses to eat due to which it quickly loses weight;
- Diarrhea appears, during the act of defecation, turkeys make a lot of noise, feces have a strong stench and a greenish tint;
- In young animals, the color of the skin becomes black, in the older bird, the skin turns blue.
- The body temperature of birds decreases.
The livestock begins to gather in close groups, hide their heads under the wings, close their eyes. After about a week of illness, the chicks begin to be exhausted, they finally stop moving normally, walk, staggering when moving due to weakness. In turkey poults, histomonosis lasts up to three weeks, after which the animal either dies or the disease becomes chronic. Symptoms of the chronic form of histomonosis:
- Decreased appetite;
- The feather cover becomes dull;
- Weakness;
Histomoniasis lasts up to several months. Most often, the livestock becomes infected in the summer, when it can easily forage for worms and feed on small insects. However, keeping in unfavorable conditions can contribute to infection at any time of the year.
Pathological signs
Opened birds will differ in the following features:
- The intestinal tract is hypertrophied, the walls are much thicker than usual, there are many mounds of different sizes on them. There is a curdled mass with blood impurities attached to the walls;
- The mucous membranes of the intestines and liver are covered with small holes;
- The intestines and the connective tissue lining of the abdominal cavity can be fused.
- The size of the liver and spleen is enlarged, it is covered with necrotic foci;
Diagnosis of the disease
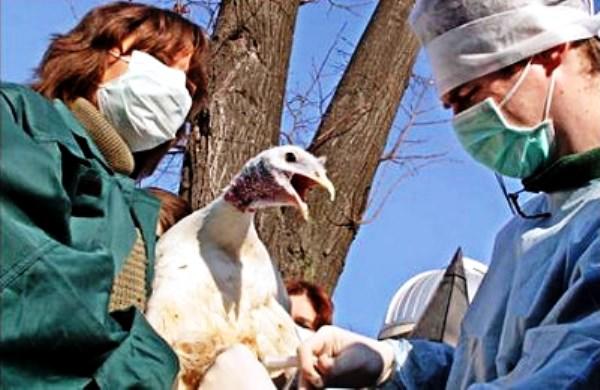
Diagnosis of the disease in turkey poults is carried out in a comprehensive manner, taking into account the symptoms and pathological changes in the body of dead birds. When examining the birds, a specialist identifies infected turkeys with obvious symptoms and tries to find out the cause of the infection.
From the opened carcasses of turkeys, histological preparations of the affected organs and mucous membranes, the contents of the intestine are taken for histological examination. It is necessary for an accurate diagnosis, due to the similarity of symptoms with other protozoonoses.
Methods for treating histomonosis
To treat histomonosis in turkeys, drug therapy is performed. Timely diagnosis of protozoonosis is important for her. Due to the high rate of spread on large farms, histomonosis can quickly develop into an epidemic. When kept in inappropriate conditions and poor feeding, it has a very high mortality rate.
All birds with suspected histomonosis are transferred to a separate room to avoid contamination of the remaining healthy livestock. Isolation of infected individuals must be complete, completely weakened individuals are killed, in this state, treatment is already useless.
Metronidazole is used to treat poultry. For treatment, a solution is used in a proportion of 0.1 mg per kilogram of live weight. You can add it to drinkers or manually bury it in the beak with a pipette. It is possible to use metronizadol in the form of tablets, in which case it is mixed with feed in a proportion of 1.5 g of the drug per kilogram of dry feed.
It is necessary to continue treating the bird for up to 7 days, after which the dosage of metronizadol is reduced and given to turkeys exclusively for prophylaxis once a day.
After the completion of treatment, to restore the body after taking antibiotics, preparations containing live cultures are added to the turkey feed to restore the microflora of the body.
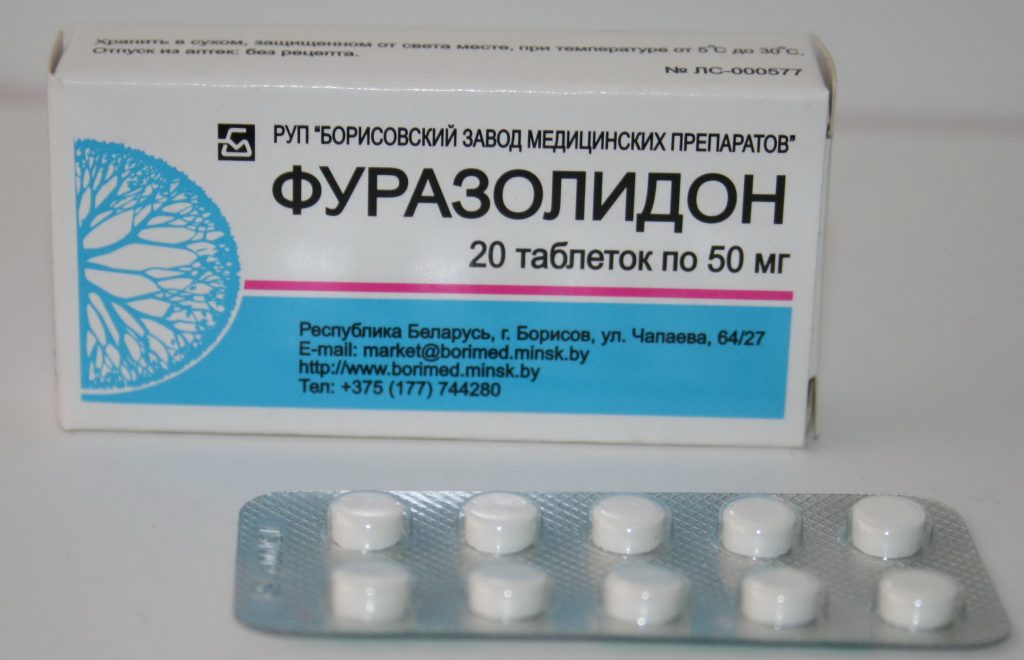
List of drugs for the treatment of histomonosis:
- Furazodolin;
- Phenothiazine;
- Tinidazole;
- Nitazol;
- Osarsol.
The recipes for these drugs describe the dosage and the required duration of the course of administration. However, before treatment, it is necessary to consult with a specialist to clarify the amount of the drug.
Histomonads can infect helminths that live in the digestive tract of most birds, so in order to finally get rid of the disease, you will need to be treated for worms. The drug and course of treatment for this is prescribed by a veterinarian or livestock specialist. To strengthen the body, the bird receives restorative feed.
Preventive actions
To avoid protozoanosis in turkeys, it is necessary to isolate young livestock from adult turkeys, to keep the room in which the bird lives in a clean state. It is desirable that it has ventilation. If possible, clean the room, bedding and feeders with drinkers. Walk the bird in a large area with good lighting.
Feed the birds only with high-quality and not expired feed. Avoid dampness of grain feed, and mold.
Histomoniasis is widespread throughout the country and is truly a popular disease. It is turkey poults that suffer most from protozoonosis, and they also have the highest mortality. If you find weakness and discoloration in animals, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible to prevent the death of the bird. Knowing what histomonosis in turkey poults is, the symptoms and treatment of the disease, you can raise more than one healthy herd.