Content:
Stability in the cultivation of common plum is ensured by proper care, which consists of pruning, feeding and watering. At the same time, many gardeners are interested in the question of how to propagate a plum, what are the methods of this procedure. This article contains all the answers.
Types of culture breeding
In order to propagate the plum, the following methods are used:
- reproduction by lignified or green cuttings;
- reproduction by layering;
- reproduction by root shoots;
- budding;
- reproduction by seeds.
It should be noted that only the first 4 methods, which are included in the vegetative category, can be used for the propagation of varietal plants. The simplest method is considered to be propagation by root shoots. With a large number of plants, budding is recommended. The same method allows you to more fully manifest varietal qualities and properties in the offspring.
Cuttings
The main advantages contributing to the spread of this method are the increased survival rate and accelerated reproduction. This is a very fast method for producing a large number of new plants. However, this does not apply to all plum varieties. Therefore, you should use those plants that form a lot of root growth. Also, the following factors can affect the results of cuttings:
- quality of cuttings;
- timing of cuttings;
- tools;
- age and condition of mother trees;
- the use of fertilizers.
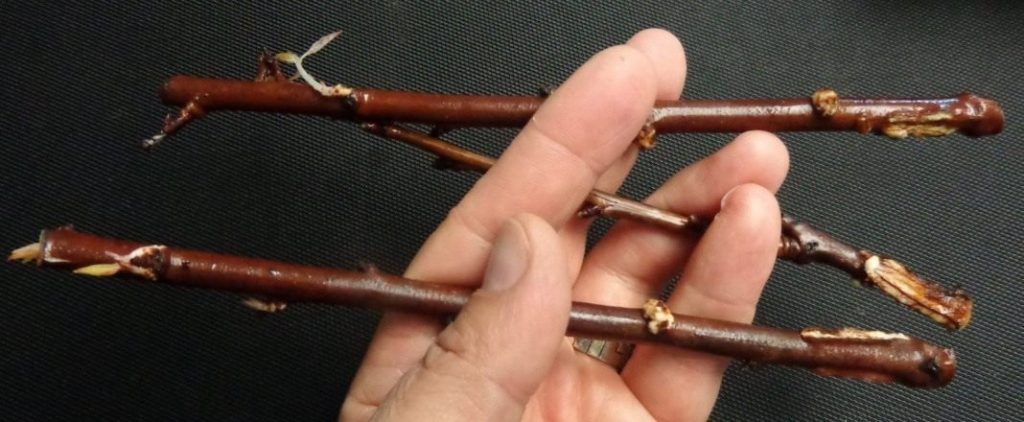
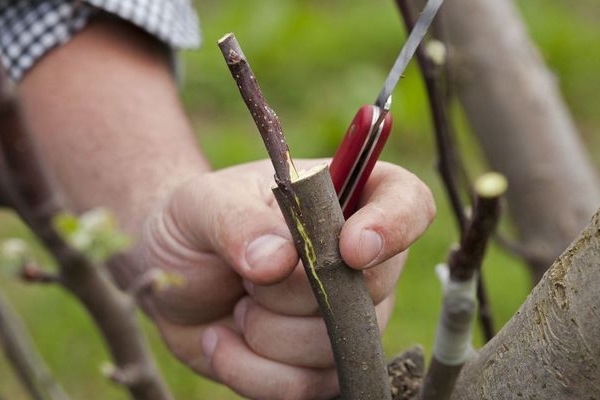
How to cut a plum? The simplest variation of the method under consideration is reproduction by lignified cuttings. A year before grafting, you need to cut off the plant shortly, after which many shoots are formed on it, which can form a root system and fully develop.
Procurement terms
Green cuttings of plums are carried out in the summer, in early-mid July, when the plants are intensively growing. For lignified cuttings, a dormant period is suitable. In regions with frosty winters, they need to be cut in late November - early December, but only before the air temperature drops to -20-30 ° C.
Harvesting cuttings
In order to cut the cuttings, you need to pick up suitable annual stems of the appropriate size on the mother tree. Ideally, it should match the width of the pencil. Thinner specimens can dry out quickly. The length of the shoot used for propagation should be about half a meter.
Harvested cuttings are usually stored at 2-4 ° C. In regions with snowy winters, they practice storing planting material under a snow layer 50-70 cm high. If there is a risk of thaw, the cuttings are covered with moistened sawdust and left in the cold. Soon the sawdust will be sufficiently frozen and will form a dense and durable cocoon. After that, the cuttings are transferred to a room where the sun's rays do not penetrate, and covered with a layer of dry sawdust (30-40 cm). From above they are wrapped in plastic wrap.2-3 days before the start of rooting, the cuttings are moved to a warm room, where they will gradually thaw.
Care should be taken to keep the cuttings in a dry place, as excess moisture is detrimental to the planting material. If, during the preservation process, they begin to dry out, you need to update the sections, place them in a container with water and put them in a cool room.
Green cuttings usually do not last long. Cut in the morning, if possible in cloudy weather, and immediately cut into small cuttings.
Rooting cuttings
For better rooting, cuttings should be placed in a solution of root stimulants before planting. It is recommended to use them as:
- IMC;
- IAK;
- zircon;
- epin-extra;
- flor-humate.
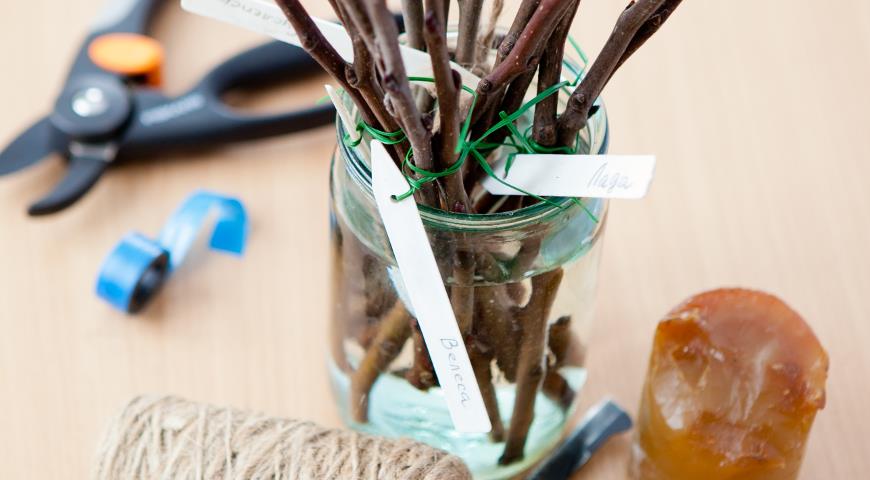
Prepared cuttings about 15 cm long are usually planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse equipped with a drip irrigation system. In the absence of such an opportunity, you need to make a homemade greenhouse from wire frame arcs and plastic wrap. Cuttings need to be watered 2-3 times a day.
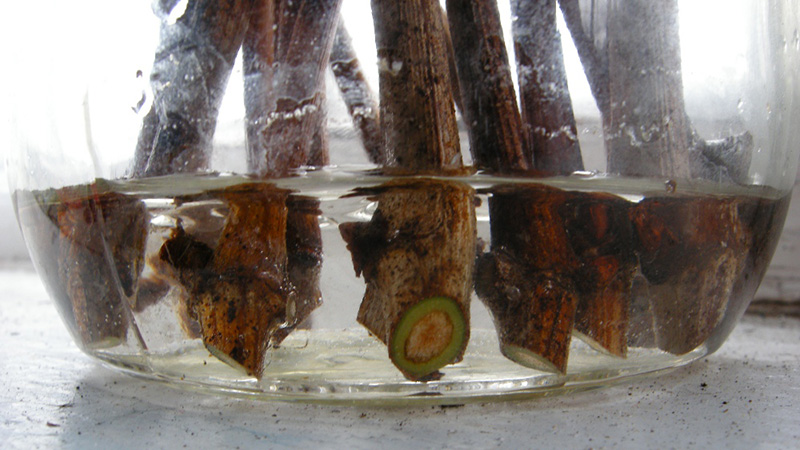
For full-fledged rooting, a normal soil saturated with nutrients is important. The sand is mixed with peat in equal proportions and the resulting mixture is scattered in a layer of 10-15 cm on the garden bed. A 2-3-centimeter layer of river coarse sand is poured over it. Immediately before planting, the soil mixture is treated with superphosphate, 1 teaspoon of which is diluted in a 10-liter container with water.
Rooting of plum cuttings from easily rooted varieties is completed after 2-2.5 weeks after planting, and those that reproduce poorly by this method - within a month. With the onset of callus formation, it is necessary to periodically lift the film to remove accumulated moisture and increase the access of oxygen to the plants. A month after planting, mineral fertilizers are applied under the cuttings, and then watered abundantly.
Knowing how to propagate plums by cuttings, you can select suitable varieties for this. These include:
- Tula black;
- Early ripening red;
- Memory of Timiryazev;
- Hungarian Moscow.
Breeding propagation
This method is simpler. It does not require continuous monitoring of propagated plants. With its help, you can quickly and successfully root your favorite varieties. Layers are formed in the spring, and in the fall they get a ready-made full-fledged plant with a formed root system.
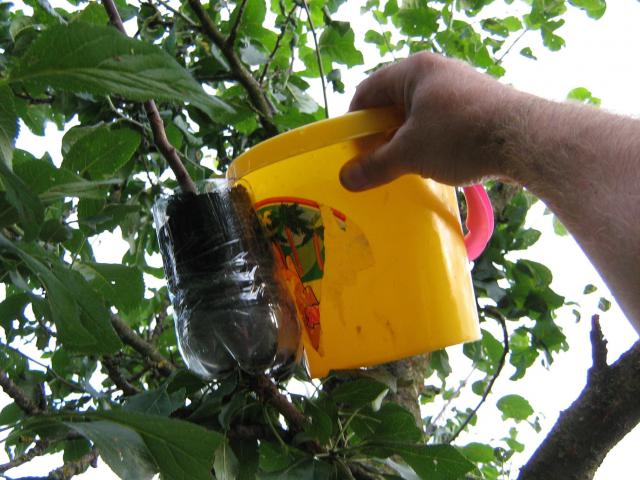
At a distance of 15-20 cm from the top of the last year's shoot, a ring of bark is cut off or cut in order to reach the wood. After that, they take moistened sphagnum and make a lump out of it, placed on the incision and fixed with a black plastic wrap. In warm weather, the roots form very quickly. The cuttings are cut off together with the resulting root system from the mother plant and with the earthen substrate moved to another place.
There is another variation of this method, how to take a sapling from a plum. A flexible shoot is found from a low plum plant and is carefully bent to the ground. At the point of contact of the stem with the ground, a narrow groove is dug up to a depth of 10-20 cm and the shoot is placed there, which had previously been treated with a root formation stimulator. The shoot is covered with soil, leaving only the top of the stem free, tamp the soil and spill it. It is recommended to pin the shoot to the ground using pieces of wire with a bent corner.
For better preservation of moisture in the soil (which must always be in a moist state), the soil is covered with plastic wrap. The appearance of foliage on the upper part of the stem signals the normal rooting of the cuttings. It is separated from the mother tree and planted in a permanent area.
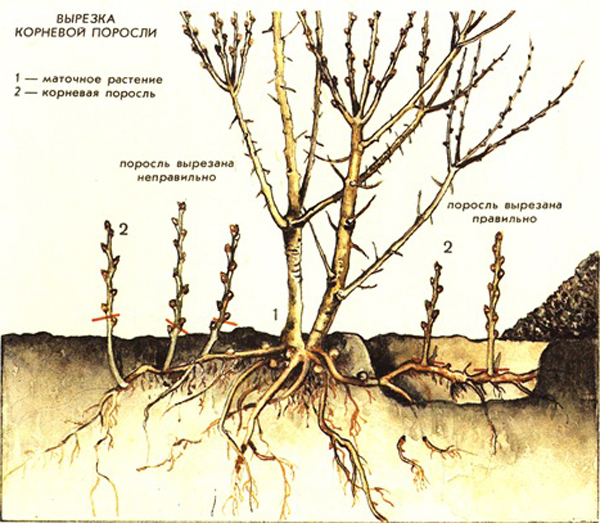
Reproduction by root shoots
How to grow a plum from a shoot and how to choose the right shoot? Those that grow next to the mother tree are not suitable. Choose as far away as possible.
A tree with a powerful branched crown, a strong tap root system and a low trunk is best suited. The shoots are dug up either in the first half of autumn, or in the spring before budding begins on the sunny side.
With this method, the roots of the plum are carefully chopped on both sides, as a result of which the shoots are separated from the mother tree. It is pulled out of the soil, damaged roots are removed, and the aerial part is cut off by a third. The offspring are planted in loose soil in the same way as with a regular seedling. In the process of growing, it is worth regularly feeding the plants with mineral complex fertilizers.
Using this method, the following varieties of home plums are usually propagated:
- Moscow Hungarian;
- Local yellow;
- Early ripening red;
- Tula black.
Budding
This method allows the most complete preservation and transfer of varietal qualities and plant properties to the offspring. It implies the presence of a rootstock - a base plant on which the inoculation is carried out. This plant is usually grown from seed or root weed. Water it abundantly, remove excess foliage and shoots. The stock should not be more than 1 year old.
The considered method is very laborious and is carried out according to a certain scheme. Long growths of this year are cut from a varietal plant with pruning shears, from which large buds and a small part of the bark are then cleaned off with a sharply sharpened budding knife. An incision is made on the rootstock at a level of about 4 cm above the ground level. The bark is carefully folded back and the cut soil is inserted there. The place of budding is tightly wrapped with a strip of plastic wrap, which is removed after 3-4 weeks. With the correct procedure and all conditions are observed, the kidney will take root and form a sprout.
Seed propagation
Reproduction of plums, like other fruit crops, by seeds does not allow the progeny to transmit their varietal qualities. At the exit, plants with completely different properties are formed. This method is usually used to remove rootstocks.
Plum pits are placed in a container of water for 4 days, renewing and stirring every day. Then the seed is dried and placed in a container.
In autumn or in the second half of spring, seeds are sent to loose prepared nutrient soil. A year later, full-fledged rootstocks will be obtained, which can be used in propagation of other varieties.
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing a breeding method.So, to carry out cuttings, it is desirable to have a greenhouse or greenhouse with a drip irrigation system available. For budding, it is not superfluous to have special skills, since this is a very difficult and time-consuming process. Propagation by root shoots is not carried out with grafted trees.
The timing of reproduction also has an impact. In the summer, the best options are green cuttings and budding. In spring, propagation by layering is recommended.
Knowing how plums reproduce, you can always choose the most suitable breeding method. With the proper organization of work, gardeners and summer residents will be provided with new high-quality plants every year.