Content:
Natural cow's milk is a valuable product. Therefore, it becomes a big problem for cattle owners if milk yield falls. When an animal's milk disappears completely, it becomes a real tragedy. Moreover, it is scary not only that the owner will suffer losses in economic terms, because the loss of milk or a decrease in milk yield may indicate major health problems in a dairy cow.
Breeding rules for cattle
In order for the animal to fulfill its purpose, in the case of cows, to give maximum milk, it is important to provide it with proper care and maintenance. First of all, the animal must be in a well-equipped barn. It should be warm and clean, as well as a ventilation system.
The cow should be getting enough food. In summer, she independently obtains her own food during grazing, in winter the owner must provide her with the necessary set. For this, hay, root crops are harvested, feed is purchased.
Milking of cows is carried out strictly on time. Failure to comply with the established regime can greatly affect the volume of milk received, since such interruptions are stressful for the animal.
Why cows lose milk yield
In veterinary medicine, there are two main names for the concept when an animal's milk yield disappears or decreases:
- Hypogalactia is a partial loss of milk yield when a cow is milked, but milk is much less milk than before.
- Agalactia in cows is a complete loss of milk yield.
Each of the phenomena is the result of a violation of the formation and delivery of milk. They can be caused by improper maintenance, care or feeding. But do not confuse disturbances in maintenance with temporary natural changes, for example, dry periods. Agalactia and hypogalactia, which occur in this case, are temporary and do not last long. Another cause of milk loss can be the old age of the animal.
If the cow gives little milk
Sometimes owners notice that milk yield has decreased. You need to react immediately, as the reasons for the loss of milk production can be serious.
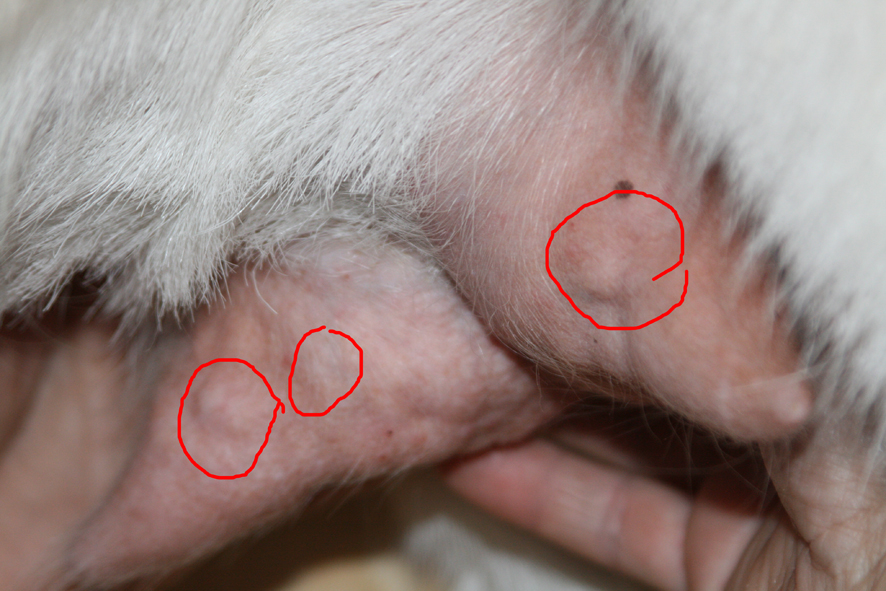
Among the most common diseases that affect volumes, mastitis should be noted in the first place. Treatment of mastitis is complex and lengthy, therefore, if possible, everything is done so as not to meet with him. Udder edema, foot and mouth disease and other diseases can affect milk yield.
Agalactia in cows
Agalaktia is divided into several groups, depending on the reasons for its manifestation. If a cow has lost milk, there may be various reasons. Therefore, they first determine them, and then begin treatment:
- Stern. A cow can stop giving milk due to a violation of the diet, lack of vitamins or poor-quality feed.Also, water imbalance is often the cause of agalactia. A complete revision of the diet with the introduction of all the necessary nutritional components will help to correct this situation.
- The disappearance of milk production due to artificial causes can form as a result of the stress experienced. Any situation can be the reason, for example, change of owner or type of milking from manual to mechanical. Sometimes nervous excitement is caused by a change in environment. You can only help the animal by creating the most comfortable conditions, as well as giving it time to recover. When the nervous state begins to disappear, milk flow will be restored.
- Climatic loss of milk yield. It is provoked by any climatic changes in the content: dampness, drafts, lack of fresh air, cooling. Regardless of the season, the animal should be taken for walks. When all stress factors are removed, it will be possible to return the milk yield to the previous level, the milk will stop disappearing.
- Operational reasons. Overexploitation of the animal is often the cause of milk loss. If, after calving, an active milk production is carried out, not observing the rules, then at first the milk yield will increase, and then it may completely disappear. Long-term lactation or very frequent milking can also cause agalactia.
- Physiological agalactia is provoked by the development of various infectious and bacterial diseases: mastitis, food poisoning, inflammation of the uterus. It is very important here to correctly diagnose and treat.
Blood in cow's milk
Each owner can detect blood in the milk of a cow, the causes and treatment in this case depend on many factors. First, diseases are excluded, then other options for the occurrence of blood blotches are sought. What to do when a cow has blood in milk will become clear only after finding out the real reasons.
Mastitis
The most common cause of bleeding is an acute inflammation of the udder called mastitis. A neglected acute form in veterinary medicine is called hemorrhagic.
A cow with an advanced form of mastitis should be immediately transferred to a separate room. She needs to organize all the conditions that will help speed up recovery:
- dry warm litter;
- reduce the consumption of juicy feed;
- elimination of any possibility of drafts.
Also, the detection of mastitis can be the answer to the question of why there are cottage cheese or curd formations in cow's milk. This indicates the presence of bacteria, which accelerates the souring and folding processes.
After milking, it is recommended to inject an antibiotic, into which 150 ml of a 0.25% solution of novocaine is added to relieve pain.
Udder contusion and open wounds
When grazing cattle in meadows, there is a high probability of damaging the udder by bruising or wounding. This bleeding can be the reason why the cow's milk is bloody. Another animal can inflict a serious wound with a horn or a calf by kicking. The result is a hemorrhage in the mammary gland, hence the blood. A similar bruise on the first day is treated with ice, and on subsequent days with warm compresses.
If the wound is open and deep enough, you will need the help of a veterinarian who will apply stitches.
With free grazing, the animal can bite any insect on the udder (tick, bee, blind, and so on), which will also provoke swelling and damage. These, in turn, will lead to bleeding.
A pregnant cow has lost milk and colostrum is flowing
Colostrum appears in cows that have calved, and goes instead of milk up to two weeks after calving.It must be completely given to the calf, so that it gets stronger faster and gets to its feet. But even during pregnancy (pregnancy of a cow), salty specific milk may begin to taste bitter or go. This suggests that there are no more than 1-2 months left before calving. During this period, great hormonal changes occur, and the milk becomes unsuitable for food. The owner should gradually prepare the cow for calving by starting it up and preparing it for dry periods.
The cow has salted milk
A salty taste may appear during colostrum flow or in an old cow.
If the cow is young, then the salty taste can be a sign of dangerous diseases:
- Udder tuberculosis. This is a very complex disease that only a veterinarian can diagnose. After diagnosis, he begins long-term antibiotic treatment.
- Mastitis is another dangerous disease that requires immediate treatment.
- Kidney problems. After the two previous options have been excluded, an examination of the digestive organs, in particular of the kidneys, is carried out.
Bitter milk from a cow
A pregnant cow, which is still far from calving, can begin to taste bitter milk. There are several reasons. One of the most common is eating foods and vegetables that affect taste:
- green onions;
- cabbage, rutabagas;
- horse garlic;
- avran medicinal;
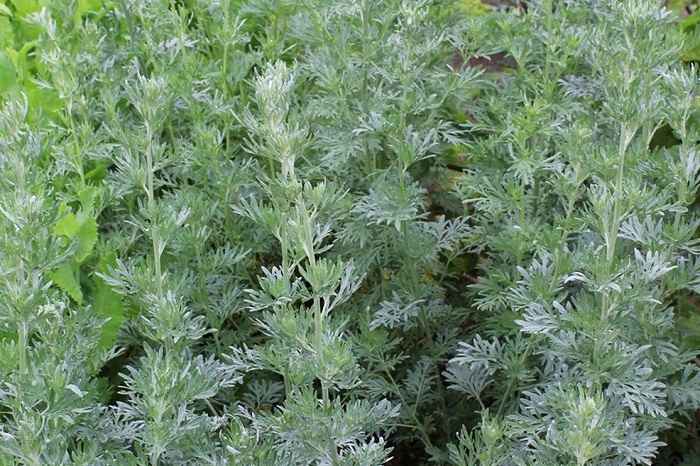
- sagebrush;
- sweet clover medicinal;
- tansy.
Bitterness can also be caused by poor-quality feed, as well as an overabundance of the same type of food in winter or early spring. Correcting a situation where bitterness arises from feed is quite simple - it needs to be removed from the diet. The bitterness should quickly disappear.
Another common reason why a cow's milk is bitter is liver disease, such as fatty degeneration or hepatitis. Here the feed plays a secondary cause of bitterness.
Another common cause of bitterness in milk is mastitis (purulent discharge in the milk mass). Subclinical mastitis is characterized by a latent course. The presence inside somatic cells and a high concentration of microorganisms leads to rapid deterioration of the dairy product, which is manifested by bitterness.
The cow has no milk after calving
For the first few days (up to two weeks), instead of milk, a viscous sticky liquid - colostrum - comes from the udder of a cow, which is very useful to give to calves to drink. Breeding should be done gradually, as the cow's milk volume will constantly increase over the course of three months.
But there are situations when, with proper distribution, milk does not appear or appears in limited quantities. In this case, a number of measures should be taken to understand the reason for its absence:
- First of all, infectious and bacterial diseases are excluded. If they are found, the veterinarian will prescribe treatment.
- Organization of correct milk production. In the first days after calving, a young cow should be milked frequently: every 4 hours to instigate maximum return.
- You should also watch out for the overnight break in milking. It should not exceed 10 hours, sometimes half an hour is enough to lose 1-2 liters of milk.
- The cow does not always give milk, sometimes it can pinch the udder, especially if it starts to leak. Therefore, when milking, the movements must be confident, not sharp, it is worth clamping the nipples with a fist.
The cow has pink milk
Red or pink milk can be the result of bleeding inside the udder or from wounds on it.
Sometimes the color of milk changes from normal to pink due to the fact that such plants as buttercup, euphorbia, horsetail, sedge and others got into the animal's food. In autumn, the animal is not very picky when free grazing.
If initially after milking the milk had a normal white or slightly yellow color, and after a while, when it managed to stand, it became with a pink tint, then this indicates the presence of a large volume of red yeast and other microorganisms in it.
The cow has yellow milk
Very often, the yellowish color of milk occurs when milking cows of fat-dairy breeds: Jersey, brown Latvian and some others. Also, this product acquires a yellow color immediately after calving and is called colostrum.
In some cases, yellowness can indicate the development of certain pathological processes:
- Hemosporidiosis;
- Foot and mouth disease;
- Jaundice;
- Leptospirosis;
- Anthrax;
- Mastitis.
Preventive actions
To prevent milk yield from falling or disappearing altogether, you should properly monitor the condition of the animal throughout its life. In order to prevent the development of agalactia or hypogalactia, it is necessary to pay attention to the following points:
- The cow's diet should be complete and balanced.
- The conditions for keeping the animal are provided with the proper level: dry bedding, no drafts, regular ventilation, and so on.
- After calving, the cow is fed according to a specific pattern that will help avoid mastitis and get the most milk.
- To increase milk yield, the calf is quickly fed artificially.
Expert advice
In order not to lose the milk yield of cows, experienced farmers have folk secrets that help to get the maximum amount of a tasty product:
- The volume of milk is strongly influenced by temperature, so in winter it should be warm and cozy in the barn.
- To avoid milk stagnation, regular massage of the udder should be performed, especially after starting and after calving.
- It is important to provide the animal with a juicy and nutritious food to get the maximum amount of milk.
- Strict adherence to the milking schedule will prevent you from losing milk.
- Any discomfort of the animal, first of all, will be said by the fact that it has stopped chewing its gum.
It turns out that a cow is an unpretentious animal, but still it should not be deprived of attention. If you do not provide her with proper care and attention, the result will be a lack of milk or a decrease in its volume.