Content:
August and early September are the time of mass ripening of many sweet and very tasty fruits. The presence of grapes and watermelons on the dining table, the aroma of freshly brewed jam attracts the attention of uninvited guests: flies, bumblebees and wasps. Among the wasp relatives, they stand out for their large size, as well as the most serious consequences of hornet bites.
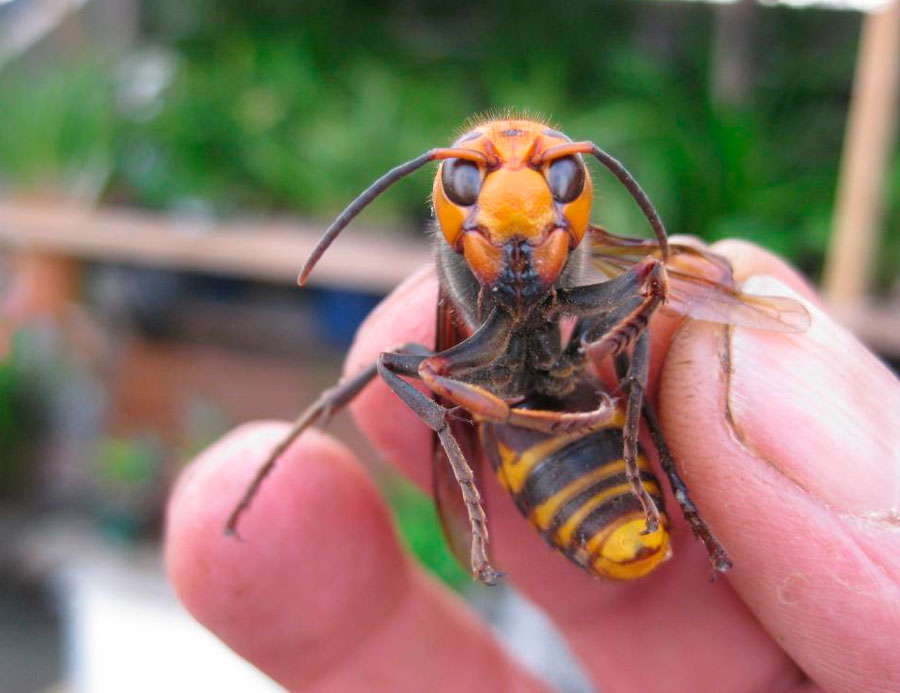
How a hornet bites
Hornets, like wasps, do not attack people for no reason. This usually happens when it comes to protecting the hive or your own life. Circumstances that can provoke a hornet attack:
- The threat of ruining the nest. Hornets jealously guard their home, near which "guards" always fly, warning the swarm of possible danger, making special sounds. Having stumbled upon a hornet's nest, you should not show curiosity, try to poke it with a stick or other objects, stick your hands inside or bring your face closer.
- Mechanical impact. When meeting with an insect, it is necessary, if possible, to remain calm, not to wave arms and other sudden movements. Often the hornet stings people who, without noticing it, stepped on or sat on a lurking insect. No less common is the situation when a hornet enters a person's mouth along with a bite off a piece of watermelon or ice cream. If the hornet stings its victim while in the mouth, then the danger of swelling of the larynx and respiratory tract increases. Such an injury can be incompatible with life for the victim.
It is important not to disregard children, who often do not even know if hornets bite, and may suffer because of their curiosity to discover a hornets' nest and disturb its inhabitants.
You should not fight the hornet settlement found in the country on your own. Numerous bites can be very harmful to health. It is more prudent to entrust the elimination of the nest to specialists who have overalls and the necessary equipment for this.
Calm and smooth movements can save you from a hornet bite. If the hornet is sitting on a hand or clothes, it is better not to breathe for a few seconds and try not to move so as not to disturb the insect. The hornet stings when scared or angry; without visible threat, he will not attack first.
Hornet venom
The hornet bite is quite painful, since up to 2 mg of poison gets into the victim's wound. Like other wasps, the hornet is endowed with the ability to attack its prey several times in a row, thereby inflicting multiple bites. The poisonous substance causes burns, which is especially dangerous if the poison gets into the eyes and on the mucous membrane of a person.
Since this insect eats waste protein food and does not disdain carrion, then, among other things, it can be a carrier of infections.
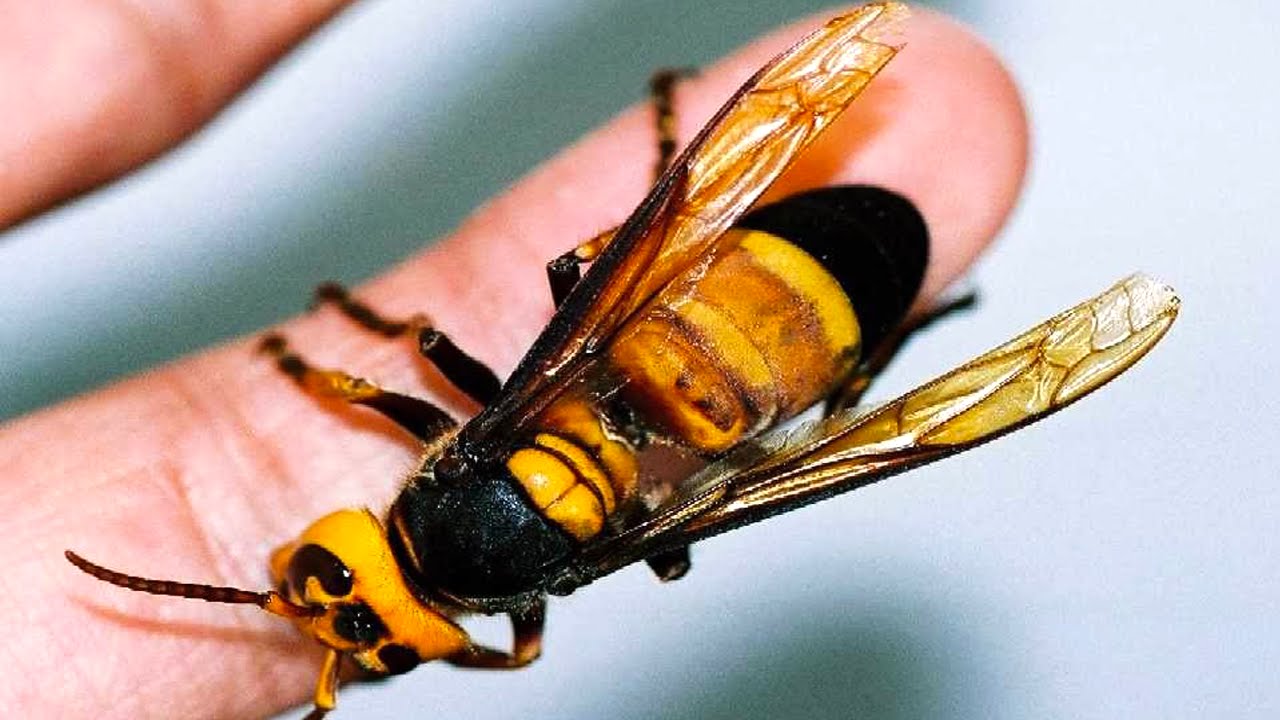
What a hornet looks like and its bite, consequences
The hornet is a member of the wasp family. Its main external difference from its counterparts is its size, thanks to which it is considered the largest species among hymenoptera. On the territory of Russia, the most common representative of this family is the common hornet, which reaches an average length of 4 cm and weighs about 200 g.
After being stung by a hornet, a victim develops a toxic reaction, expressed by the appearance of a small blister, local redness and pain at the site of the alleged bite.
If the bite occurs in the area of the face, mucous membrane, lymph nodes or large vessels, then the poisonous substance enters the bloodstream and has a toxic effect on the nervous system.
The consequences for a person who has been bitten by a hornet can be quite tragic and even fatal. Species of this insect living in the southeastern regions of Asia are especially dangerous to human life.
Japan leads in the number of deaths caused by hornets. Every summer, Japanese doctors record more than 60 fatal bites.
If a hornet stung, then the following symptoms are observed:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- difficulty breathing;
- spasms of the gastrointestinal tract;
- violation and disappearance of the pulse;
- pallor of the skin.
Also, the possibility of an allergic reaction is not excluded. In this case, the itching sensation in the bite area increases and the swelling of the skin begins. Painful sensations can last from a couple of minutes to several hours.
What to do after being bitten
A bite in a limb is less dangerous than if a hornet bites or stings in:
- head;
- upper shoulder girdle;
- neck;
- the places where large blood vessels pass through the armpits and under the knees;
- groin;
- language.
First aid
Algorithm of actions for a hornet bite:
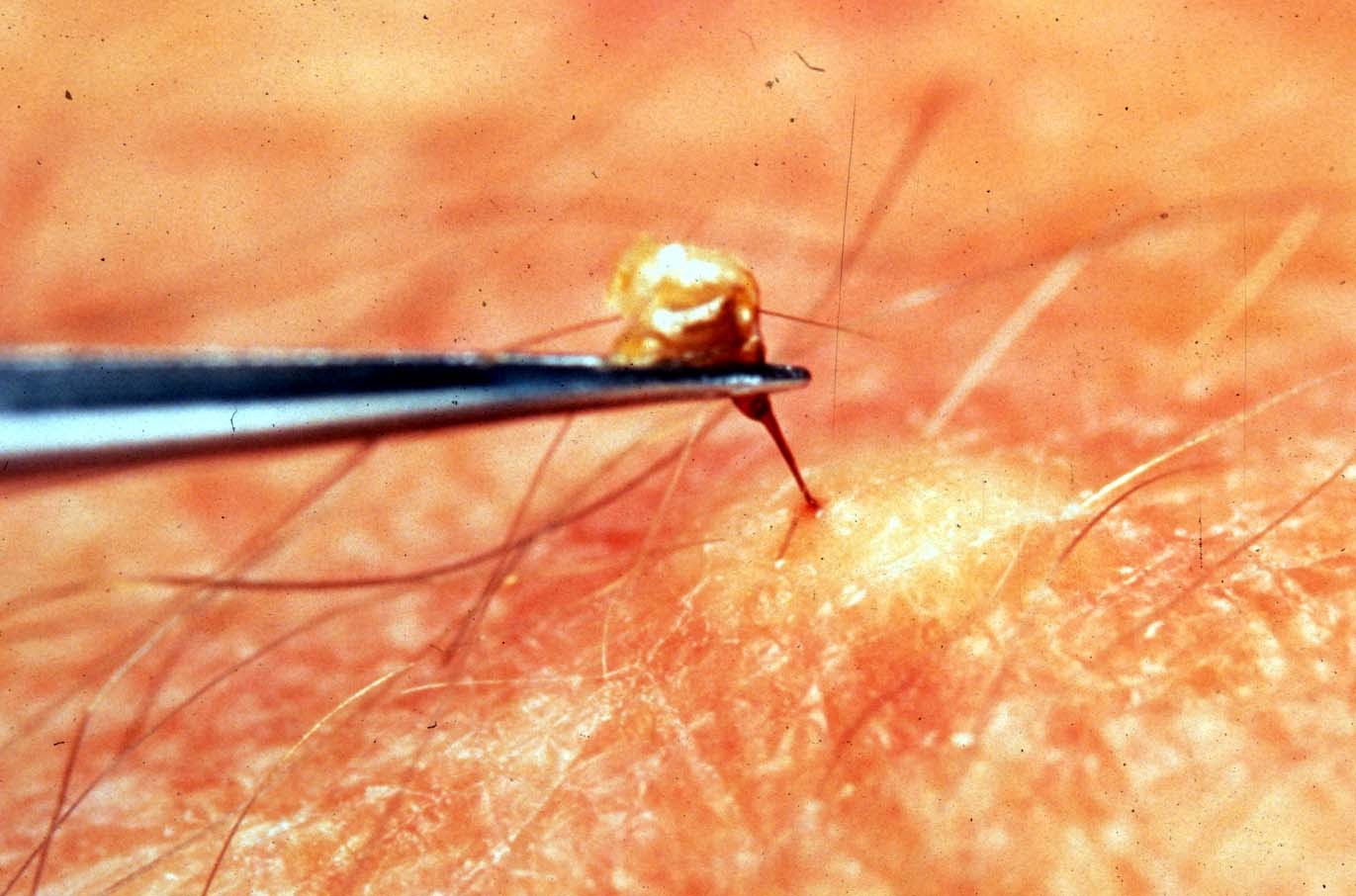
- You should start by examining the wound. If the sting remains in the skin, it must be removed. This should be done very carefully, if possible with tweezers. You should not try to squeeze out the sting, this can lead to more poison in the tissue.
- It is advisable to treat the site of the bite with a solution of hydrogen peroxide so that an infection does not get into the wound. The hornet is a predator; its diet can contain dead insects, carrion and other organic waste.
- Cold must be applied to the affected area, which will interfere with the absorption of the poison into the body and thereby slow down intoxication. If there is no ice on hand, then a cold compress will do.
- An antihistamine must be taken. This should be done even if there are no signs of an allergic reaction.
The risk group consists of people whose consequences in their strength do not correspond to the size of the injury. For example, with a bite on the toe, the leg swells up to the knee and above. This also includes a situation when the general condition of a person worsens, and the accompanying symptoms persist for several days.
If it was noticed that the victim had a hard time surviving the consequences of the bite, this means that the next time, being attacked by an insect, the reaction of his body will be more active and allergic processes will manifest themselves much faster.
Anyone who suffers from allergies is strongly advised to always have a special anti-shock kit with them, which includes special syringes with adrenaline solution. If necessary, injections are injected through clothing into any part of the patient's body.
In addition, the allergist issues a special passport to his registered patients. The information contained in this document should help the people around the injured person who happen to be nearby to act correctly.
How to treat bites
If the body recovers after a bite within 3-5 hours, then, most likely, a person does not need medical assistance. In this case, you can smear the wound with gels and ointments sold in the pharmacy without a prescription. Such drugs perfectly relieve itching from the affected skin area. Antihistamines are also available over the counter. They not only relieve the desire to scratch the wound, but also help reduce puffiness.
Treatment should be prescribed by a healthcare professional if the area of redness exceeds 10 cm in size, and fever, headache and nausea continue over the next few days.
No one is immune from insect bites. But adherence to simple rules of conduct in a critical situation will help not to waste precious minutes necessary for salvation and avoid tragic consequences.