Content:
Large-fruited cranberries are the result of the work of breeders who have improved the quality of the wild-growing cranberry shrub. The plant, which naturally grows in swamps, shady and damp places, has not yet taken root in Russian gardens. It is a pity, because cultivated cranberries are large, juicy, high in vitamin C and other vitamins and minerals. Planting large-fruited cranberries on the site means providing yourself and your family with a useful product for the whole year, because cranberries contain a full set of vitamins that can be stored frozen, processed and dried. It is no coincidence that cranberries can be found in any store in every city. But the reserves of this valuable gift of forests and swamps are not eternal. So why not plant it as a culture in the country?
This useful shrub as a culture was first studied in the early 19th century in America. Breeder Hall from Massachusetts established the first plantation of this plant, and ten years later, in 1829, the US Department of Agriculture developed and launched a cultivated cranberry breeding program. The task was set to the scientists as follows - to bring out varieties that will be immune to disease, will become high-yielding and large-fruited. So six varieties appeared that met these requirements, they were called American or large-fruited:
- cranberry pilgrim;
- Franklin variety;
- Stevens;
- Bergman;
- Bekaat;
- Wilcox.
In the middle of the 20th century, Europeans also began breeding cranberries; they are engaged in this in Belarus, Ukraine, Finland, since 1966 and in Russia. It should be noted that from time immemorial cranberries were used by the Russians and were popular in ancient Russia. Suffice it to say that the name Prince Cranberry was given to the character of the story of Boris Akunin with the same name, which tells about the events in Russia of the 13th century.
Thus, the studies of Russian scientists have proved that in our country it can be successfully cultivated, but this requires its own varieties, focused on certain climatic conditions of Siberia and the northeastern part of the country. Then at the Kostroma forest station, the first seven varieties of domestic cranberries were bred, which repeated the properties of marsh cranberries. First of all, a cultivated plant needs a special soil that differs from the soil of other orchards. These are highly acidic soils, similar to peat.
Features and characteristics of varieties
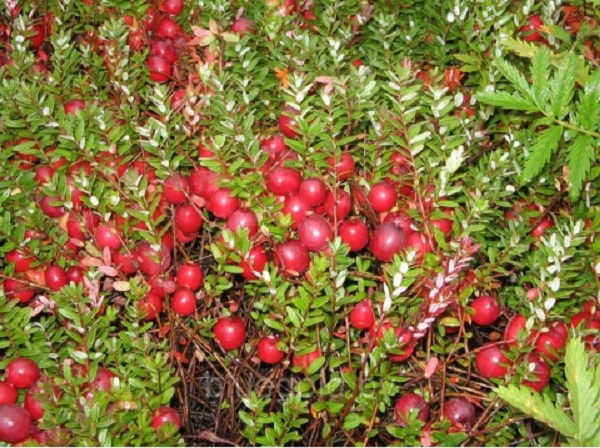
Cranberries are called northern lemons for their pronounced sour taste. The large-fruited cranberry shrub differs from the marsh cranberry by the presence of two types of shoots: erect and creeping. Erect shoots are thicker than those of marsh cranberries, and creeping shoots develop up to two meters in length in one season. It is from them that the roots are formed, which give life to a new upright shoot. Flowers are formed just on such erect shoots, berries appear from the flowers. Flowering time - June-early July.
The list is not entirely complete, but reflecting the main trends in cranberry and northern berry cultivation on private plots:
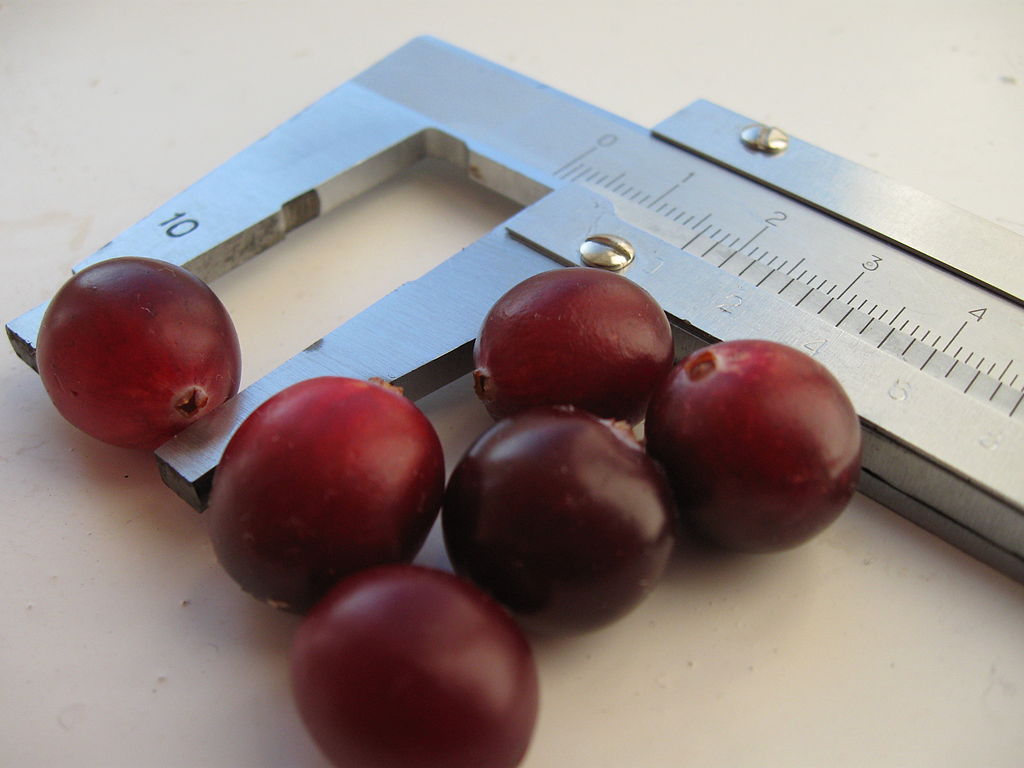
- The queen of the garden is a variety of Russian selection, zoned for our low temperatures. The variety is practically without flaws, with large berries up to 1.9 cm in diameter, with a yield of 300 g per bush. Branched bushes, evergreen, undersized.Refers to mid-season;
- Cranberry The Russian beauty of the north is a high-yielding variety (produces berries up to 2.5 kg per square meter), zoned to our conditions. Stems are high, up to 70 cm, ripens late, from about mid-September;
- Red Star cranberries are one of the most popular and modern varieties. Differs in excellent productivity and the ability to adapt to any conditions, including severe frosts, up to minus 30. It grows very quickly, expands, enters into a period of active fruiting. In addition to its high taste, this variety is decorative. Many summer residents plant a cranberry fence or use it to decorate alpine hills;
- Earley black cranberries are rather large cranberries with berries reaching 2.5 cm in diameter. A productive frost-resistant variety, belongs to the dwarf species. It grows very quickly, the creeping shoots quickly grow back and attach to the ground, taking root. The fruits are bright, juicy, red with purple;
- Pilgrim is the oldest American cultivar and matures late. The berries are dense, crispy, and have high technical characteristics. Large-fruited variety, berries weighing up to 2.2 g;
- Ben Lir cranberries are one of the earliest varieties, ripening in August. Differs in good, up to 2 kg per meter, productivity. Maroon berries are beautiful, juicy, but cannot be stored for more than two weeks;
- Russian variety Sazonovskaya - cranberries are quite small-fruited, refer to mid-season varieties. Positive characteristics - high content of nutrients, sweet and sour taste, good keeping quality, beautiful appearance. Disadvantages - low yield and the formation of a large number of berries inside the bush;
- Cranberry Stevens - planting and leaving this variety, well-zoned for the conditions of central Russia, is not difficult, since the variety perfectly tolerates changes in climatic conditions, is highly winter-hardy. Stevens cranberries are similar in description to other mid-ripening and late-ripening varieties. It begins to ripen in late September - early October, gives a good harvest.
Site preparation
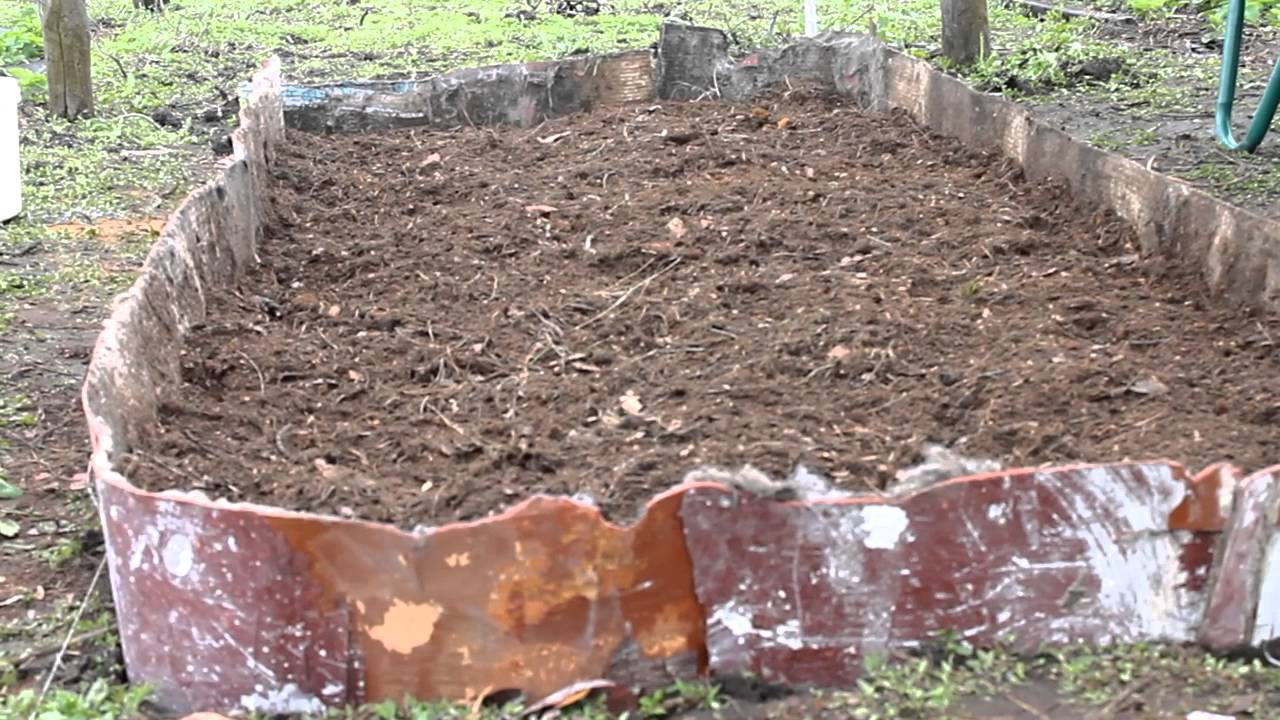
Any large-fruited garden varietal cranberry, like its wild fellow tribesman, needs special soil. The soil must be acidic, so planting in peat bogs is done after deep digging, and if the soil is mineral, then berry seedlings are planted in trenches. The trench is dug with a shovel bayonet depth, half a meter wide or wider. It is important to protect the plot from the spread of weed rhizomes; for this, the walls are usually laid with plastic wrap or roofing felt, boards are also suitable. Next, you need to lay out high moor peat, sprinkling it with sand.
Growing from seedlings
Most often, large-fruited cranberries are propagated by seedlings, which are grown by specialized horticultural enterprises or farms. Saplings can have a type of root system, both open and closed. It is better to take them as adults, that is, between the ages of two to two and a half years. Although there are also very young on sale, from 7 to 9 months. The older the planting material, the more expensive it will be, however, the harvest will be faster.
Planting seedlings and caring for them
Young seedlings are planted in spring, in May. Cranberries love well-moisturized soil, and acidic. For planting, you need to dig a hole larger in size than the pot in which the seedling grew. It is necessary to plant without disturbing the coma, immediately water, sprinkle with mulch.
Top dressing is done with complex fertilizers, after two to three years of planting, it is good to maintain acidity with solutions of acetic or citric acid.Any varieties, including Pilgrim cranberries, are similar in planting and care. At first, the shoots are not removed, but after the planting is compacted, it is necessary to thin out the plants, achieving multi-tiered. The main rule is to keep vertical shoots and cut out creeping horizontal ones. This is usually done in the spring to nourish the buds and form large berries, or in the fall.
For the winter, cranberries can be sheltered if the winter in the region is not very snowy. The shrub is covered with a peat layer. In the spring it is not at all necessary to get him out of the shelter - the bushes will sprout themselves.
Propagation of cranberries by cuttings and seeds
All types of garden cranberries, except for seedlings, can also be propagated by seeds and cuttings. Before sowing, the seeds must be kept in the cold for 4-5 months at a minimum above-zero temperature. This improves their germination.
Cranberries are propagated by cuttings from adult plants. You can simply let the creeping shoots overgrown and accreted to the ground take root, but it is better to cut cuttings up to 15 cm long from an adult plant and plant them in the soil, deepening by 4 cm.The planting scheme is 3 by 6 cm.If you plant them in peat, then the cuttings are quite take root quickly in about a month. They can already be planted in a permanent place.
Diseases and pests: prevention, treatment
Breeders, developing large-fruitedness in marsh cranberries, tried to save the varieties as much as possible from disease damage, to give them more resistance against pests. However, this issue has not yet been fully resolved. Pests hardly affect this shrub, but diseases can significantly reduce the yield. First of all, it is berry rot.
Snow mold is no less dangerous - this is the name of the spore fungus, which manifests itself as a cobweb on the branches, and also affects the flower cups, causing the death of the ovary.
The fungal disease red spot is also very dangerous for leaves and young shoots.
The third enemy is the overgrowth of cranberries, and this is also a disease that has a pathogen in the form of mycoplasma, it grows in the cells of the plant and gradually leads to its death.
Cranberry seems to be a very promising crop for horticultural production, which has not yet been properly appreciated by Russian gardeners. However, the fashion for a healthy diet, care for the fortification of the body should lead many to understand the usefulness and importance of this plant, among others in summer cottages.