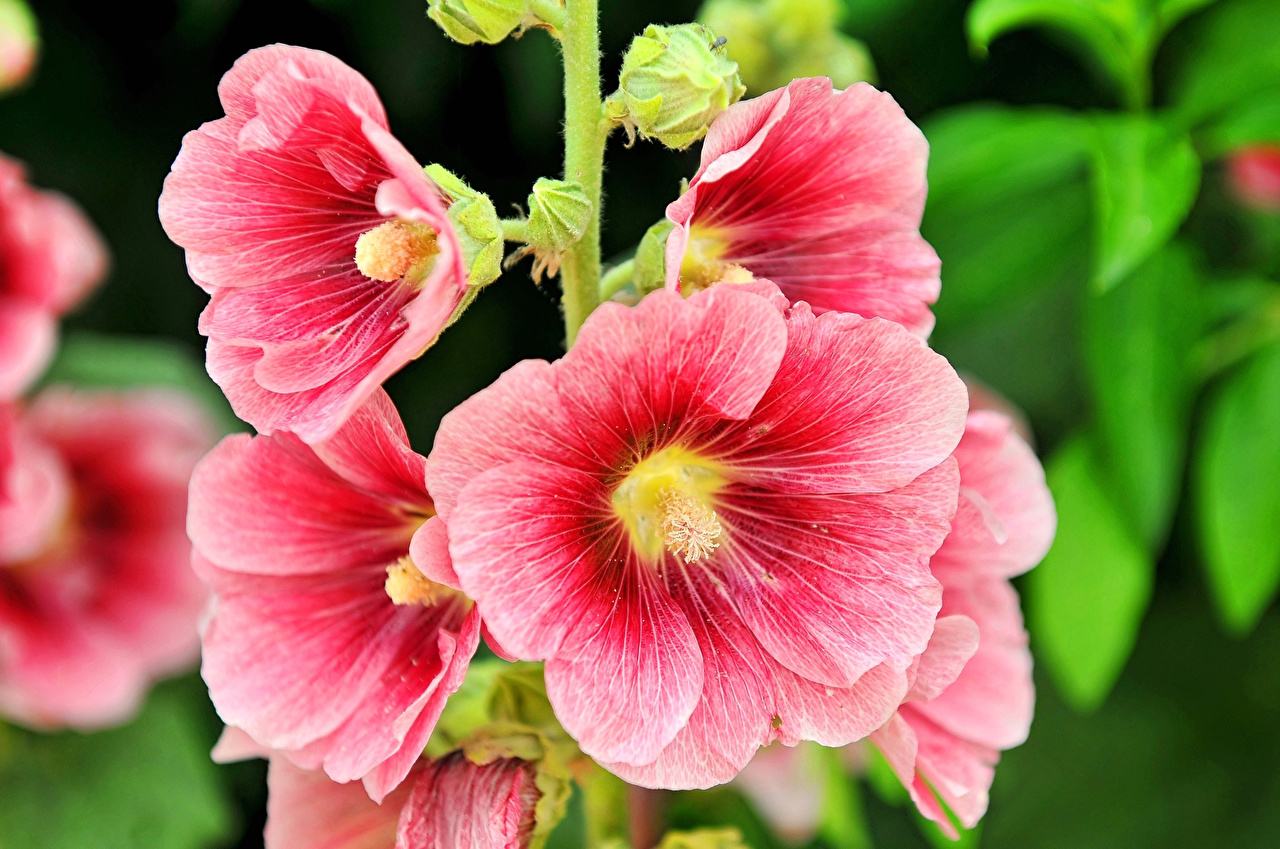
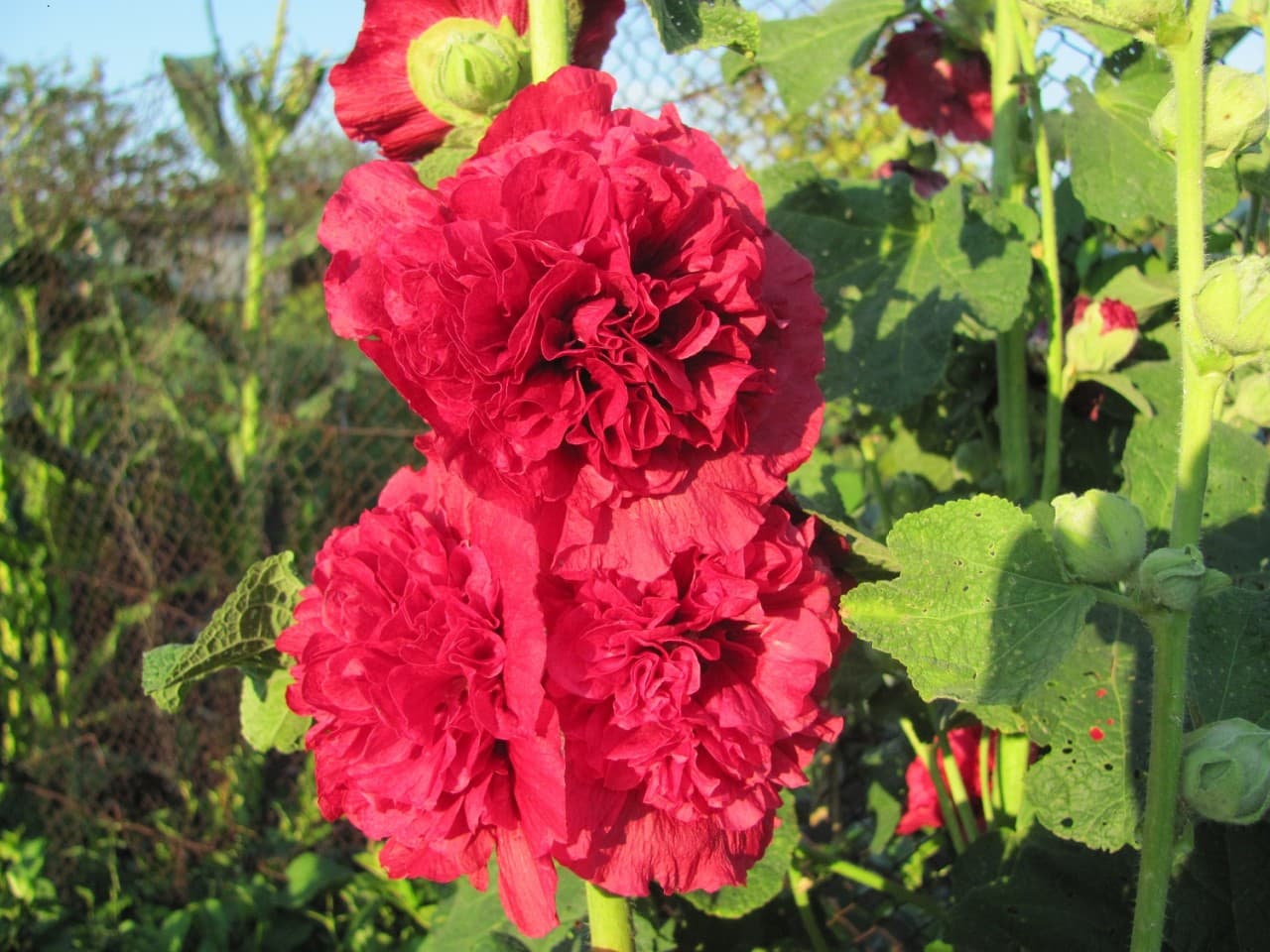
Mallow, mallow or stockrose, blooms with very beautiful flowers of various colors. Today there are more than 30 varieties of this gorgeous plant. Different in color, height, flower size, they delight the eyes of the gardener and become an adornment of any garden plot.
Stockrose has spread since the distant 1400. In the middle and late twentieth century, it lost its popularity. But recently it has again started to gain leadership positions among agricultural technicians. Mallow is used in landscape design. These tall plants can cover an unsightly fence or a deformed wall at home. Flowers will look better if planted in small groups.
Description and care of stockrose
There are many varieties of stockrose. The most common for planting in personal plots are:
- Zebrina;
- Apple blossom;
- Blackberry;
- Fiesta Time;
- Pink lace;
- Newport;
- Bahamas, etc.
Stockrose is not a capricious plant, so it does not require special care. Caring for mallow, which grows in the open field, consists in timely watering, in especially dry weather, weeding, loosening, removing diseased or dry branches and flowers. Before the buds appear, the plant needs fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. If a mallow grows on the site, which reaches 2 meters in height, it must be tied up. You can also make a perennial from an annual plant. To do this, immediately after the stockrose flowers have faded, they must be cut off. This flower does not need more careful care.
Stockrose propagates by the seed method. It is recommended to purchase two year old seeds. They have the highest germination rates. When planting (most often it is carried out at the end of August or at the beginning of September), the distance between future flowers should be maintained, which is at least 40 cm. If necessary, transplant an adult plant to another place, dig it out with a clod of earth that will be on the roots.
Mallow tolerates drought well. You can plant it in places where there is a lot of sunlight. In partial shade, it will also grow, but it will not be so high and bloom much less luxuriantly. The soil for mallow should not be marshy and clayey. If the soil is fertile, the mallow does not need additional feeding. If the soil is not fertile, stockrose can be fed once a month with mineral fertilizers.
In autumn, after the mallow has faded, it is recommended to cut the plant to a height of 30-40 cm from the ground. For the period of winter frosts, stockrose is covered with agrofibre. You can use fallen leaves or dry grass instead of agrofibre. The soil next to the flower should be mixed with peat in a 1: 1 ratio. With these simple procedures, the mallow will bloom in the middle of the first summer month.
The mallow reaches a height of 250 cm. The petals have pronounced veins, which are more saturated in color than the bud itself. Mallow has a variety of colors and shades. It all depends on the variety chosen by the gardener. There are flowers with smooth, glossy surfaces, and there are varieties with velvety leaves.
Mallow is widely used both in light industry and in medicine. Mallow flowers can color wine and woolen products. A decoction from the roots of this wonderful plant has a beneficial effect on the human respiratory system. This broth will remove excess fluid from the body, relieve inflammation.It also has a good effect on the digestive system.
Diseases characteristic of mallow
Mallow diseases are quite common and can cause irreparable harm to the plant. The following questions will be considered below:
- Why do the leaves of mallow dry and turn yellow;
- Why does rust appear on mallow;
- How to deal with mallow rust disease;
- What are the diseases of stockrose;
- What pests affect mallow;
- Who devours the leaves of the mallow flower, etc.
Mallow is very fond of various pests, more often than other agricultural crops, it is attacked by diseases. Stockrose is of great interest to slugs that are present in every site. In order to rid the plant of these unpleasant "guests", it is necessary to pour a little beer into small containers and place them at different ends of the plot. The next day, the slugs will leave the mallow and relocate to containers with a low-alcohol drink.
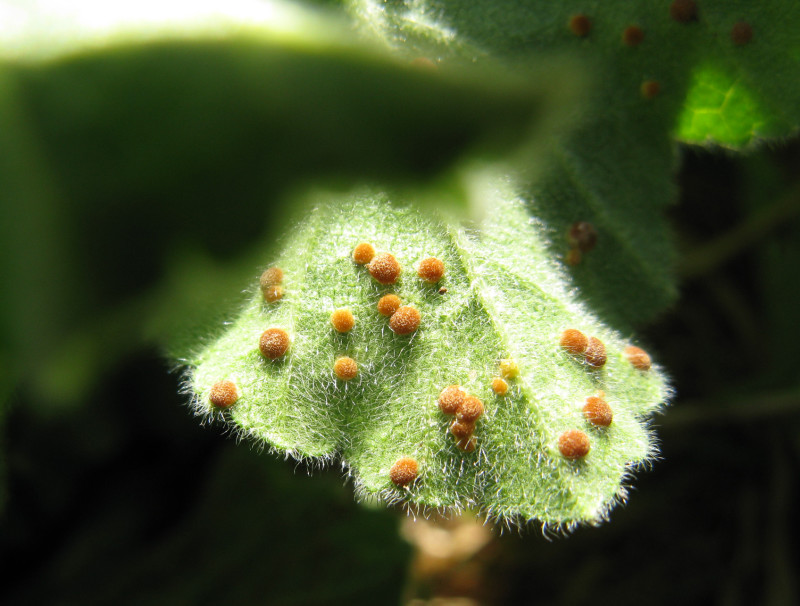
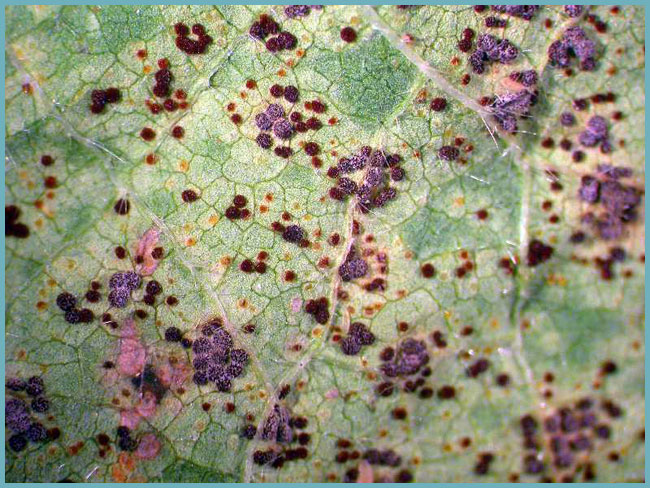
Rust is very dangerous for mallow. You can find it on the back of the leaves. Those plants that are close to iron structures or a metal fence are especially susceptible to disease. The disease begins with a slight yellowing of the leaves of the plant. The treatment of rust on mallow consists in the fact that the leaves on which this disease was noticed are cut off and burned, and the plant is treated with the necessary preparations that contain fungicides in the composition.
Colloidal sulfur can also help with diseases such as powdery mildew. If rust appears on an adult plant, it can be treated with Bordeaux mixture. She has proven herself well in the fight against diseases that appear on the leaves.
Spider mites are also very common in mallow. The disease manifests itself at the initial stage with white dots on the leaf, and the neglected state is characterized by yellowed and dried leaves. When white dots appear on the leaf, it is recommended to spray the plant with soapy water. The same solution will protect the plant from aphids, which infect flowers and buds.
A common rose stem disease is ascochitis. It manifests itself as brown pimples on the leaves of the stockrose. Brown spots begin to appear on buds and flowers. The last stage of the disease is leaf curl. After the leaf dries up. What to do if the leaves of mallow dry and turn yellow? To get rid of the disease, it is required to pluck and burn all the leaves affected by the disease. Remove all weeds from the territory adjacent to the mallow.
The reason why the leaves of mallow turn yellow are fungi that provoke the development of a disease called cercospora. The lesions are yellow with a brown border. Over time, if you do not start to get rid of the disease, the yellowness increases in size and merges into one large spot, the leaf dries up.
At the initial acquaintance of the gardener with this gorgeous flower, it is important to know what mallow can hurt in order to get rid of diseases at the initial stages, preventing their widespread distribution.
Disease prevention consists in the timely identification of the disease. For the treatment of many diseases, it is recommended to use Bordeaux liquid or soap solution.
Any of the varieties of stockrose is capable of rapidly developing and decorating the site for more than one year, despite the fact that, for the most part, this plant is annual.