Content:
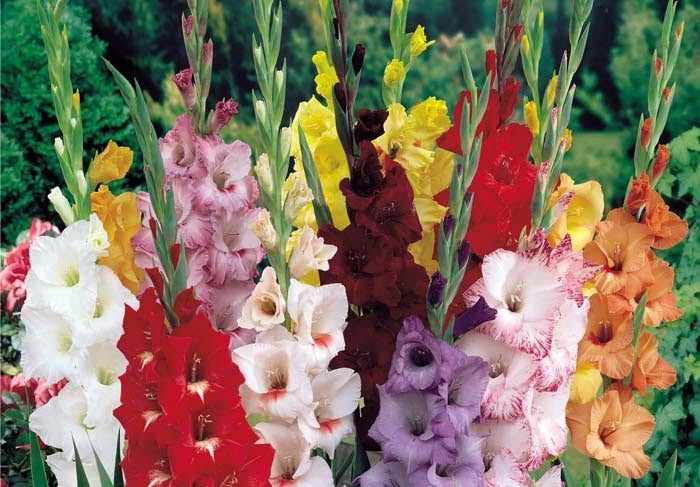
Gladiolus (also called the skewer) is a perennial bulbous flowering plant of the Iris family. Translated gladius means "sword." The flower was named so because of the external resemblance of the stem to a sword or sword.
In total, there are more than 200 species of gladioli, and breeders have already bred more than 5,000 varieties. These flowers are simply adorable. They are suitable for decorating gardens, flower beds and for cutting into bouquets. But sometimes something goes wrong. Flowers do not form an arrow or change the shape of peduncles and leaves. And many novice flower growers ask the question why gladioli do not bloom, what to do and can they be made to bloom? And today's article is about these flowers, what to do if gladioli grow poorly: how to feed, how to cure.
Why gladioli grow crooked and fall
It often happens that gladioli are planted on time, and watering is done in a timely manner, but the flowers can bend - grow with a crooked stem and inflorescences. And again, novice florists have a question why gladioli have crooked peduncles and what can be done. In this case, there can be two reasons:
- Gladiolus bulbs are slightly buried when planted. If they are buried 5-7 cm, then often during the heat the topsoil dries up and the plant does not have enough moisture. As a result, the gladiolus does not have enough strength to hold the stem, so it leans towards the ground and quickly stiffens. Therefore, when planting, the bulb must be planted to a depth of about 15 cm (4 bulb diameters on light soils and 3 on heavy soils). It is also useful to mulch the plantings of gladioli. In these cases, moisture will last longer.
- There is a lack of calcium or excess nitrogen in the soil. In this case, the stem becomes loose and can also bend and not hold the weight of the peduncles. In this case, feeding with calcium nitrate or potassium phosphate will help. Fertilizer must be applied according to the instructions.
Why gladioli do not bloom: the reason
It happens that the leaves of gladioli are beautiful, even, but they don't want to bloom. There may be several reasons for this:
- improper storage of bulbs;
- insufficient nutrition;
- cold or rainy summers;
- the bulbs are old, small or weakened;
- plant adaptation, for example, Dutch bulbs can bloom luxuriantly in the first year, and then do not give flower stalks for 2-3 years, getting used to local conditions;
- crop rotation is not observed;
- the presence of pests (wireworm, thrips).
Rapid flowering
Gladioli fade quickly for several reasons:
- very rainy weather;
- there are few nutrients in the soil or it is clayey;
- overdried corms.
Diseases of gladioli and their treatment
Gladioli can suffer from the same diseases and be affected by insects from which neighboring flowers and vegetables suffer. It:
- viruses;
- mushrooms;
- bacteria and mycoplasmas;
- ticks, thrips, aphids, caterpillars.
Fusarium or dry rot
This disease is caused by a fungus. Bulb, stem and foliage are affected. The lower leaves turn yellow, and then the disease affects the entire flower. On the bulb, you can see watery spots that turn brown, and the larger the lesion, the faster it dies. If there are few spots, this is not a reason for joy, since the bulb will die anyway, but a little later - in winter. And if it persists (for example, the lesion was very small), then the shoots will not appear or will be very weak.
Unfortunately, it is useless to treat this disease, you need to burn the diseased plant in order to prevent spreading on the site. For prevention, before planting, the bulb must be treated in one of the following ways:
- soak for half an hour in a foundationol solution;
- soak for 10-12 hours in an infusion of marigolds, celandine or calendula;
- dip the onion first in hot water, and then immediately in ice. Repeat several times. Then dry thoroughly;
- monitor crop rotation. In one and the same place, the plant can be planted no earlier than after 4 years.
Gray rot
This is another fungal disease. It develops more often in a humid environment. Dark spots form on the leaves, which, as they grow, affect large areas. As the disease develops, it descends along the stem to the bulb, affecting the base of the stem. Whitish watery spots appear on blossoming flowers, and if the bud has not yet blossomed, then it changes its color to brown and does not open. Dark brown spots appear on the bulbs, which die in winter during storage.
Prevention of gray rot includes:
- high-quality drying;
- treating bulbs with fungicides before planting;
- you need to plant plants in sunny areas;
- use nitrogen fertilizers moderately;
- observe crop rotation.
Cancer
It is the most common bacterial disease transmitted by nematodes. Ugly growths form on the bulbs. Mostly young gladioli are affected.
Bacteriosis (bacterial scab, varnish disease)
Small reddish-brown spots first appear on the bottom of the stem and leaves. Which, expanding, form longitudinal stripes of the same color. Shiny spots form on the bulb that are easy to remove. The appearance of the bulb will be worse, but the disease will stop and it can be planted again next year.
Viral diseases
Here we are talking about:
- Various mosaics, when strokes, stripes, specks appear on the leaves, the petals of flowers become variegated with white and green spots. Bulbs do not develop.
- Jaundice. The leaves turn yellow, and, on the contrary, a green tint appears on the flowers. Many thin shoots grow instead of one strong one.
These diseases are also not cured, the plant must be destroyed.
Rust on gladioli: how to get rid
When infected with this fungal disease, rusty spots appear on the leaves of gladiolus, and then they completely dry out. And you can see brown circles on the petals, and orange dots on the bulbs.
The plant cannot be treated, it must be burned, and the site must be cleaned of weeds and treated with antifungal drugs. Without processing, mushrooms remain in the soil for a long time.
Pests of gladioli
Not only because of disease, flowers look bad. Insect parasites can cause its unimportant appearance:
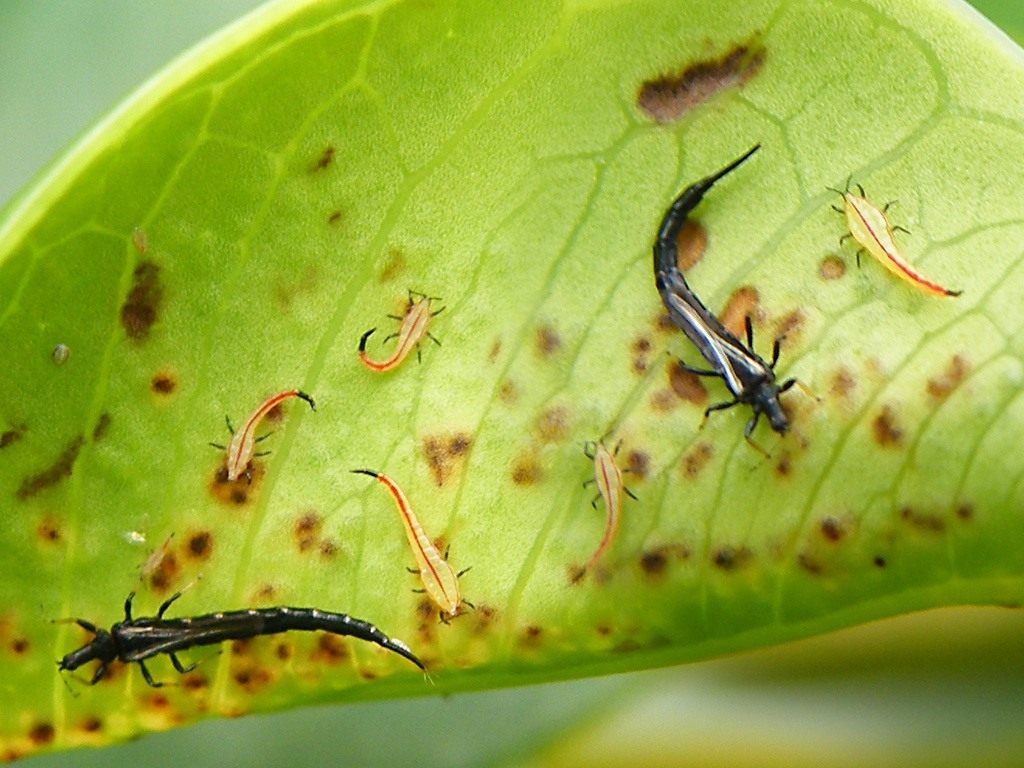
Thrips
Thrips are very dangerous for gladioli - small brown flying insects, especially their larvae. They settle on the leaves of gladiolus and suck the juices out of them.You can recognize the presence of thrips by the whitish spots on the leaves, which subsequently turn brown. For flowers that have bloomed, the petals look burnt, and buds that have not opened do not bloom at all.
For prophylaxis, when planting corms, you need to process them in hot water or Aktelik solution.
After detection already on growing gladioli, it is recommended to spray the plant with a solution of karbofos. After a while, it can be treated with a decis solution. Pest control should be carried out in dry weather.
After the bulbs have been dug up, they also need to be treated with a decis solution.
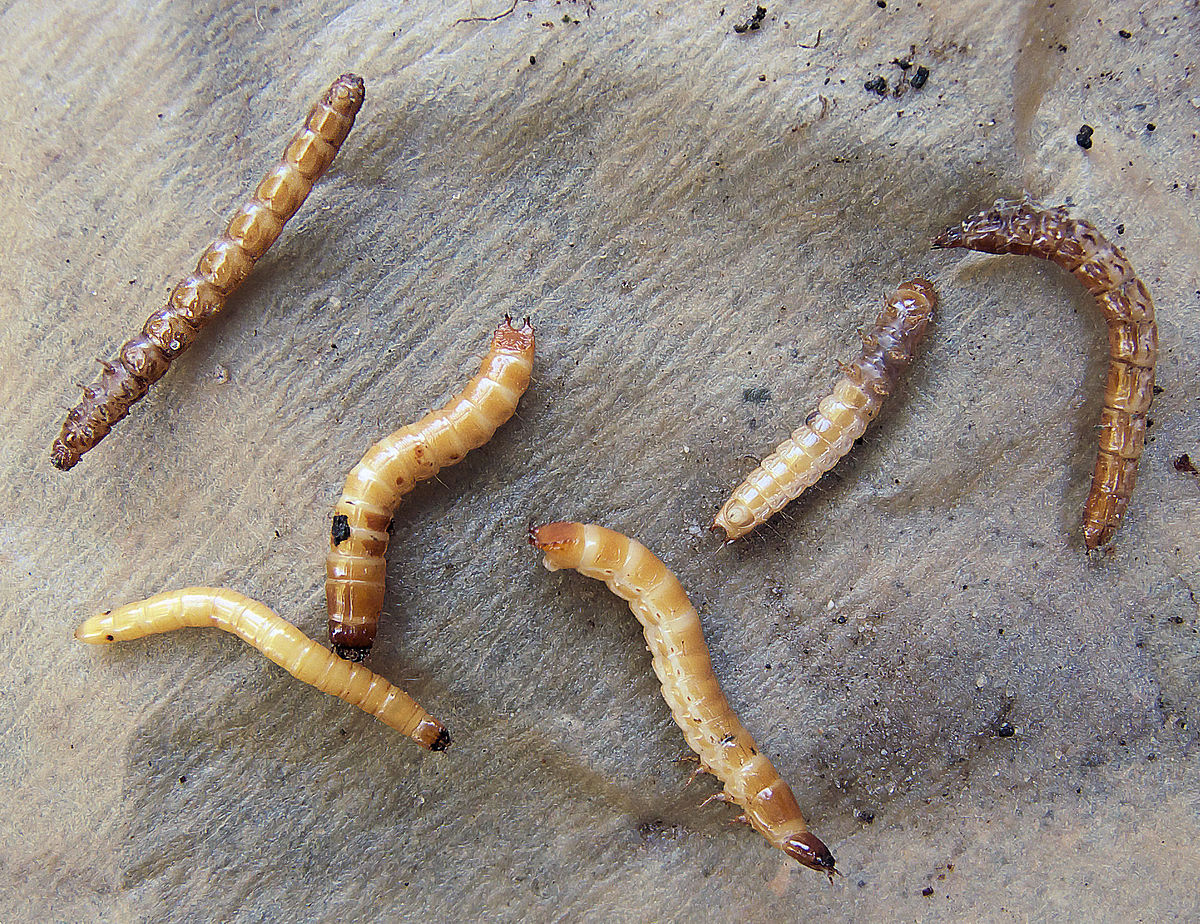
Wireworm
These are the larvae of the click beetle. He gnaws the outer shell of the bulb and eats away its inner part, in connection with which the plant dies.
It is best to plant gladioli after legumes and garlic, since the wireworm does not like these plants. You can also plant beans or beans in the plantings of gladioli.
Root onion mite
This pest infects the plant through damage to the bulb. In a diseased flower, the leaves first turn yellow, then they wither, and the bulb becomes rotten. The growing plant is treated with a 10% solution of karbofos, and the dug out bulbs are soaked in a 0.1% solution of karbofos.
How to breed malofos for the treatment of gladioli? The working solution must be prepared immediately before use. It is recommended to take 7-10 g of malofos powder, dilute in 1 liter of water and mix thoroughly. Using a spray bottle, apply the solution to the leaves and stem of the plant. It is desirable that the solution covers the entire surface. Plants cannot be processed during flowering.
Caterpillars and aphids
Leaf-gnawing caterpillars and aphids cause irreparable harm to the landings of gladioli. They gnaw many holes in the leaves, which makes the flowers lose their attractiveness. You can use any of the insecticides to fight parasites.
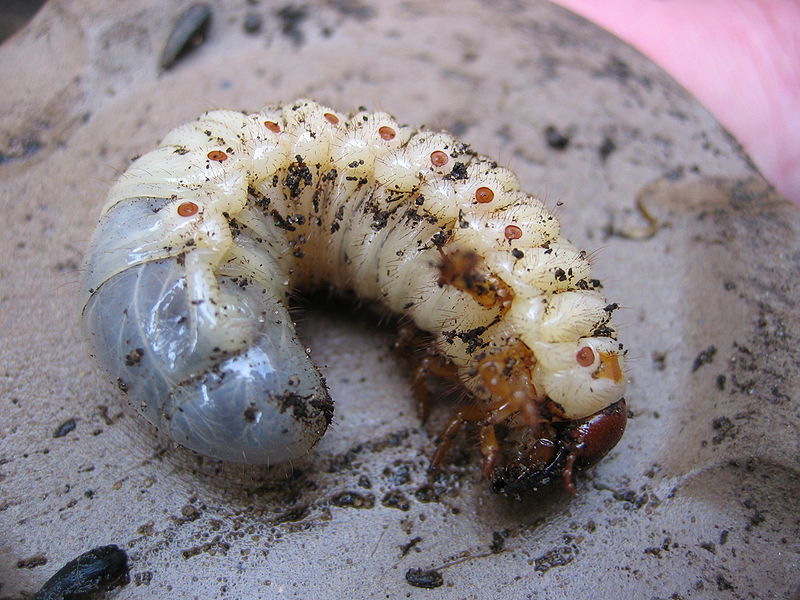
May beetle larvae
Gladioli and beetle larvae spoil. They eat up its corms, and the plant dies. Garlic planted between plants scares them well.
Slugs
Another pest that gnaws holes on the leaves, and the mucus they produce, adversely affects the flowers. To combat them, fluff lime is used. It is best to process the plant late in the evening, as slugs are night guests.
Knowing everything about diseases and pests of gladioli, even a novice grower will not have problems with growing them. Do not be afraid of difficulties, everything will definitely work out!