Content:
Ammonia in the medicine cabinet of any amateur gardener or summer resident is an indispensable tool, especially for those who love to grow everyone's favorite berry - strawberries. It is quite acceptable to use ammonia for strawberries as a top dressing. Unlike chemical fertilizers, it will allow you to get an absolutely pure product and significantly increase the quality of the crop.
About feeding and watering strawberries
Strawberries love care, which means that to achieve high yields, you need proper watering and timely feeding of the plant.
What should be watering strawberries:
- timely, it is not necessary to allow the earth to dry out, especially when it comes to freshly planted berries;
- it is necessary to water the berry in the morning so that the ground does not remain wet overnight, which can affect its resistance to various diseases;
- before flowering, it is better to water by sprinkling, and during the flowering period it is not recommended to get on the flowers;
- the water should not be too cold, the optimum temperature is 15 degrees and above;
- newly planted plants should be watered every day until rooting, and already rooted bushes - once every two to three days.
In addition to moisture, a plant needs nutrients for good growth. However, after one to two years of fruit bearing, the soil loses its nutritional properties. Ammonia for strawberries can be used as an excellent bait. This remedy has been tested by experienced gardeners for years and is absolutely safe.
Ammonia for strawberries can be used:
- to enrich the soil with nutrients, i.e. fertilize;
- as protection against pests such as weevils, beetle larvae, ants.
The use of ammonia (ammonia) for strawberries in the garden and vegetable garden
Ammonia is a drug used in medicine to remove a person from a fainting state. You can find it in every pharmacy at a fairly reasonable price. Gardeners recommend using this medicine as an additional nitrogen source for plants.
The advantages of using ammonia are:
- cheapness;
- convenience;
- harmlessness;
- universality, i.e. can be used as a fertilizer and as a pest control agent;
- does not oversaturate plants with nitrogen.
Ammonia is used in the garden and vegetable garden for feeding strawberries, as well as crops such as:
- potatoes;
- eggplant;
- pepper;
- cabbage;
- pumpkin;
- zucchini.
Crops that require low amounts of nitrogen:
- cucumber;
- tomato;
- carrot;
- beet;
- garlic.
It is too often not recommended to feed these plants with ammonia, while, for example, for strawberries, fertilizing with ammonia is simply necessary. She begins to bear more fruit.
Feeding strawberries with ammonia
The use of ammonia for strawberries is a universal technique that will allow not only to significantly increase yields, but also to avoid problems with the influx of pests. The benefits of using ammonia for strawberries have been proven by millions of gardeners across the country. This feeding must be carried out three times a year:
- the first feeding for strawberries with ammonia is carried out in the spring, when the plant begins to gain green mass;
- the second - after the end of the flowering period or during the harvesting of berries;
- the third - before the beginning of winter, so that the plant can better endure frost.
First, top dressing is carried out in early April with a weak solution of ammonia. Its purpose is to rid the plant of harmful insects and give strength to gain mass of greenery. To dilute the ammonia solution, you must:
- 10 l. water;
- 1 bottle of ammonia 10% (usually their volume is 40 ml.);
- 1 bar of regular laundry soap (so that ammonia does not evaporate during watering).
Before diluting all these ingredients, you need to grate the soap and dissolve it in 1 liter of hot water. Add soapy water to a bucket of water, and only then dilute the ammonia.
The second dressing should be less concentrated and is carried out around the end of July, after the berry has bloomed.
The recipe for preparing a solution for the second watering does not differ much from the first, only you need to take not 40 ml. ammonia, and 30 ml.
The third feeding is carried out in the fall, at the end of September, in order to give the plant the strength to endure the harsh winter. At the same time, a few drops of iodine are diluted into a solution prepared according to the recipe for the first feeding.
As a result, for fertilizing strawberries for the entire gardening period, the consumption of ammonia will be 2 bottles of 40 ml each, which is about 100 rubles.
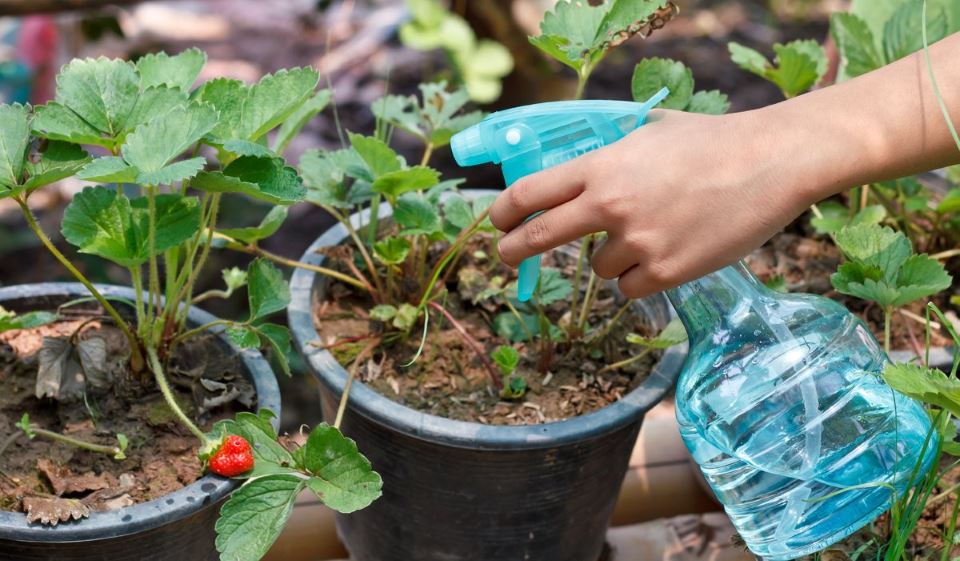
Garden strawberry is a plant that poorly absorbs nitrogen from the soil, therefore, in order to achieve good results in the cultivation of this plant, it is imperative to water it with alcoholic ammonia in the spring. To do this, you need to dilute ammonia water according to the recipe described above. You need to process each plant separately, without fear of getting on green leaves. Once absorbed into the soil, ammonia will destroy all pests that have wintered with strawberries, strengthen its root system and allow it to gain green mass faster.
When processing strawberries with ammonia alcohol, the following simple rules must be observed:
- use personal protective equipment;
- do not allow the presence of animals and children near the irrigation;
- prepare the solution strictly in the open air in order to avoid poisoning with ammonia vapors;
- use special sprayers for feeding, they allow you to avoid oversaturation of the soil and plants with ammonia;
- dilute the solution only according to the proportions given in the recipe.
From answers to common questions
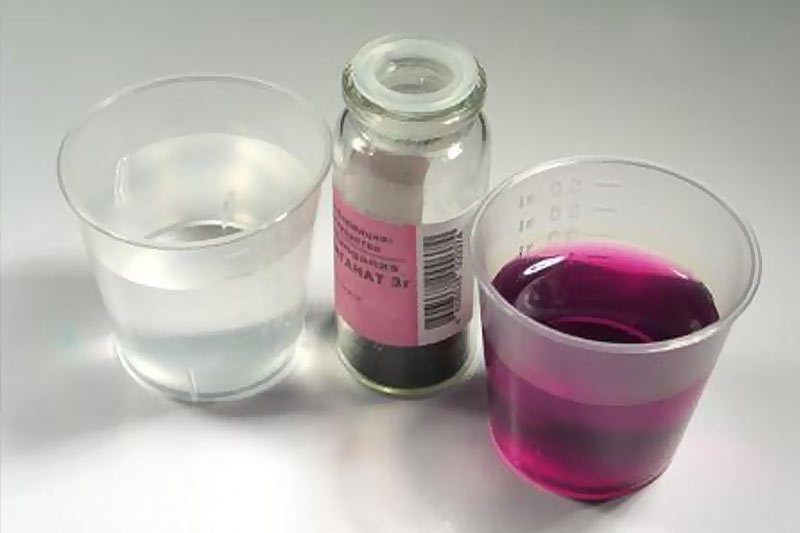
How to properly pour potassium permanganate on strawberries?
Potassium permanganate is widely used by gardeners. It has a disinfecting effect, which means it can help in the fight against pests. Potassium permanganate can also be used as a mineral fertilizer. For these purposes, gardeners treat strawberries in the spring with a solution of potassium permanganate, which increases yields. for the solution you need:
- 10 liters of water;
- ¼ part of a teaspoon of potassium permanganate.
To prepare a solution, dilute potassium permanganate in water until a bright color and spray the plants without fear of getting on the soil.
To stimulate the growth of strawberry bushes and enrich the soil with nutrients in early spring, feed with a mixture of boric acid and potassium permanganate. To prepare such a solution, the following ingredients are required in the appropriate dosage:
- 1 gr. boric acid;
- 1gr. dry potassium permanganate;
- 10 l. water;
- 1 glass of ash.
All ingredients are mixed, the roots of the plant are watered.
How to properly iodine strawberries?
In addition to the fact that you can feed strawberries with ammonia alcohol, many gardeners use an iodine solution for these purposes. Watering the plant with iodine will avoid fungal and other diseases, and will also give an impetus to growth. How to properly process strawberries with iodine:
- carry out processing in the spring;
- it is necessary to remove old and rotten leaves;
- water the bushes with plenty of water;
- combine 10 liters of water and up to 10 drops of iodine;
- pour the resulting solution over each bush.
Before flowering, gardeners practice spraying strawberry bushes with a solution of iodine with the addition of boric acid. Ingredients for solution preparation:
- 10 liter bucket of water;
- 20 drops of iodine;
- 5gr. boric acid;
- 1 bar of laundry soap;
- 250 gr. wood ash.
It is necessary to mix all the ingredients and let it brew for an hour. Pour strawberry roots with this solution, the total volume of poured top dressing per root should be no more than 0.5 liters.
The following recipe is good for feeding strawberries:
- 1 gr. boric acid;
- 1gr. dry potassium permanganate;
- 10 l. water;
- 1 glass of ash.
All ingredients are mixed, the roots of the plant are watered.
Thus, it will not be difficult to grow a rich harvest of garden strawberries in your country house or garden. The use of ammonia will allow you to avoid unpleasant "guests" and protect the berry from parasitic insects, and, equally importantly, enrich the soil with minerals, which will noticeably affect the quantity and quality of the harvested crop.