Content:
Rabbits are bred for the sake of tasty dietary meat and valuable fur. But sometimes these cute animals get sick. One of them, and, perhaps, I myself am terrible - is the hemorrhagic disease of rabbits (VGBD). Due to the fact that it affects all the organs of the animal, and first of all - the liver and lungs, it is called necrotizing hepatitis or hemorrhagic pneumonia, and is popularly called “hemorrhagic in rabbits”. The Latin version of the name of the disease is "haemorrhagic". This is one of the acute infectious diseases in which all organs of the animal are affected. This disease appears suddenly, develops and spreads very quickly. Livestock dies in a matter of days. Because of this, the people gave it another name - "chumka".
The first diseases of HBV
In 1984, this disease was first detected in Angora rabbits on a farm in China, imported from Germany. But Germany itself, until 1988, was silent about the presence of VGBK. The disease began to spread at an unprecedented rate and reached Russia in 1986. In the Far East, in the Far Eastern state farm of the Khabarovsk Territory, which borders China, the first focus of this disease was discovered. The veterinarians could not immediately diagnose the sick rabbits were put under the knife. Seeing the affected guts, the meat was disposed of, and the skins were sent to factories. They did not even imagine that in this way the disease spread throughout the regions of Russia.
Pathways of transmission of the pathogen
The causative agent of this disease is RNA, which contains a pathogenic virus of the calicivirus family. It retains its properties for more than five years. It is not affected by freezing, ether, or chlorine.
Rabbit HBV virus is transmitted through food and water, soil, feed, as well as by the respiratory route. The causative agent of hemorrhagic disease can be in the transport in which rabbits are transported. Also, the virus can be transmitted by insects in contact with a sick animal. The causative agents of this disease are perfectly preserved for a long time in animal skins and down, and, as a result, in products made from them. If an animal has undergone this disease, then it is better to slaughter and dispose of it immediately. Rabbits older than three months and weighing over 3 kg are the most susceptible to this disease.
Distemper in rabbits: symptoms and diagnosis
This disease is very fast. Sometimes the incubation period only lasts a couple of hours. It may happen that after feeding and not noticing any changes in the animal's behavior, by the next feeding the owner finds an already dead animal. If the course of the disease is not so acute, then about 3-4 days after contact with a sick animal, the rabbit may develop a disorder of the nervous and digestive systems, the stool is liquid and foamy. He refuses food, his legs twitch convulsively, his head throws back, breathing becomes intermittent, irritability appears, they squeak and moan. A yellow-red discharge from the nose may also appear. All this happens in a matter of minutes, some 5-10 minutes and the rabbit is dead. One of the first symptoms of HBV in rabbits may be an increase in body temperature. In a healthy rabbit, it is 38-39 ° C, and in an infected rabbit, it is above 40 ° C.It is practically impossible to make an accurate diagnosis at the onset of the disease, which is why the mortality rate of rabbits from this disease is so high.
Scientists conducted an experiment: they introduced a virus to a healthy animal - the animal died in two days, while the individuals in contact with it - on the 5-6th day.
When a virus enters, the following processes occur in the rabbit's body:
- once in the body, the virus develops rapidly;
- affects the circulatory system;
- affects the lymphatic system;
- body cells change;
- subcutaneous edema and nodes are formed;
- hemorrhage occurs in the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- causes vomiting with copious impurities of blood;
- affects the liver, kidneys, lungs - there is a strong increase in these organs;
- the spleen fills with blood.
Treatment
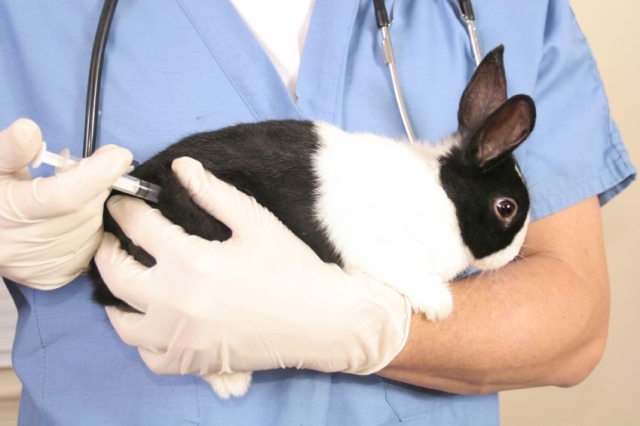
Unfortunately, hemorrhagic fever in rabbits cannot be treated. There is no drug that could kill this terrible virus. If such a misfortune befell the fluffy animal, then it will definitely die. To preserve the livestock, it is necessary to vaccinate animals in a timely manner and all livestock breeders must always have a vaccine against this disease. It can be stored in the refrigerator for up to two years. For prophylaxis, serum should be administered to all rabbits, starting at six weeks of age. Then every 3 months.
Although the use of a special vaccine still does not give a 100% guarantee that the rabbit family will be protected.
Prevention measures
If an infection occurs in one of the rabbit families, it is necessary to immediately carry out prophylaxis in all other families. Livestock breeders in whom rabbits have contracted this disease need to understand that:
- such rabbit meat cannot be eaten, as well as sold;
- sick rabbits cannot be transferred from one cage to another;
- do not happen with rabbits from other nests;
- allocate a separate inventory for caring for infected animals, and then thoroughly disinfect it;
- the rest of the rabbits are urgently vaccinated;
- litter from sick individuals must be biothermally treated and disposed of outside the farm;
- after contact with sick animals, clothes and tools must be disinfected, hands should be thoroughly washed using disinfectants;
- dead animals are burned.
The following substances can be used as a disinfectant:
- carbolic acid;
- freshly slaked lime;
- sodium hydroxide.
The virus has mutated
Many rabbit breeders are in a panic - VGBK has mutated. The official name of the new form is RHDV-2 (Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus - 2). Since 2010, the new disease has already visited countries such as France, Italy, Portugal, Spain.
This virus no longer reacts to old vaccines, moreover, if the first viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits did not affect young animals younger than 3 months, then RHDV-2 affects babies 3-4 weeks old, vaccination at this age is out of the question.
The new virus differs from the old one by an even greater transience of the disease, the defeat of unvaccinated babies and an even greater mortality - an almost 100% lethal outcome of infected rabbits. And so, in general, the disease proceeds with the same symptoms: shortness of breath, lack of appetite and fever. How do chronically infected eared animals behave? Will they be carriers of the virus or will they completely recover? Experts are not yet ready to answer these questions. Infection occurs in the same way as in classic VGBK.
Animals infected with HBV cannot be saved. Therefore, in order to protect the rabbit population from the terrible virus, it is necessary to carry out timely vaccination and observe the rules of hygiene when caring for the animals.