Content:
To preserve the qualities of the tree variety, grafting is used. Also, this procedure allows you to update the garden without replacing the trees with new ones. The grafting procedure is based on the ability of trees to maintain integrity. Fusion occurs due to the cambium substance located under the bark.
A distinction should be made between the scion and the stock. The graft is the material that is grafted, the stock is the plant that will be grafted onto.
Summer grafting of fruit trees
The essence of the procedure:
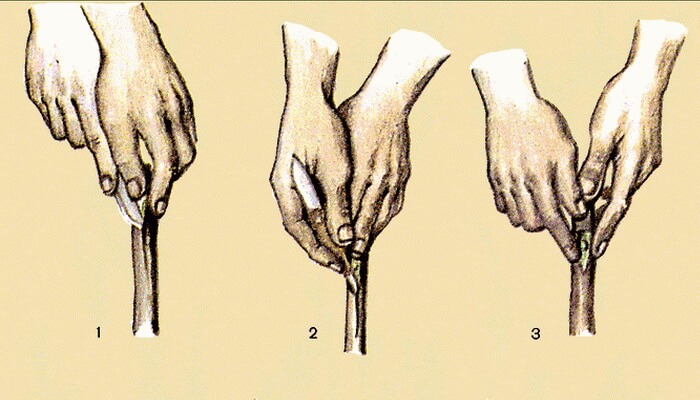
- cuts are made on the scion and rootstock;
- the grafting material is applied to the plant at the incision sites, connecting the cambium layers;
- press the scion tightly to the stock;
- give time to grow together.
The advantages of grafting fruit crops are:
- in maintaining the value of the variety;
- in reducing the timing of fruiting;
- in the rapid ripening of fruits, if a dwarf plant is obtained during grafting;
- in the possibility of obtaining a variety adapted to unfavorable climatic conditions;
- in obtaining from one plant several varieties with different fruits;
- in increasing the amount of harvest and plant endurance;
- in the renovation of the garden.
Above are the main advantages of vaccination. It should be noted separately what are the advantages of the summer vaccination.
Updating your garden in the summer brings some benefits. First of all, it is an opportunity to assess the condition of trees after the winter period. The rootstock plants must be healthy. If the spring grafting fails, you can repeat the procedure.
In the summer, tissue grows faster in the cut area, so the place of fusion is durable. If the material is with last year's bark, then there is a high probability that the graft will take root, in contrast to the spring grafting.
Another plus is that fewer cuttings are required and their shelf life is reduced.
Grafting of fruit with green cuttings
In the summer, the method of propagation by green cuttings is used. This method can be done using budding (in the butt or in the T-shaped split).
Fruit crops suitable for propagation by green cuttings: gooseberries, currants, cherries, plums and some apple varieties.
For summer grafting, certain cuttings are selected. For selection, the type of kidney should be distinguished. Buds are flowering and growth. Growth buds are located on the upper part of the stem. In the middle part - both growth and flowering. The lower part mainly consists of growth buds.
How the shoots are located is also important for determining the type. In the central part inside the crown there are flower buds, in the lateral part - growth buds. The appearance of the buds is different: growth buds are long and flattened, flowering buds are large and round.
Cuttings are cut from the side of the branches where the growth buds are located. Shoots should be covered in wood with smooth bark and healthy leaves. The shoot is cut off with a length of thirty centimeters, with a diameter of five to six millimeters.
Cuttings are harvested on the day when grafting is scheduled. The preferred time period is from four to ten in the morning.In the event that the cuttings are used within two to three hours after cutting, then they are not placed in the water. The workpieces are placed in the shade, all leaves and the upper part are removed. The petioles are left one centimeter long and the stipules are removed. After completing the preparation, the blanks are wrapped in a damp cloth.
Budding fruit trees
Not all vaccination methods are suitable for summer use. Summer grafting of fruit trees with green cuttings is most effectively carried out by bud budding. There are two main ways: in the butt and in the T-split.
The T-cut grafting is intended for plants where the bark easily falls off the tree. The knife with which the cut is made must be sharp.
First you need to make an incision on the rootstock. To do this, being next to the tree, it should be tilted and an incision is made. The cut should go across and reach the wood. The procedure is performed at a slight slope to the vertical axis of the tree. This is to facilitate the insertion of the shield. The length of the cut depends on the thickness of the plant or branch. The length varies from two to three and a half centimeters.
After the first incision is made, another one should be made, which goes already perpendicular to the first. Its length is from one to three centimeters. If the bark is well separated, the incision is made shorter. The result should be a "T" cut. To prevent the knife from sliding in your hand, place your index finger below the blade. The finger serves as a stop. The blade should be perpendicular to the bark.
When the second incision is made, the knife is not removed, but rotated from side to side to raise the corners of the bark.
Next, you should take the scion with the tip towards you with your left hand and select a suitable bud.
The bark on the handle is cut transversely, so that the distance from the top of the kidney is one to one and a half centimeters. This will be the pinnacle of the future shield. The next transverse incision is made one and a half centimeters below the base of the kidney. You should cut through both the bark and some wood. To do this, the knife is placed one and a half centimeters from the base of the kidney, deepens, then it should be carefully held, grabbing both the bark and a little wood. It is necessary to cut the vascular fibrous bundle that feeds the kidney. The upper part of the flap is cut off, the peephole should be centered. The shield that has turned out should be inserted into the incision in the rootstock bark. The stock bends slightly in the direction opposite to the cut.
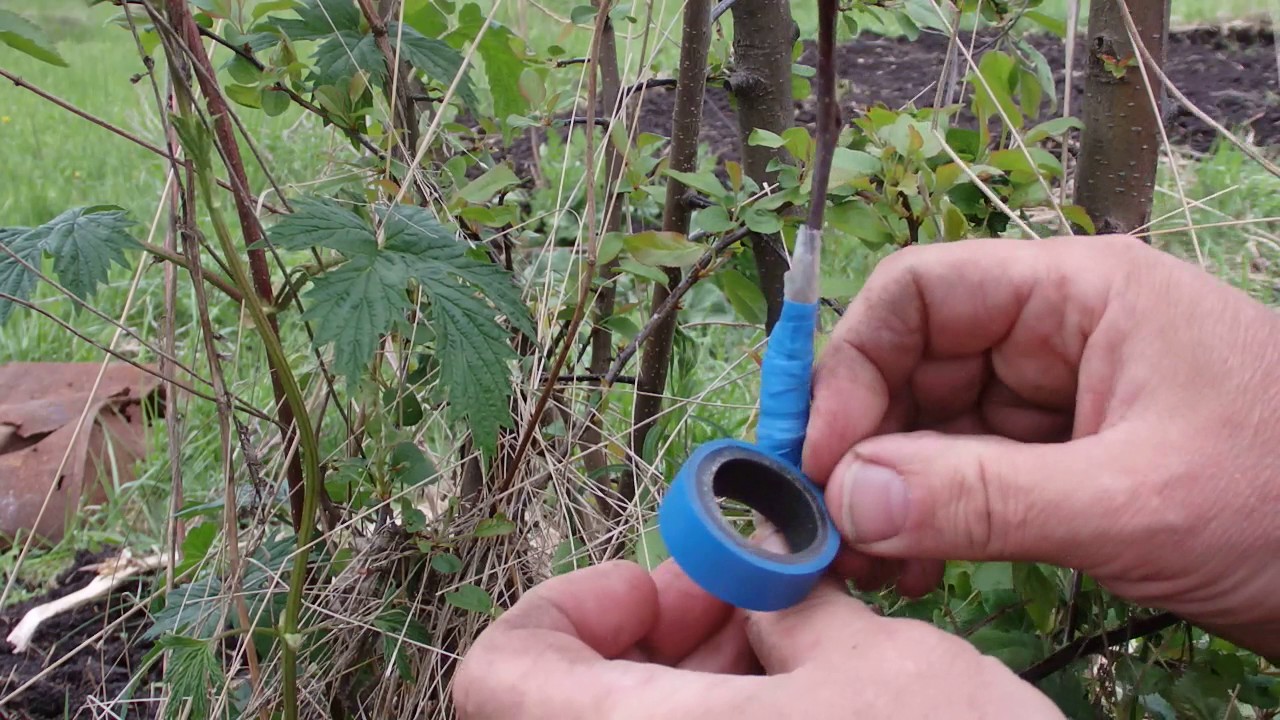
The correctness of the procedure is checked by placing the kidney in the center of the longitudinal incision. Seal the connection by running your fingers along the cut. The resulting place should be tied with polyethylene. It should be tied from the bottom of the longitudinal section to the top of the transverse. The place where the vaccine is located is tightly bandaged. The bud and petiole are not subject to tying. Displacement of the shield is inadmissible. The uncovered parts of the cut are covered with garden pitch.
The next method is budding in the butt. This method is intended for branches in which the bark is tight and difficult to separate.
On the tree to which the cutting is grafted, in the selected place, cut a strip of bark from top to bottom. The strip should correspond to the size: length - two and a half to three centimeters, width - half a centimeter. Most of the strip is cut off (2/3). The piece that remains is slightly set aside.
An incision must be made where the strip attaches to the barrel. The knife is placed at an angle of 30 degrees, the depth of the cut is five millimeters. The result is a wedge cut into which the lower end of the flap will be inserted.
The scutellum is cut from the cutting in the same way as in the previous method. The shield is inserted under a piece of bark. The graft is combined with the stock. The vaccine is tied with polyethylene, the open places are smeared with pitch.
When budding, the harness is removed after two to three weeks. This is enough time to see if the vaccine was started or not. This will be indicated by the state of the petiole. If it has dried up and fell off, then the process is successful. If not, then the re-vaccination should already be in the spring. The place of damage is smeared with var.
Terms of vaccination
Midsummer is the best time to plant cuttings. This is due to the fact that the shoots, which are only one year old, do not grow so intensively, the distance between the buds is minimal, and the top is finishing forming. The wood becomes hard, the bark is easily peeled off.
Whether to plant fruit trees in summer
Experts note that planting fruit trees in the summer is a rather difficult task for beginners. This is due to the fact that you need to know the right moment for the procedure. If inoculated too early, the buds will sprout, young shoots will not ripen. Then they will die in winter. If you are late, the material will not grow together with the tree.
Grafting of trees can be done not only in spring, but also in summer. This procedure has its advantages. The most effective vaccination method is budding. The method is simple. The two variations of the method depend on how tightly the bark adheres to the stock. The timing of vaccination depends on many factors: region, type of culture and the right moment.