Content:
Broiler turkeys are popular all over the world. Growing on farms and backyards allows you to get tasty dietary meat and nutritious healthy eggs. The bird is versatile among other breeds and has excellent characteristics.
Bird description
Hybrid Converter turkeys were bred by US breeders by crossing White Dutch and Bronze Broad-breasted Turkeys in the 1960s. They were brought to the territory of the USSR in the 1970s. The bird began to enjoy popularity among poultry farmers due to its rapid growth, high egg production and adaptability to our climate.
The wide gene pool allowed us to obtain three subspecies of turkeys: light, medium and heavy:
- light: male weight - up to 10 kg, female - up to 6 kg;
- medium: turkeys - up to 17 kg, turkeys - up to 7 kg;
- heavy: male - up to 26 kg, females - up to 11 kg.
The light subspecies is bred on a large industrial scale, the heavy one - in private farms and farmsteads.
Varieties of wide-breasted turkeys
Several varieties of white broad-chested:
- Hybrid Grade Maker (in Europe called "festive") - refers to the average meat subspecies. Feature - fast maturity. Ready for slaughter at 12 weeks, carcass weight up to 5 kg.
- Big 6 is a heavy meat variety. Carcass weight 15-17 kg, female - 7 kg.
- But 8 - heavy cross. The carcass of the male weighs 17 kg, that of the female 8 kg;
- The Stavropol turkey is the largest of all types of turkeys, live weight up to 28-30 kg. The appearance, care and maintenance does not differ from the white broad-breasted.
Appearance
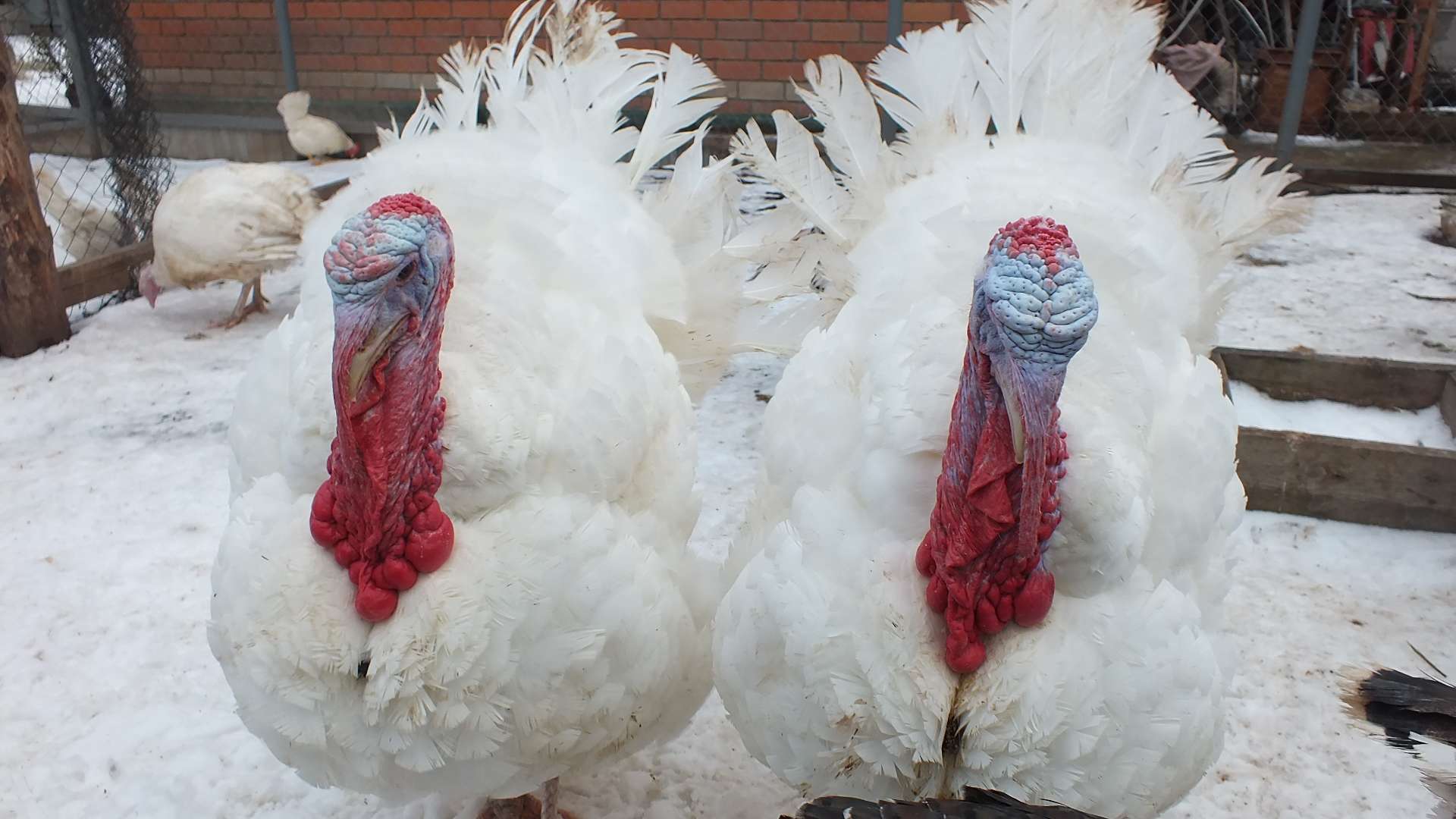
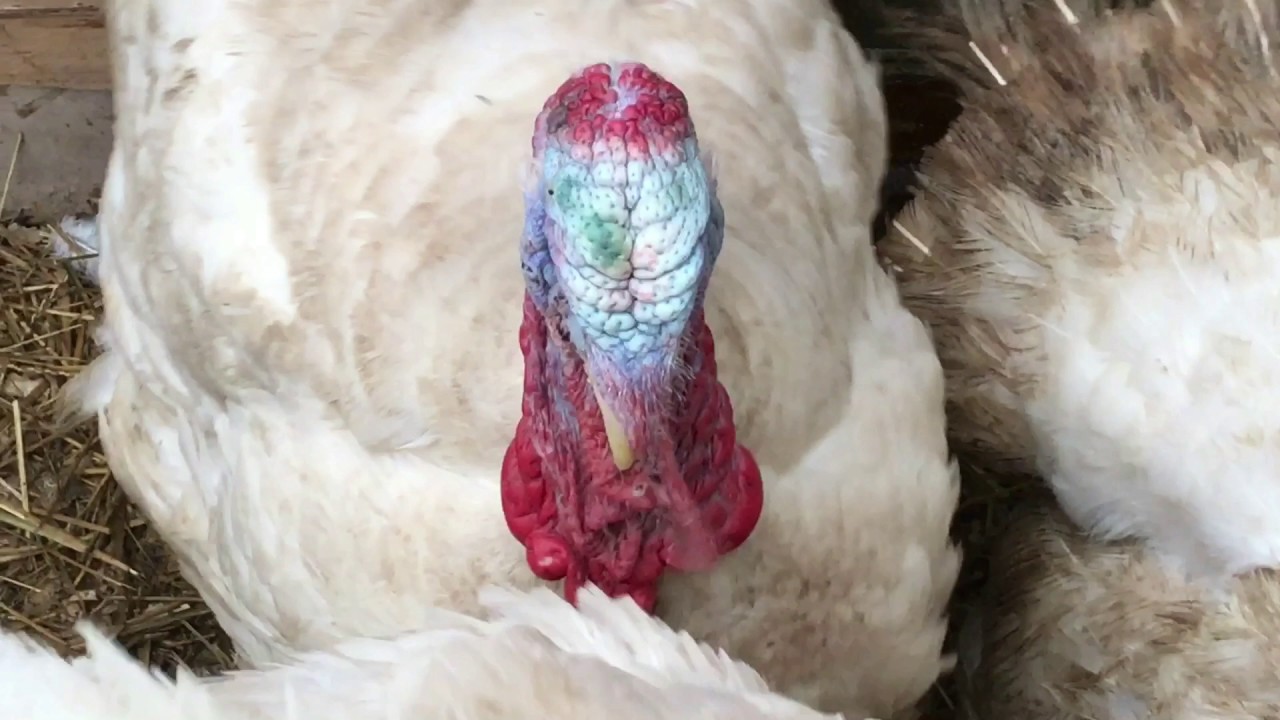
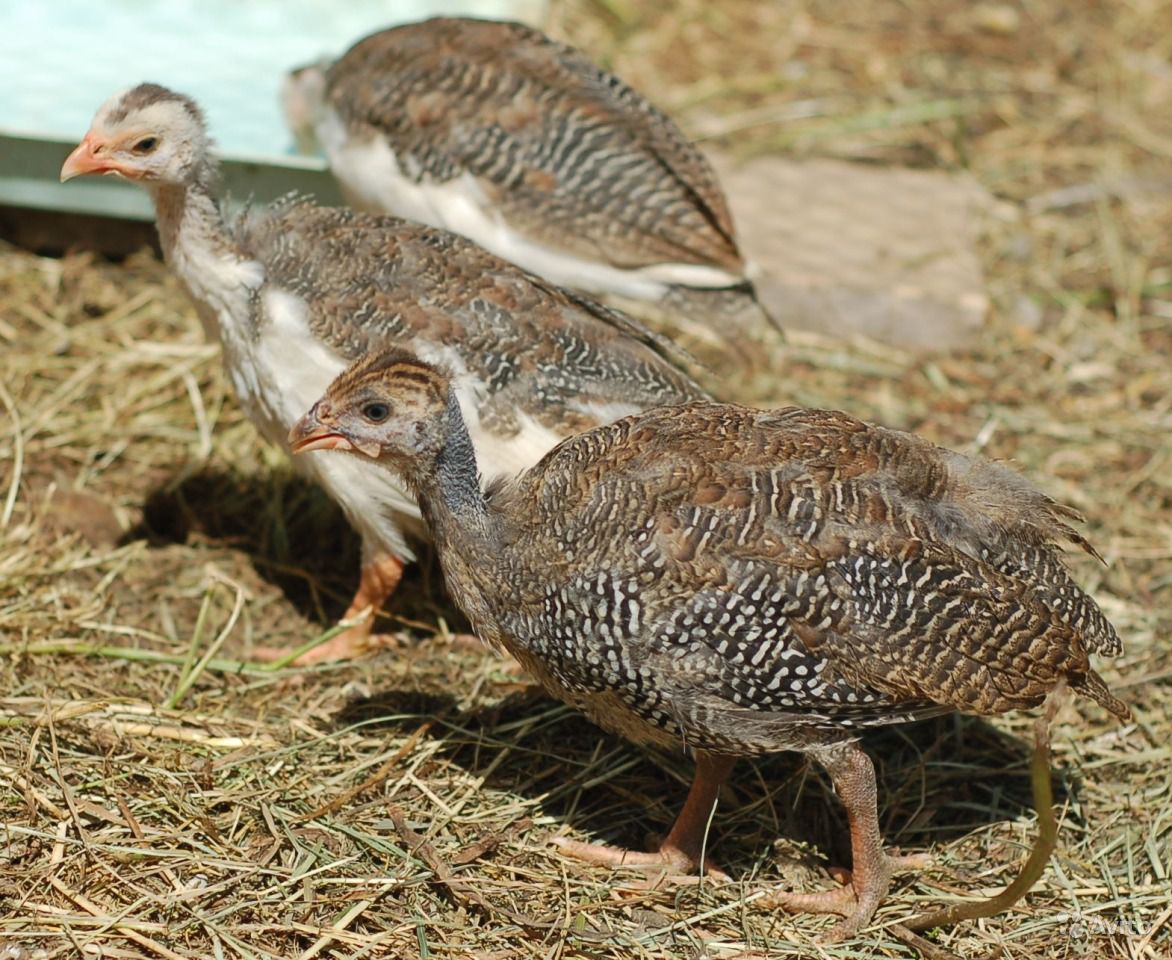
Broad-chested turkeys have an impressive appearance: a large oval body, a wide chest, strong, wide-set pink legs. The neck is of medium length without feathers. There is a characteristic skin growth on the head above the beak. This is the main difference between a male and a female. The plumage on the body is lush, snow-white. Another feature of the appearance is a bunch of black feathers on the chest, poultry farmers call it a "medallion".
The size
An adult turkey reaches impressive size by 1.5 years: the height of the bird is up to 70 cm, the length of the body is up to 100 cm.The size of the females is slightly smaller: height - 50 cm, body length - 85 cm.
Mass indicators
Domestic wide-breasted turkeys belong to the heavy subspecies. The bird grows rapidly and gains body mass during the first 90 days:
- At the end of the first week of growth, the turkey is gaining 160 grams;
- in two weeks of growth, the male is 390 gr., the female - 360 gr.;
- at 30 days of age, male up to 1.5 kg, female - 1.1 kg;
- at 90 days, the weight of the turkey is about 9 kg, the female - 6-7 kg.
At six months of age, males weigh up to 14 kg.
Egg production
Females begin to lay eggs at 8-9 months. During the period of egg production (180-210 days), the bird lays 100-120 eggs weighing 70-80 g.
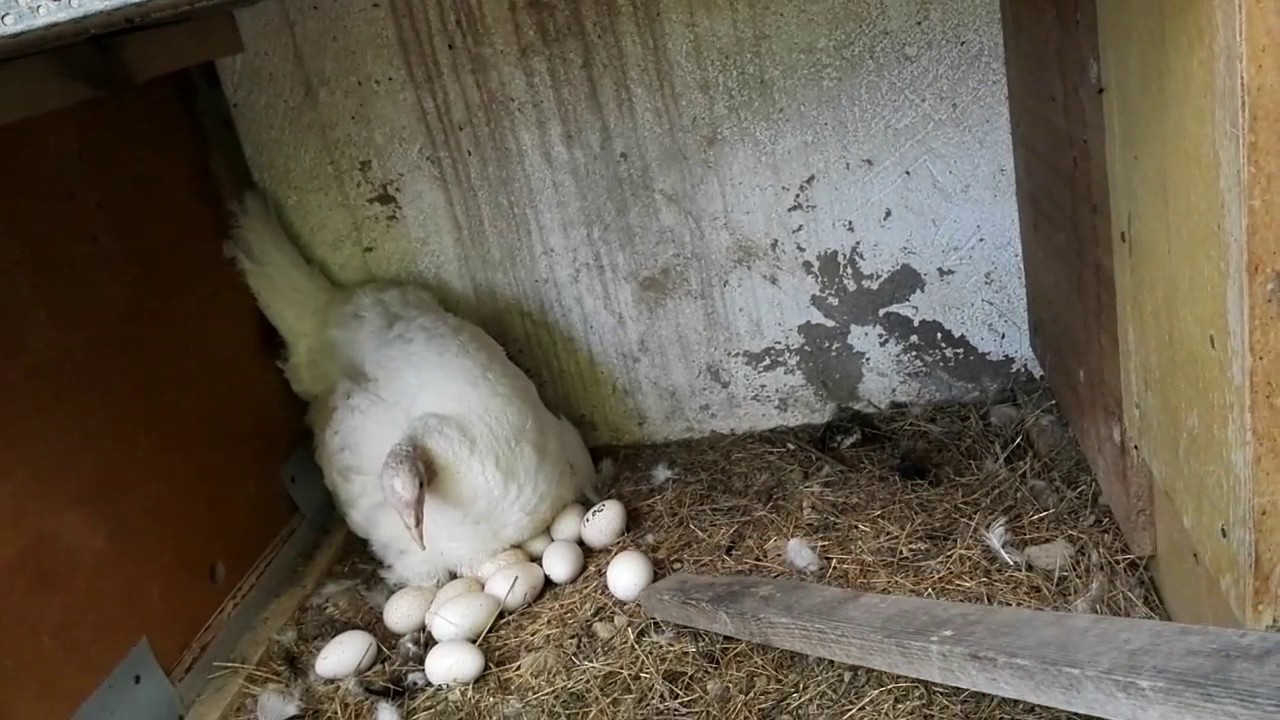
Broad-breasted females are wonderful hens and caring mothers. This makes them easy to breed naturally. One female can hatch and raise up to 80 turkey poults.
Features of caring for white broad-breasted turkeys
Successful growth of young stock requires rules:
- in the room, light is required;
- the presence of drinkers, feeders, nests and perches;
- warming the poultry house in winter;
- need a bedding on the floor made of straw or sawdust;
- the presence of a walk, fenced with a net.
Turkeys need a stable microclimate in the house. Temperatures below zero and an increase of more than 22 degrees should not be allowed.
Breeding
The process of hatching turkeys is no different from other poultry:
- Eggs are collected from laying turkeys within five days, placed in a special container with the blunt end up.
- They put the brood in the nest or in the incubator.
- The period of incubation and incubation of eggs lasts 27-28 days.
Feeding
In order for young animals to grow healthy and strong, quickly gain weight, high-quality and complete feed is needed. It is easier to feed with purchased compound feed. If there is none, a boiled egg with herbs is crumbled to turkeys in the first days. They give crushed grain with meat and bone meal, feed yeast and chalk, cottage cheese. Feeding every two hours.
Three to four week old young animals are gradually transferred to the diet for grown birds:
- crushed from a mixture of wheat, corn, barley, sunflower;
- protein supplements from meat and bone meal or fish meal;
- juicy food made from herbs and grated vegetables.
The number of feedings is reduced to five times a day. Warm water is poured into drinkers. For the prevention of intestinal infections, a weak solution of potassium permanganate is added once a week.
Conditions of detention
If additional space is required, the livestock is transferred to another room, more spacious. Necessary requirements:
- temperature regime in summer - not higher than 22 degrees, in winter - not lower than minus 5 degrees;
- an exhaust hood is required for the supply of fresh air;
- an area of at least 1 sq.m. is required. for one bird;
- light mode 14 hours a day;
- arrangement with perches at a height of 1 meter from the floor, for one bird you need spaces of at least 40 cm;
- installation of jacks in a dark place.
From two weeks of age, turkey poults are taken out for a walk in an aviary or on a lawn.
Prevention and treatment of diseases
Turkeys, like all poultry, are susceptible to infections and diseases. If you do preventive vaccination and provide timely treatment, the death of the bird can be avoided.
List of typical diseases:
- Helminths (worms). They enter the digestive tract and respiratory tract through food and water. The bird does not eat, it loses weight, its immunity falls. Prevention - disinfection of the premises. Treatment with specialized drugs.
- Smallpox is a dangerous viral disease. The first signs are ruffled feathers, lowered wings, red spots appear on the mucous membranes and legs. There is no cure, the bird is destroyed. Healthy livestock are vaccinated.
- Tuberculosis. Symptoms are manifested by nodules on the skin, diarrhea. The defeat of internal organs through water and food. There is no prior bird prophylaxis and treatment. The livestock is destroyed. The room and the walking area are disinfected by direct sunlight.
- Histomoniasis is liver damage. Occurs due to insufficient disinfection of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms are diarrhea, apathy, ruffled feathers. Treatment with Phenothiazine.
- Coccidiosis is a lesion of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms are white bloody diarrhea. Prevention - soldering turkey poults with drugs Koktsidiovit and Amproleum. Treatment - with the same drugs in a higher dosage.
Keeping turkeys does not require supernatural efforts from the poultry farmer. The main thing is compliance with the rules of care, prevention of infections and proper feeding. The only drawback of this type of bird is that the turkey is a thermophilic creature, and in winter it requires additional attention.