Content:
Observance of crop rotation of vegetable crops allows you to get a good harvest. Many plants can be grown in the same place for years, but subject to regular fertilization. Some crops require a yearly change of beds. Knowing after which crops you can plant tomatoes in the garden, you will be able to significantly increase their yield.
Tomatoes: botanical description
Tomato is a herb of the Solanaceae family. In our climate, it is cultivated as an annual crop. The homeland of tomatoes is South America.
In botany, the fruits of a plant are considered berries, but in everyday life they occupy a leading position among vegetables.
Annual tomato bushes reach 60-90 cm. The tips of the shoots are covered with buds. Fruit ripening is amicable. After fruiting, the ground and underground parts of the plant die off.
Perennial tomatoes have curly shoots. In the process of vegetative development, culture needs support. Long-term fruiting, until the very frost. The species is characterized by high productivity. The height of the bush can reach 3 m if provided with good support.
Tomatoes are a thermophilic vegetable crop. You need to grow in well-lit areas or in greenhouses. It grows and develops well at temperatures of +25 ° C and above.
When planting, the bushes must be given a lot of space so that the plants do not interfere with each other as they grow.
After which it is better to plant tomatoes
Correctly changing the place of planting tomatoes is a guarantee of a good harvest, so it is worth figuring out after which crops you can plant tomatoes.
Tomatoes after legumes
Plants such as beans, beans and peas sometimes take very little space on the site. On the one hand, this is justified: why occupy a useful area with crops, if their fruits can be bought for a penny in a store? On the other hand, after cultivation of legumes, the soil is enriched with important trace elements necessary for the full development of tomatoes, for example, nitrogen. After planting them, the land should rest for some time.
On a note! After harvesting beans, peas and beans, you should not throw away the green mass of plants. It needs to be finely chopped and buried in the ground. Thus, you can enrich the land with useful substances. The foliage is a good fertilizer.
After all the preparatory work, you can grow tomatoes.
Legume tops are good organic fertilizers. As a result of growing beans, beans, peas on the site, it will be possible not only to get tasty fruits that can be eaten fresh, canned for the winter and dried, but also to enrich the soil on which tomatoes will grow well.
Attention! Solanaceous plants and legumes are susceptible to Fusarium. If this disease is noticed in the process of growing legumes, tomatoes cannot be planted, they will also be susceptible to fusarium. It is better to plant crops with high disease resistance.
Tomatoes and potatoes
The natural similarity of the two crops suggests that they prefer fertile soils rich in nitrogen. After growing potatoes, the soil is deficient in nitrogen, therefore, if there is a need to grow tomatoes later in a potato field, nitrogen-containing fertilizers must be intensively applied.
Attention! It is simply unrealistic to provide the soil with sufficient nitrogen in one season. And an overdose will affect the quality of the tomatoes.
Potatoes and tomatoes are affected by the same parasites and bacteria. It is not possible to harvest the entire potato crop - a couple of potatoes will still remain in the ground, no matter how hard you try, because harvesting in small plots takes place "under a shovel", and in large areas using technology.
The fruits remaining in the soil are attacked by bacteria, which will gladly dilute their diet with tomatoes in the next season. Therefore, you should not count on a good harvest of tomatoes when planting on a site after growing potatoes.
To minimize the labor costs of fighting parasites, you need to be on the lookout.
Pests of tomatoes and potatoes:
- Colorado beetle. The overseas visitor expands its distribution area every year. With enviable activity, it massively affects potatoes and tomato tops. Treatment from the pest gives a positive result, however, it requires a constant change of drugs, since the Colorado potato beetle adapts perfectly to any chemicals. With repeated treatment with the same remedy, pests develop immunity: they live and live, as if nothing had happened.
- Wireworm. Another pest that causes a lot of trouble. As a result of its vital activity, gnawed stems and damaged fruits can be observed.
- Medvedka. The pest loves moist soil. He will not miss the opportunity to eat either potatoes or tomatoes. Loves green stems of plants.
- Late blight - a fungal disease that affects both cultures. The disease develops on leaves and stems. If you do not fight, the disease will spread to the fruit: potatoes and tomatoes will turn black and will be unusable for food.
Output: planting tomatoes in the potato garden is not recommended!
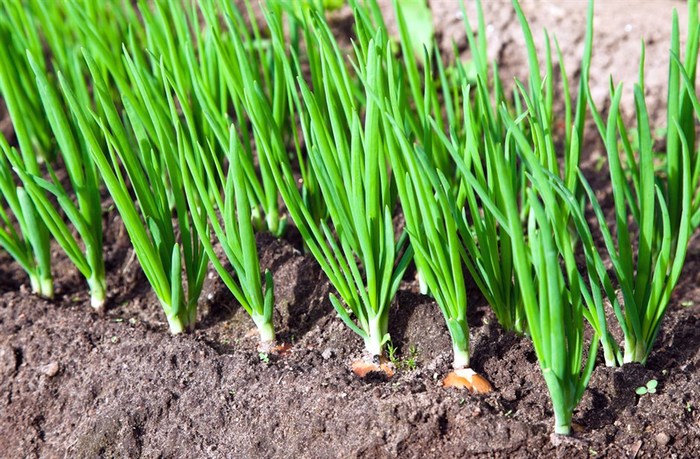
Tomatoes after onions
The succulent plant, due to its specific taste, is rarely affected by pests. In the absence of proper care, green onions become wild and thrive among weeds. The exotic taste of the plant and the phytoncides released by it into the soil scare away pests, so gardeners tend to plant tomatoes after onions. How does the earth feel? Is it possible to plant tomatoes in the garden if their predecessor was a fragrant vegetable - onions?
Green onions are perennials, but in our climatic conditions they are grown as an annual crop. After harvesting the bulbs, the soil is prepared for planting the following crops.
Characteristics of the soil after growing onions:
- there is a slightly alkaline reaction of the soil, which has a beneficial effect on nightshade crops;
- onions are indifferent to potash and nitrogen fertilizers, so the soil after onions is rich in potassium and nitrogen;
- onions release phytoncides - special substances that, getting into the ground, help scare off pests and destroy bacteria;
- bacteria do not linger in the soil, as they are indifferent to onion roots.
Output: the considered factors allow us to conclude that it is possible to grow tomatoes after onions and then carry out the correct rotation of fruit crops.
Tomatoes after strawberries
Strawberry and strawberry plantations grow over time and require a new planting site. The challenge is to choose the right plants for planting in this place. Can tomatoes be planted after strawberries or strawberries? Will the predecessors of tomatoes affect their development and fruiting?
Strawberries are not the best precursor to tomatoes when planted. If you still decide to plant nightshades, you need to be prepared for the poor harvest.
Strawberry bushes absorb all useful elements from the soil, so the soil after its cultivation is depleted in minerals and nitrogen. And the last element is extremely important for the normal development of nightshade crops.
There is a way out of this situation, but you need to prepare for the laborious work:
- The soil after a strawberry plantation must be thoroughly treated. First of all, you need to dig it up well.
- When digging, it is recommended to remove all weeds, especially wheatgrass. The root system of the weed is often intertwined with the roots of the strawberry making plantation maintenance difficult.
- After all the manipulations, they dig up the ground again and apply organic fertilizers, for example, manure. You can add peat top dressing, but in a minimal amount. Wood ash will help develop tops and fruits.
- After the strawberries, the soil should rest a little. After that, a complex fertilizer containing nitrogen and potassium should be added to it.
During the cultivation of tomatoes, they need to be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers, so that other vegetable crops can be grown in the future.
Zucchini and tomatoes
There is such a thing: squash boom, when plants build up a good green mass and spread throughout the garden. Thanks to modern breeding, more compact varieties have been developed. What kind of tomato harvest can you get if you plant them after the zucchini have grown in the garden?
After zucchini, all types of tomatoes grow and develop well, even Cherry, since the predecessors enrich the soil with all useful substances. In addition, the root system in nightshades is located much deeper than zucchini, so tomatoes will receive all the nutrients from the depths of the soil, which the zucchini roots could not reach.
However, there are certain limitations that are important to pay attention to. You can not plant tomatoes after zucchini, if the latter had viral diseases - they will easily spread to tomatoes.
And if you do nothing?
What will happen if you do not comply with the crop rotation and next season leave the plantings as they were this year? This approach is justified only in greenhouses, because not a single summer resident has the opportunity to change the location of the greenhouse annually. If you grow tomatoes in a greenhouse in the same place, you need to take care of the condition of the soil in advance in order to get a good harvest.
Rotation advantage:
- as a result, an exchange of trace elements occurs;
- harmful microflora dies;
- the soil is enriched with nutrients necessary for the growth of tomatoes;
- pests for the winter, without receiving food, are doomed to death.
As the season changes, you can alternate between different plant species and families. When growing tomatoes annually in greenhouses, the following methods should be followed:
- organic and mineral fertilizers should be applied to the ground in increased quantities;
- as necessary, carry out soil cultivation from pests and in order to prevent late blight;
- make a partial replacement of soil;
- The following composition will help reduce the acidity of the fertile layer: it is recommended to add 50-80 g of lime per 1 m2 of usable area, because tomatoes need a neutral medium;
- it is necessary to automate watering.
Output: when growing tomatoes in greenhouses, you should not puzzle over which crops to plant, you need to apply the described measures and follow the conditions. Only in this way can you get a good harvest every year.
Crop rotation planning rules for tomatoes
If the rotation is not observed, the soil is depleted, therefore, plants cannot be planted in the same place; seasonal or intraseasonal alternation must be observed.Complex fertilizers must be regularly applied to the soil. A good result is given by changing the seed fund. This method is especially recommended for potatoes.
However, in order to remove all questions and get high yields, it is necessary to observe the seasonal change of crops:
- When planting vegetable crops in the beds, you need to divide them by type and family.
- First, you need to draw a detailed planting plan, you can draw up a table.
- Seasonal crop rotation must be carried out with the rules of agricultural technology.
After fulfilling the above conditions, you need to find out, after which it is better to plant tomatoes.
Ideal precursors to tomatoes when planted outdoors:
- Carrots and beets;
- White and cauliflower;
- Pumpkin;
- Beans, peas, beans;
- Roots;
- Onions, garlic.
If there is not enough garden area, flower beds are reduced and vegetable crops are grown in place of ornamental crops.
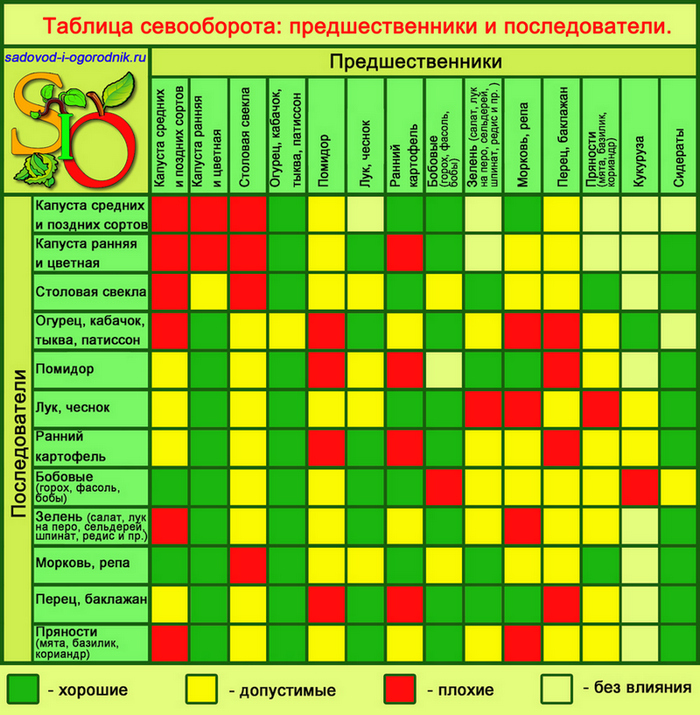
Crop rotation: table
| Vegetable name | Best predecessors | It is possible, but not desirable to plant after these crops | It is strictly prohibited |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Carrots, beets, green manure, pumpkin, white cabbage and cauliflower of early and medium ripening periods, onions, cucumbers, radishes, peppers, herbs. | Late cabbage | Tomatoes, potatoes |
Gardening requires a careful planning from the summer resident. It is necessary to carry out an analysis of planting plants annually, this is the only way to make amazing discoveries for yourself, to understand, after which it is better to plant tomatoes in open ground and, thus, influence an increase in yield.
On a note! Tomatoes should not be grown after cineraria and petunias, as these flowering plants and tomatoes belong to the Solanaceae family. Tansy, flax, coriander, nasturtium can grow together with tomatoes.