Content:
The apple tree grows in almost every garden, delighting the gardener with its flowering and delicious fruits. Its yield largely depends on the natural characteristics of the area. Having studied all the features of the North-West region, you can learn how to properly plant an apple tree in the spring in the Leningrad region.
Features of the climate of the Leningrad region
Apple trees can be grown in a wide variety of climates. They tolerate the hot climate of Africa and the cold of Canada well. But achieving a high yield in the North-West regions is fraught with great difficulties, which is associated with natural and climatic factors.
The climate of the Leningrad region is moderately continental, formed by the proximity of the Atlantic. High humidity due to frequent precipitation, especially in summer, low summer and high winter temperatures are typical for this area. The breakouts of cold arctic masses make the climate at times unpredictable. In winter, severe frosts can alternate with thaws, and in summer there may be an unexpected cold snap with recurrent frosts.
The soil is poor podzolic with a weak humus layer (only 20-30 cm), loam, deep peat with high humidity, sand with an admixture of rubble. The climate is not conducive to the cultivation of fruit trees, it is even more difficult for a young seedling to acclimatize. The level of adaptation of the apple tree to local climatic characteristics depends on the correctly selected variety.
Apple trees are vigorous, medium-sized (semi-dwarf) and dwarf. Depending on the quality of the soil, one or another variety is chosen.
How to plant apple trees in the spring in the Leningrad region
A competent choice of varieties is the key to a quality harvest. Apple trees for the Leningrad region should have high frost resistance, immunity to diseases and pests, early ripening of apples. Most Russian varieties take root successfully and give a good harvest. The most popular ones are:
- Summer: White Fill, Memory of Lavrik, Dream;
- Autumn: Melba, Delight, Auxis;
- Winter: Antonovka, Gift to Grafsky, Star, Antey.
In one area, you need to grow apple trees with different ripening periods. This makes it possible to harvest during the entire warm season. If the site is distinguished by the close standing of groundwater, then it is better to purchase varieties of dwarf or semi-dwarf apple trees with a shallow root system.
Landing dates
Planting apple trees in the Leningrad region can be carried out in spring and autumn. Difficulties in choosing the timing of planting are associated with the fact that in warm spring, return frosts can suddenly occur. Autumn can be interrupted by a sudden onset of winter, followed by a thaw again. Planting of apple trees in the spring in the Leningrad region is carried out at the end of April, autumn - all September until early October. The deadline is October 15th.
Autumn planting is carried out at the end of the growing season. In order for the seedlings to develop a strong root system before the soil cools, they must be acquired by those that have already dropped their foliage and entered a state of dormancy.Thanks to this, the seedling does not need nutrition and will be able to start growing in early spring.
Sapling selection
One-year or, in exceptional cases, two-year-old seedlings have the best survival rate, as they retain a stronger root system after digging. If you buy a seedling with an open root system, with leaves that did not have time to fall, then such a tree will not have time to prepare for the spring due to unfinished vegetation.
An annual seedling with an open root system will take root only if the suction roots were not damaged during digging, if it was stored in a humid environment. A seedling with dried roots is not worth taking. The open root system of a two-year-old or older seedling is most often damaged after digging, as it has more branches. The spring tree should have buds that have not yet blossomed.
Landing
The place on the site for the future apple tree is selected near another pollinator seedling. The apple tree needs good lighting, fresh air. Water stagnation is contraindicated for her.
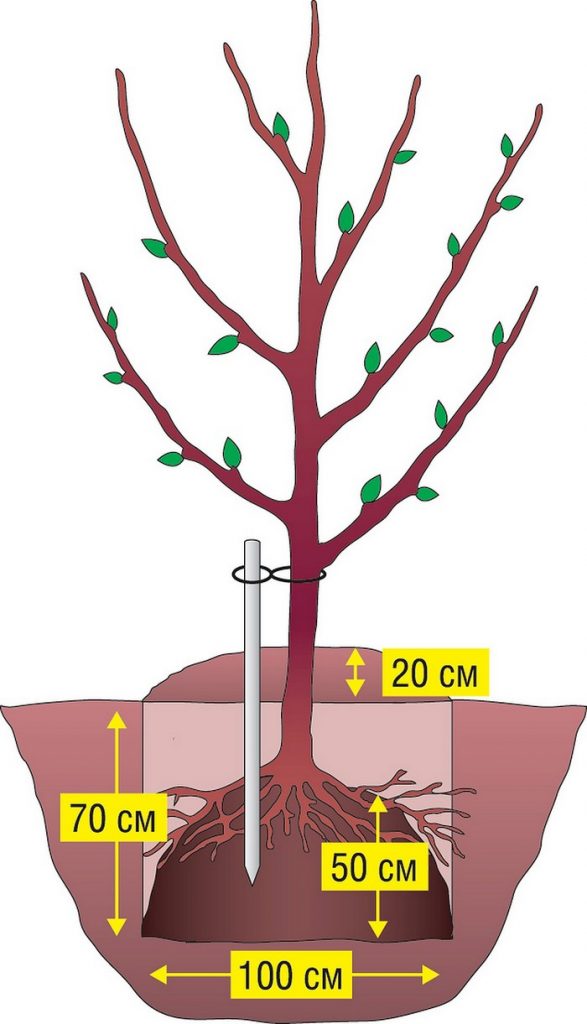
The pit measures about 90 cm in diameter and 60 cm in depth. Immediately before planting the seedlings, feeding activities begin. In a pit with sandy soil, it is required to lay drainage from a layer of stones and pieces of bricks, and then fill up with dry clay, rotted manure, peat. If planting is carried out in peat bogs, then it is necessary to deacidify the soil with river sand, clay. It is also recommended to add fluff lime or dolomite flour to acidic soil. In the spring, ash is used; for each apple tree seedling, one liter can is needed.
Do not plant the apple tree in clay, as it retains moisture, which leads to decay of the roots. It is necessary to dig a hole with a diameter of at least 1 m, to a depth of about 40 cm to the clay layer. In this case, you should take care of the availability of drainage. If the soil on the site is heavy, loam or clay, then it is recommended to plant the apple tree on a hill.
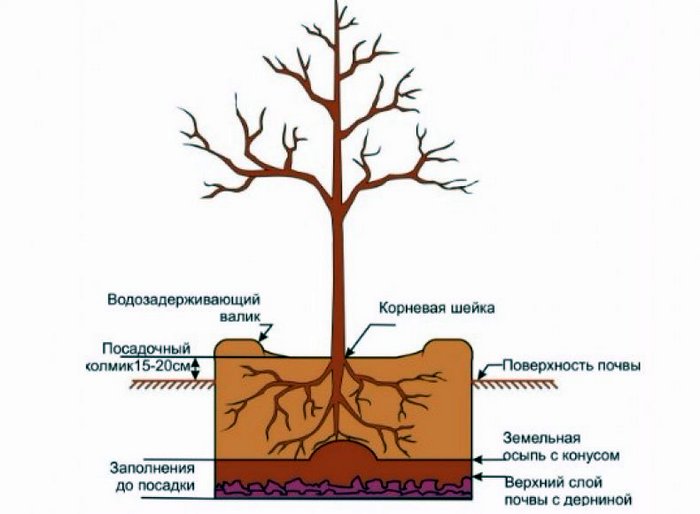
The soil for filling the hole is prepared by cleansing it from weeds, adding rotted manure, humus, river sand, peat. After filling the soil into the pit, it is compacted, and a layer of inverted turf, about 20 cm thick, is placed in the central part.It is necessary to drive a stake or a small pointed board into it, preferably from the south side, to protect the plant from the sun. A package with a tree is placed on the turf. For backfilling, you will again need the previously prepared soil with nutrients.
Carefully removing the package, the earthen lump with the seedling is covered with fertile soil and compacted. It is worth closely monitoring the vaccination site, trying not to cover it with earth. The root collar should also not go deep, it should be left at the level of the soil surface or slightly higher, a couple of centimeters. The seedling is tied to the peg with an eight-loop loop. It remains to water the tree with 2 buckets of water, having previously created a side around the perimeter, 50 cm from the trunk. A layer of mulch is poured around the seedling. In order for the seedling to give side shoots, its top must be pinched.
It is recommended to add Kemir fertilizer corresponding to the season when planting in the spring or autumn, 100-120 g is enough. While the apple trees are growing, you can apply mineral fertilizers. After the beginning of flowering and fruiting, the apple orchard needs to be fed with rotted manure, humus, green fertilizer.
Features of preparation for winter
The unpredictability of winter weather is reflected in the possibility of an unexpected thaw after severe frosts. Such conditions require more attention to the care of the seedlings. Newly planted trees must be insulated for the winter by wrapping them in burlap, cloth or bags. With the onset of a thaw, the shelter must be removed so that the tree does not grow again.
Whitewashing of trunks serves as protection against sunburn, rodents, severe frosts. In the preparatory pre-winter period, the soil is mulched with peat.
Correct care
Growing an apple orchard in the Leningrad region consists of the usual stages of care:
- trimming;
- top dressing;
- watering;
- measures against pests and diseases;
- preparation for winter.
Apple trees grow well on neutral soils, so the soil of the Leningrad Region does not suit them. The way out is in the obligatory feeding. Nitrogen is added in the spring, and potassium and phosphorus in the fall. Throughout the season, it is necessary to use complex fertilizers, mulch the trunk circle with organic fertilizers. You can also use imported soil.
Spring pruning is distinguished by a later date than in neighboring areas. Autumn pruning occurs in October. The procedure consists in the removal of dry, thickening crown, growing inside the shoots.
Diseases and pests
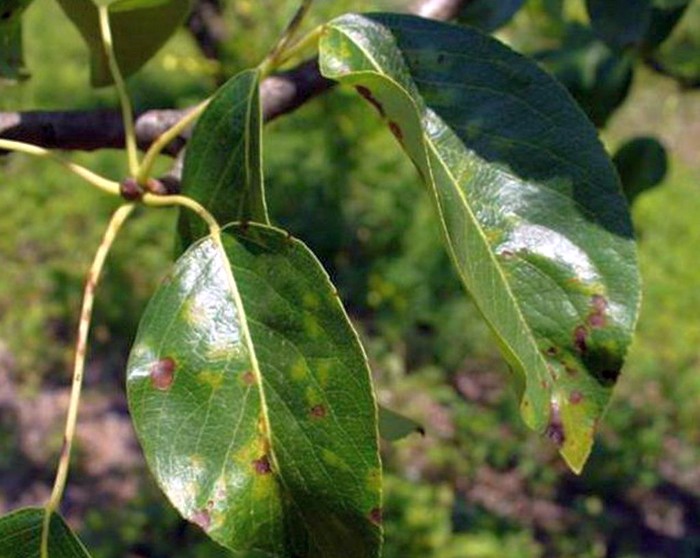
The apple tree growing in the Leningrad region is characterized by diseases such as scab and fruit rot.
Fruit rot appears as a brown spot that tends to grow and take over the entire apple. The pulp becomes brown and soft. A week later, fungal spores can be found on the surface of the fetus in the form of concentric circles of beige pads. The fight against fruit rot is carried out through the use of fungicides, Bordeaux liquid (3%). Preventive measures include regular pruning, removal of dying branches and fruits. Care for the near-trunk circles and timely feeding are necessary.
The scab on the leaves and fruits of the apple tree looks like oily spots of a green-brown hue. It is necessary to spray the apple tree before bud break with 7% urea or Bordeaux liquid (4%). A mixture of mineral fertilizers (10%) is also used, consisting of 350 g of superphosphate, 300 g of urea or ammonium nitrate, 350 g of potassium chloride, diluted in 10 liters of water.
The most common pest is green apple aphid. The pest sucks sap from plants, leading to curling of leaves and curvature of shoots. Effective drugs against aphids: Karbofos (0.3%), Ambush (0.1%), Actellik.
The apple mealybug is also common in the Leningrad region. It feeds on the sap of the tissues of the bark and leaves, especially young trees. The biological way of fighting is the use of the parasite pseudoficus. Other protective measures include pruning affected branches, cleaning trunks, and spraying with scale insects in early spring and summer.
Achieving a good harvest is not always easy, it takes perseverance and a competent approach. For all efforts, a well-groomed apple tree will surely thank the gardener with lush flowering in spring and a rich harvest in autumn.